Ask five people what types of AI exist, and you’ll get five different answers. That’s because AI classification depends on the lens you use: capabilities, functionality, learning method, and how models are built. We can look at what they can do, how they learn, how they’re built, and how we can trust them.
Ongoing AI research plays a crucial role in shaping the development and understanding of AI technologies, driving advancements and addressing ethical considerations.
Each way of thinking about AI reveals important truths. This article maps the entire landscape. We’ll cover the major groups, show how they connect, and give real examples. You’ll understand any AI system you encounter, from chatbots to self-driving cars to medical tools.
Advanced AI systems and AI technologies are transforming industries and raising new societal and ethical questions as they become more sophisticated and capable.
Types of AI by Clay
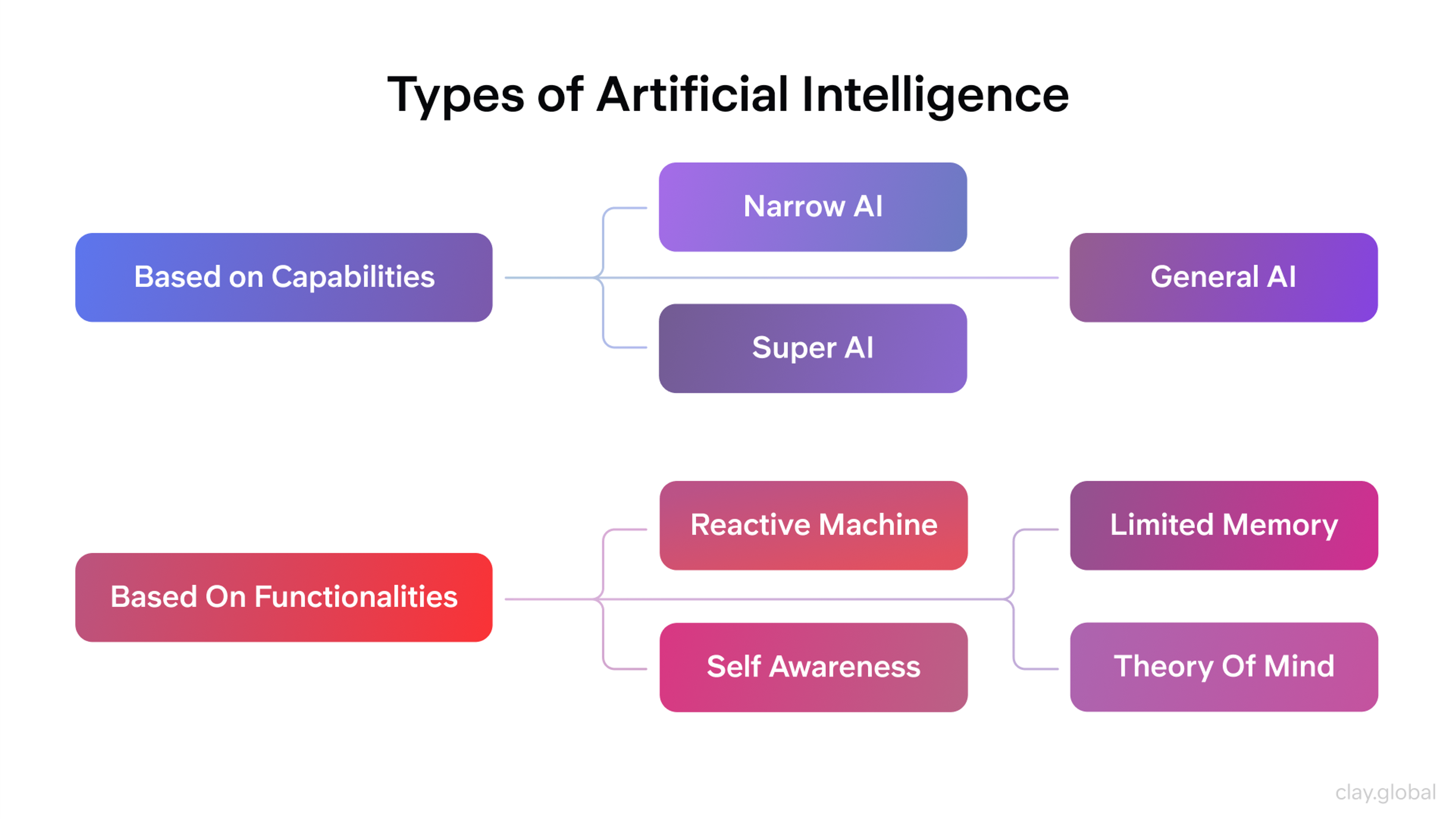
Types of AI: 7 Types Explained (3 by Capabilities + 4 by Functionality)
This section uses two common AI classification frameworks: capabilities (3 types) and functionality (4 types).
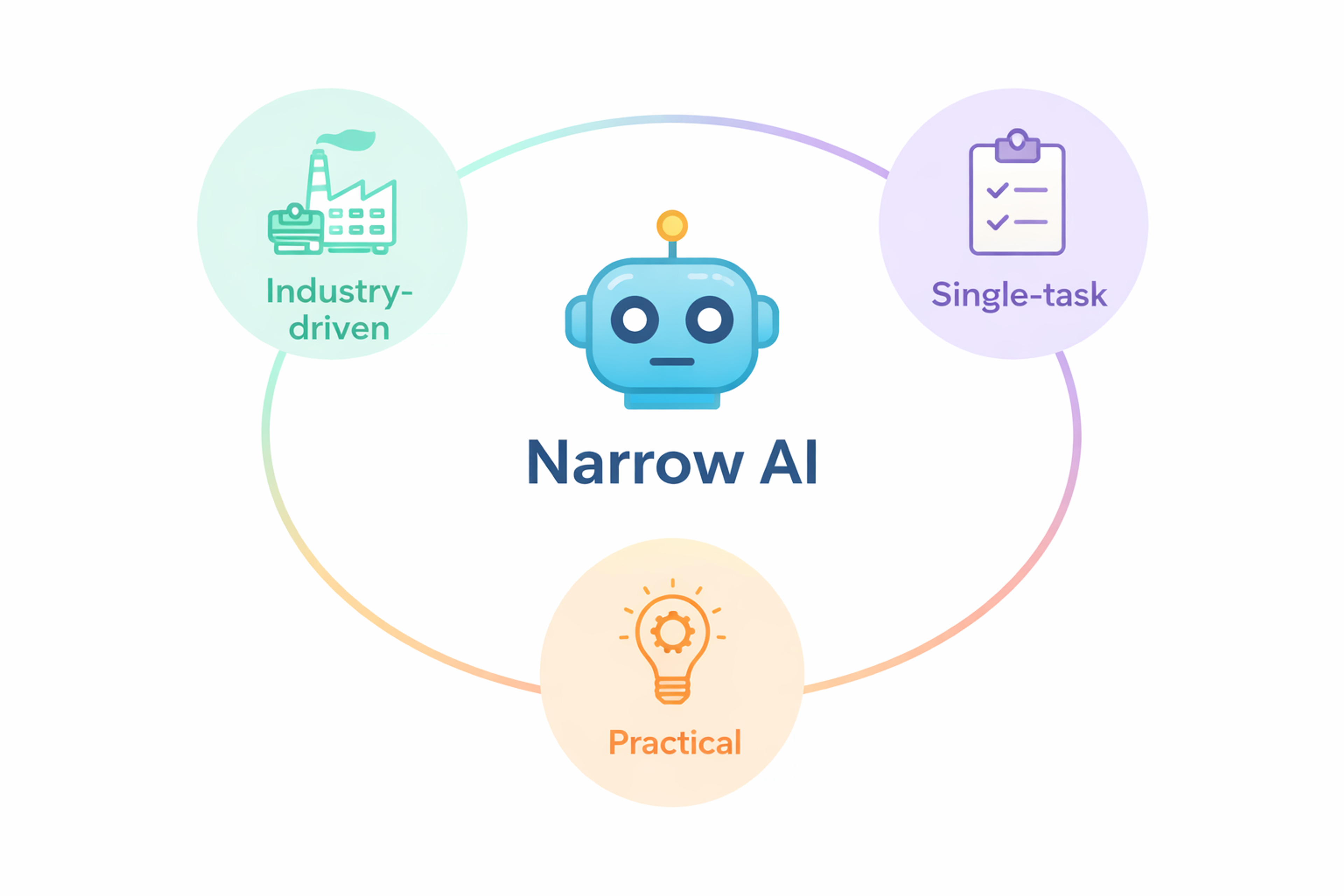
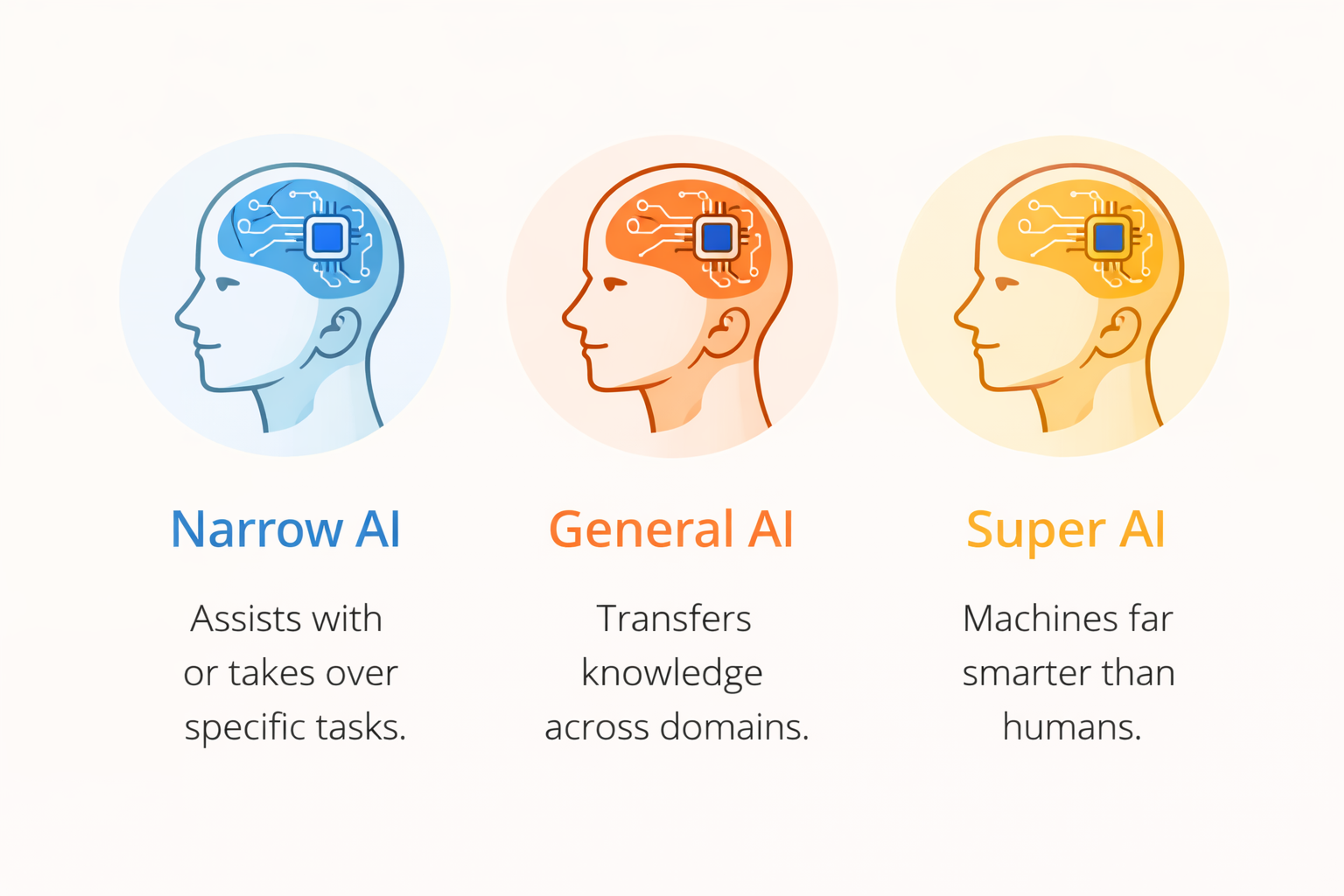
Narrow AI
Narrow AI (limited-memory AI) is built for specific tasks and excels at them — like spam filtering, recommendations, face recognition, and medical image analysis. Most are reactive systems: they respond to current input without retaining memories or learning on the fly.
They boost efficiency and automate routine work across logistics, manufacturing, healthcare, and agriculture. But outside their training domain they fail quickly and require frequent updates to stay accurate — useful tools today, not general “brains.”
Examples: email spam filters in Gmail/Outlook; fraud scoring for credit card transactions.
Narrow AI Scheme
General AI
General AI, also known as artificial general intelligence (AGI), refers to a type of AI that would match or beat human performance across many different tasks. It would adapt quickly to new challenges. AGI is also referred to as strong AI and is currently a theoretical concept, as such systems do not yet exist.
Some modern systems show broad abilities, but reliable human-level performance across all areas hasn’t been achieved. AGI would be able to perform any intellectual task that a human can. We’re not there yet.
The goal of AGI is to achieve human-like intelligence, allowing it to adapt to tasks in everyday life just as humans do.
Ultimately, AGI aims to match the cognitive abilities of human beings, including understanding complex concepts such as theory of mind.
Super AI
Super AI is an advanced form of AI that surpasses human intelligence in virtually every area. This is a hypothetical concept, and AI remains in the realm of theory for such advanced systems. Super AI is mainly discussed in the context of long-term planning and safety research, rather than something engineers work on today.
Ethical considerations, known as AI ethics, are central to discussions about Super AI, especially regarding the potential for self aware AI with self awareness.
Types of AI
Mind AI and such AI represent future possibilities for AI systems with consciousness and emotional intelligence.
The 4 Types of AI Based on Functionalities
These four types of AI describe how an AI system behaves in the real world. The key difference is memory and social understanding.
Reactive Machine AI
Reactive AI has no memory. It looks only at what is in front of it right now. For the same input, it tends to give the same output.
This makes it reliable in stable environments. It can be strong at a single, well-defined task.
Limited Memory AI
Limited Memory AI can use recent past data to make better decisions. It learns patterns from training data. It may also use short-term context during a task.
Most modern AI products fit here. They use history to predict what comes next. But they do not store life-long experiences like humans do.
Theory of Mind AI
Theory of Mind AI is a future concept. It would understand that people have emotions, intentions, and beliefs. Then it would adjust its behavior to match the social context.
That could make AI feel more human in conversations. It could respond to frustration, uncertainty, or stress in a smarter way. Today’s systems do not truly do this.
Self-Aware AI
Self-Aware AI is also theoretical. It would have a model of itself, not just of the user. It could reflect on its own state and goals.
This idea is mostly discussed in long-term research and safety debates. It is not something we can build and deploy today.
How AI Learns
Supervised Learning
These machine learning models learn from examples with correct answers. You show them input data paired with the right output. This powers fraud detection, medical diagnosis help, and product recommendations.
Supervised learning typically uses structured data, such as labeled spreadsheets or databases, to train models.
You need quality labels and lots of examples to train effectively. This works best when you have historical data with known outcomes.
Examples: classifying whether a transaction is fraudulent; predicting house prices from features; labeling images of animals for a photo app.
Unsupervised Learning
These models find hidden patterns in data without being given answers. They discover customer groups, spot unusual patterns, or compress complex information into simpler forms while using natural language processing.
This approach works well for exploring data, grouping customers, finding anomalies, and reducing complexity in large datasets.
Examples: clustering e-commerce users into segments; anomaly detection for server logs.
Self-Supervised Learning
This powerful modern approach lets models create their own training tasks from raw data. Language models predict missing words. Vision models guess what missing image pieces look like.
This method scales well with huge datasets and powers most foundation models. It's perfect for learning general patterns from massive amounts of unlabeled data like text, images, or video.
Reinforcement Learning
An agent learns by taking actions, getting rewards or penalties, and improving its strategy over time. This excels at games, robot control, trading strategies, and dynamic pricing.
It works best for problems where feedback comes through sequences of decisions and you need to develop complex strategies.
Meta-Learning
This is "learning to learn." Systems improve their ability to pick up new skills quickly. Instead of starting from scratch on each task, they use past learning experiences to adapt faster.
This approach helps when you need rapid adaptation to new but similar tasks with limited data.
How AI Works
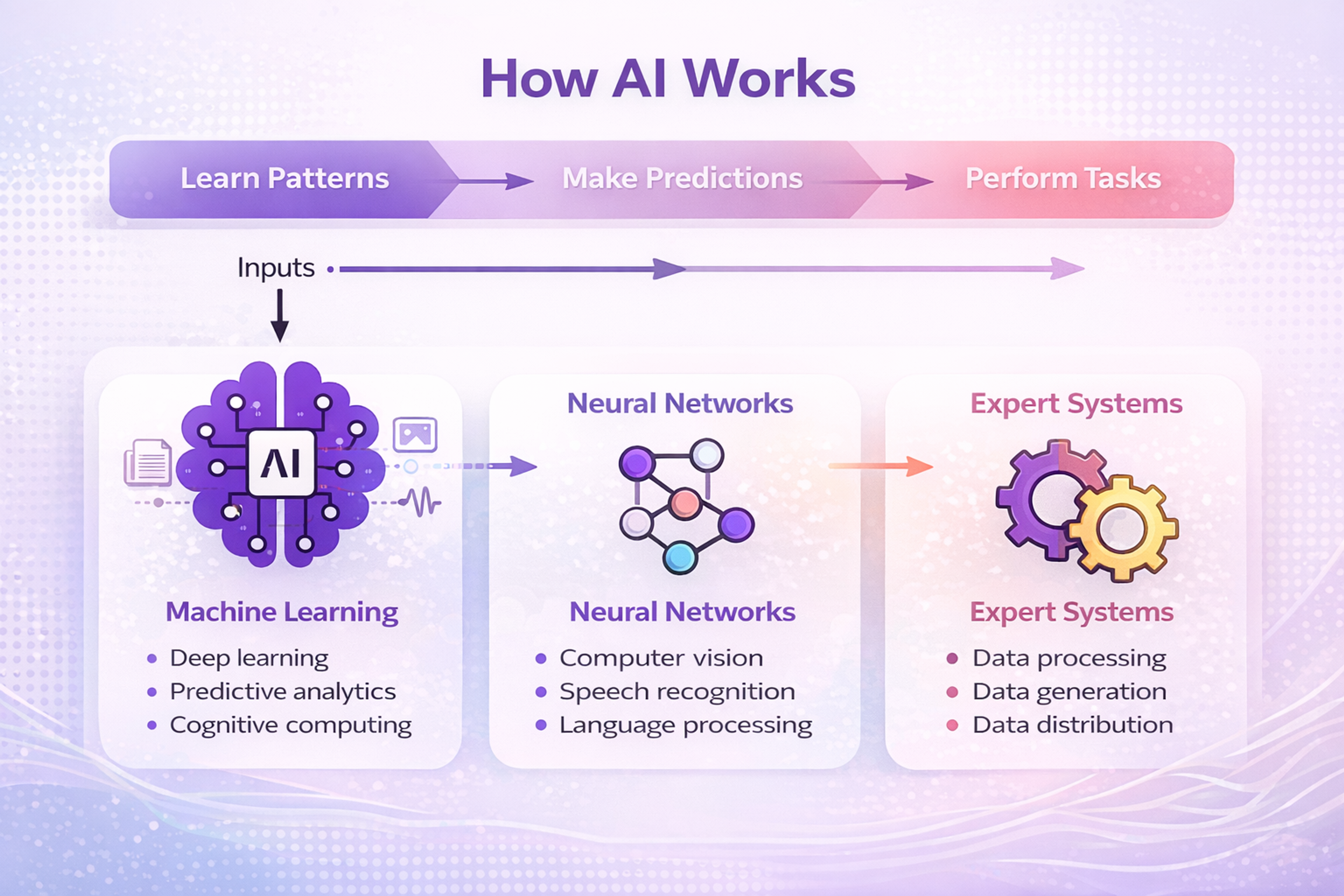
How AI Is Built
In this section, we break down different types of AI models by how they are built, including transformers, GANs, and neural networks.
Traditional Neural Networks
These are multi-layered networks that transform inputs through weighted connections. They work well for basic pattern recognition but struggle with complex, long-range connections in data.
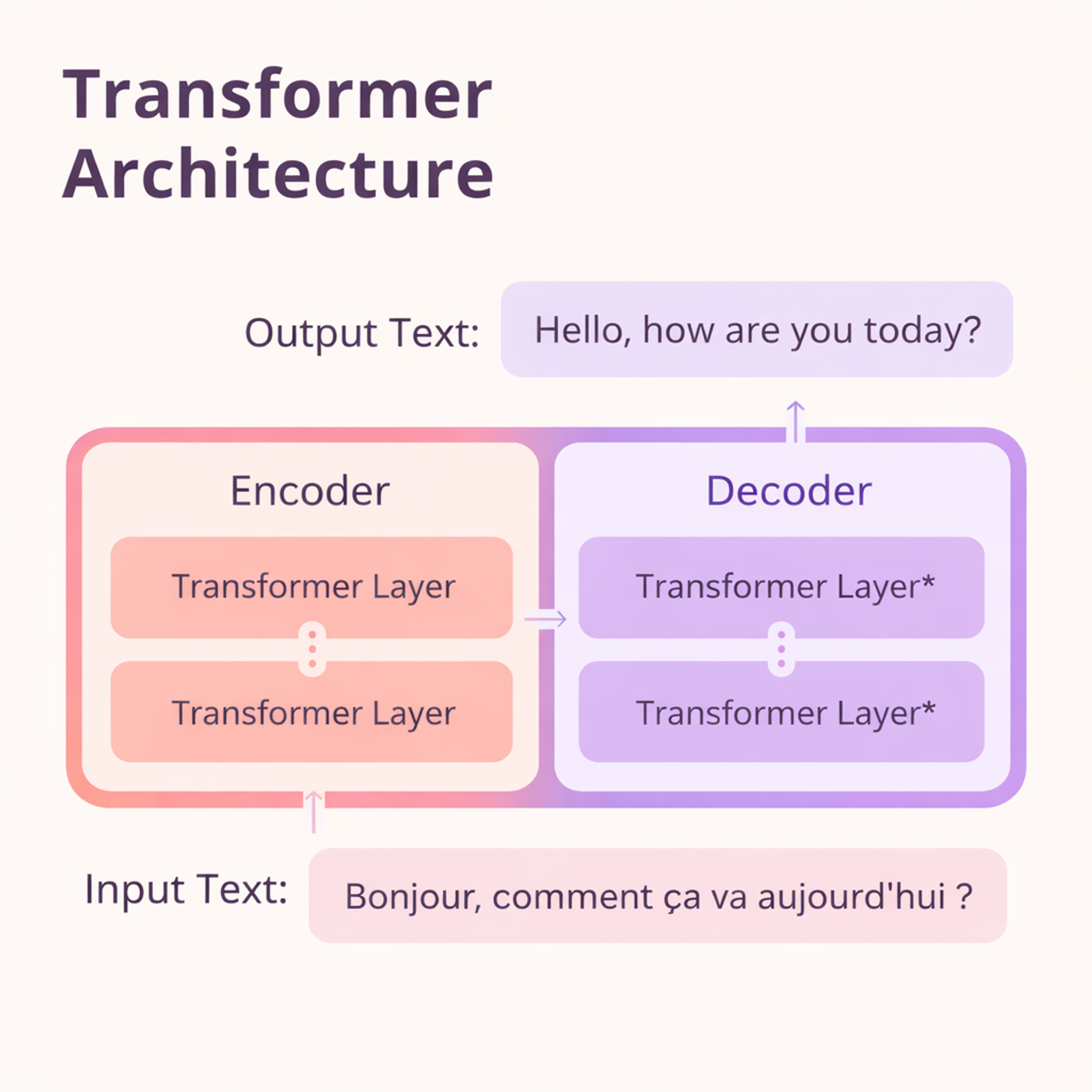
Transformer Architecture
This is the foundation of modern AI breakthroughs. Transformers use "attention mechanisms" to focus on relevant parts of input data. They handle long sequences and complex relationships perfectly.
The key insight is that attention lets the model decide what information matters most at each step. This makes transformers incredibly effective for language and increasingly for vision and other areas.
Transformers power GPT, Claude, BERT, and most large language models you hear about.
Transformer Architecture
Generative Adversarial Networks
These involve two neural networks competing against each other. One generates fake data, the other tries to detect fakes. This competition creates remarkably realistic synthetic content.
Common uses include creating realistic faces, generating artwork, improving datasets, and transferring artistic styles.
Neuromorphic Computing
This hardware mimics brain architecture, using spikes and continuous adaptation instead of traditional digital computation. It's mostly experimental but promising for ultra-low-power AI applications.
How AI Reasons
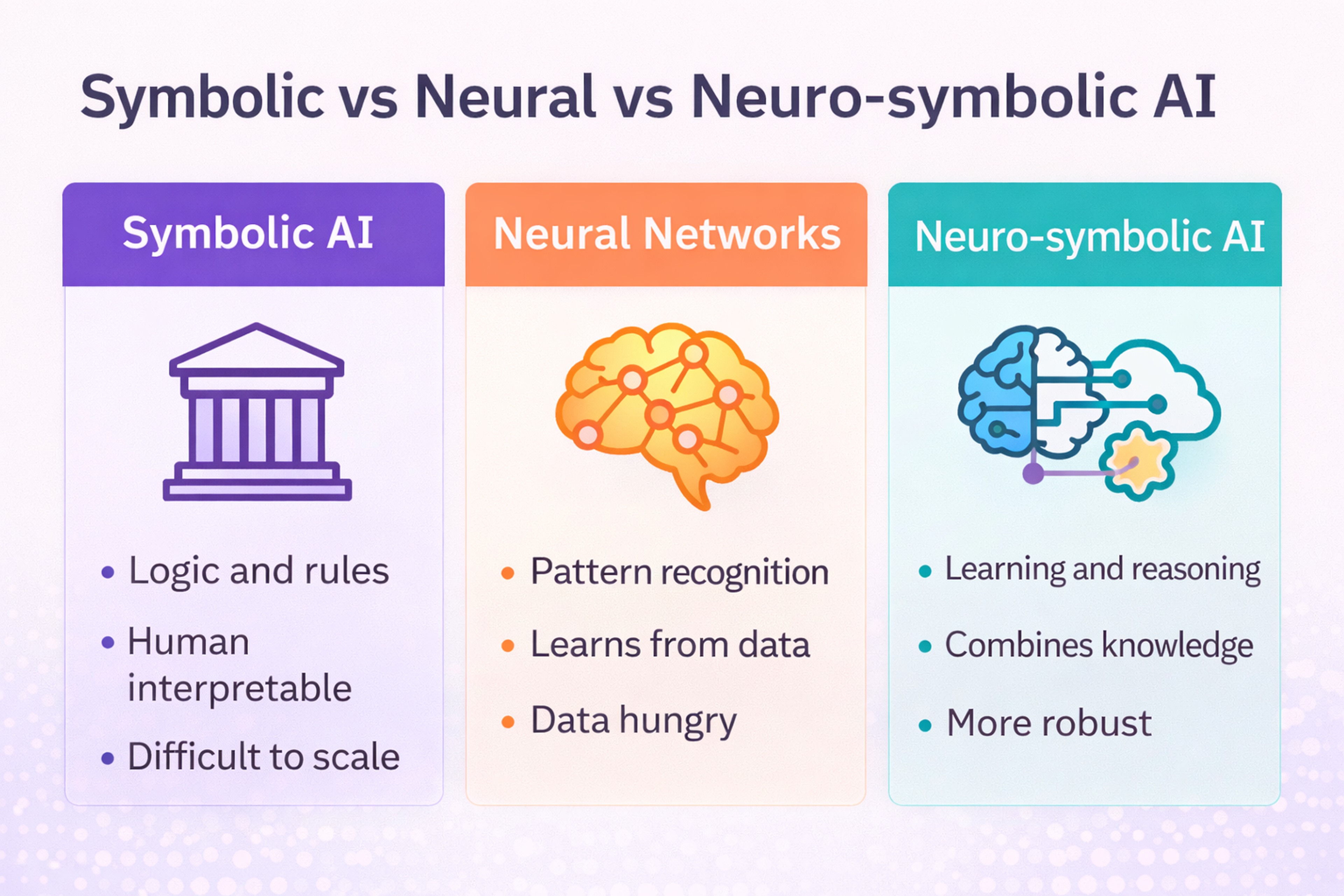
Symbolic AI
Knowledge lives in explicit rules, logic, and structured databases. These systems are transparent and follow domain constraints perfectly. They work great for compliance, legal reasoning, and situations requiring clear explanations.
You can easily audit and modify these systems. They incorporate expert knowledge directly. But they struggle with messy, complex data like images or natural language.
Examples: tax computation engines using rule sets; medical triage systems with explicit clinical guidelines.
Neural AI
Knowledge hides in learned parameters. Millions or billions of numbers encode patterns the system discovered. Deep networks excel at perception, language understanding, and pattern recognition.
They learn excellently from raw data and handle complex patterns humans can't easily specify. But they act like "black boxes" and can be unpredictable.
Examples: image classifiers for defect detection on a factory line; speech-to-text systems.
Hybrid Systems
These combine neural perception with symbolic reasoning. A vision model might read a contract, then a rule-based system applies legal regulations to it.
Hybrids blend accuracy, robustness, and explainability. Neural networks handle messy input data while symbolic systems provide reliable, explainable reasoning.
Symbolic vs Neural vs Neuro-symbolic AI
Causal AI
This goes beyond correlation to understand cause-and-effect relationships. Instead of just predicting that customers who buy X also buy Y, causal AI understands why this happens.
The critical advantage is enabling "what if" reasoning and avoiding misleading correlations that fool other AI types.
How We Trust AI
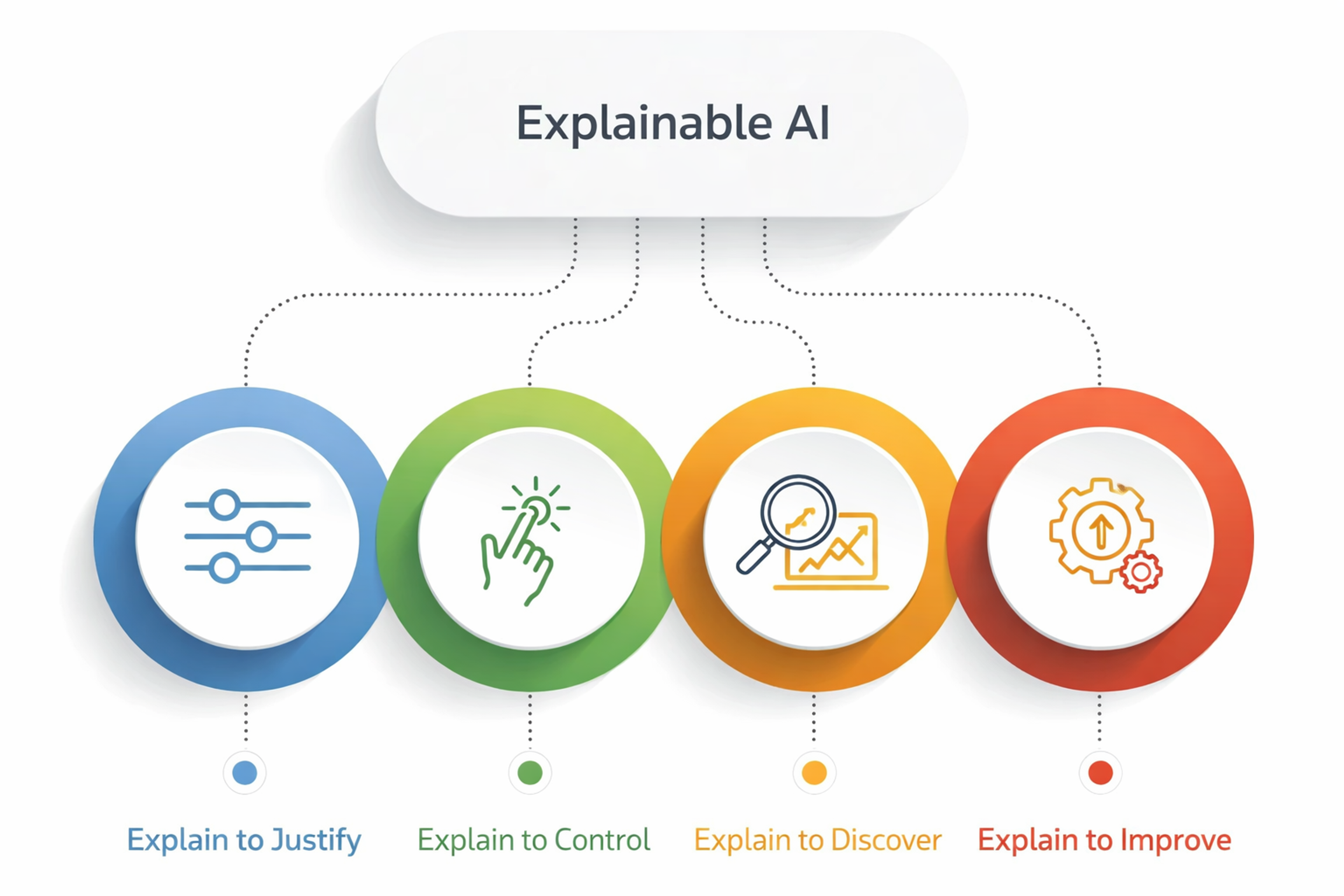
Explainable AI
These methods make AI decisions clear to humans. They include techniques like showing what the AI paid attention to, scoring feature importance, and generating natural language explanations.
This matters for regulatory compliance, debugging problems, building user trust, and detecting bias.
Explainable AI
Ethical AI and Bias Prevention
These frameworks ensure AI systems are fair, transparent, and aligned with human intelligence and values. This includes detecting unfair bias, ensuring representative training data, and implementing fairness rules.
Key challenges include historical bias in data, hidden discrimination, and balancing fairness across different groups.
Examples: debiasing recruiting models to avoid gender or age bias; fairness audits on lending models
AI Safety and Alignment
This ensures AI systems behave as intended and stay under human control. It includes testing for robustness, building fail-safe mechanisms, and aligning with human values.
Current focus centers on making sure systems are helpful, harmless, and honest, especially as they become more capable.
What AI Produces
Predictive Models
These forecast outcomes or assign scores. Customer churn probability, demand forecasting, risk assessment, and recommendation rankings all fit here. They power dashboards, automated decisions, and business intelligence.
The value comes from data-driven decision making, risk management, and resource optimization.
Examples: churn risk scores to drive retention offers; demand forecasts for inventory planning.
Generative AI
This creates new content like text, images, audio, video, code, or data. It excels at drafting, brainstorming, design variations, content creation, and improving datasets.
Generative AI relies on deep learning models trained on large amounts of structured data, such as text, images, and numbers.
Applications include writing assistance, image creation, code generation, synthetic data creation, and creative collaboration. These systems require careful oversight for accuracy and legal concerns.
Examples: code generation for boilerplate functions; synthetic images to augment rare classes.
Conversational Systems
Chatbots, voice assistants, and autonomous agents can plan, use tools, retrieve information, and take actions. They’re moving beyond simple chat to managing complex workflows across multiple systems.
Conversational AI systems are designed to interpret, understand, and generate human language, enabling natural interactions between users and machines.
The evolution goes from answering questions to taking actions like booking appointments, analyzing data, and managing business processes.
Examples: customer support bots that resolve billing issues; voice assistants scheduling meetings and sending follow-ups.
Perception Systems
Computer vision, speech recognition, document processing, and multimodal understanding transform raw sensory input into structured information. Other systems can then use this information.
These are essential building blocks that enable AI to interact with the physical and digital world. Perception systems often rely on present moment data from sensors to interpret the environment in real time.
Edge AI
This AI runs directly on devices like smartphones, cameras, or sensors rather than in the cloud. It enables real-time processing, privacy protection, and reduced bandwidth usage.
Benefits include lower delay, better privacy, less dependence on internet connections, and cost savings at large scale. This type of AI can be used in different fields.
Edge AI
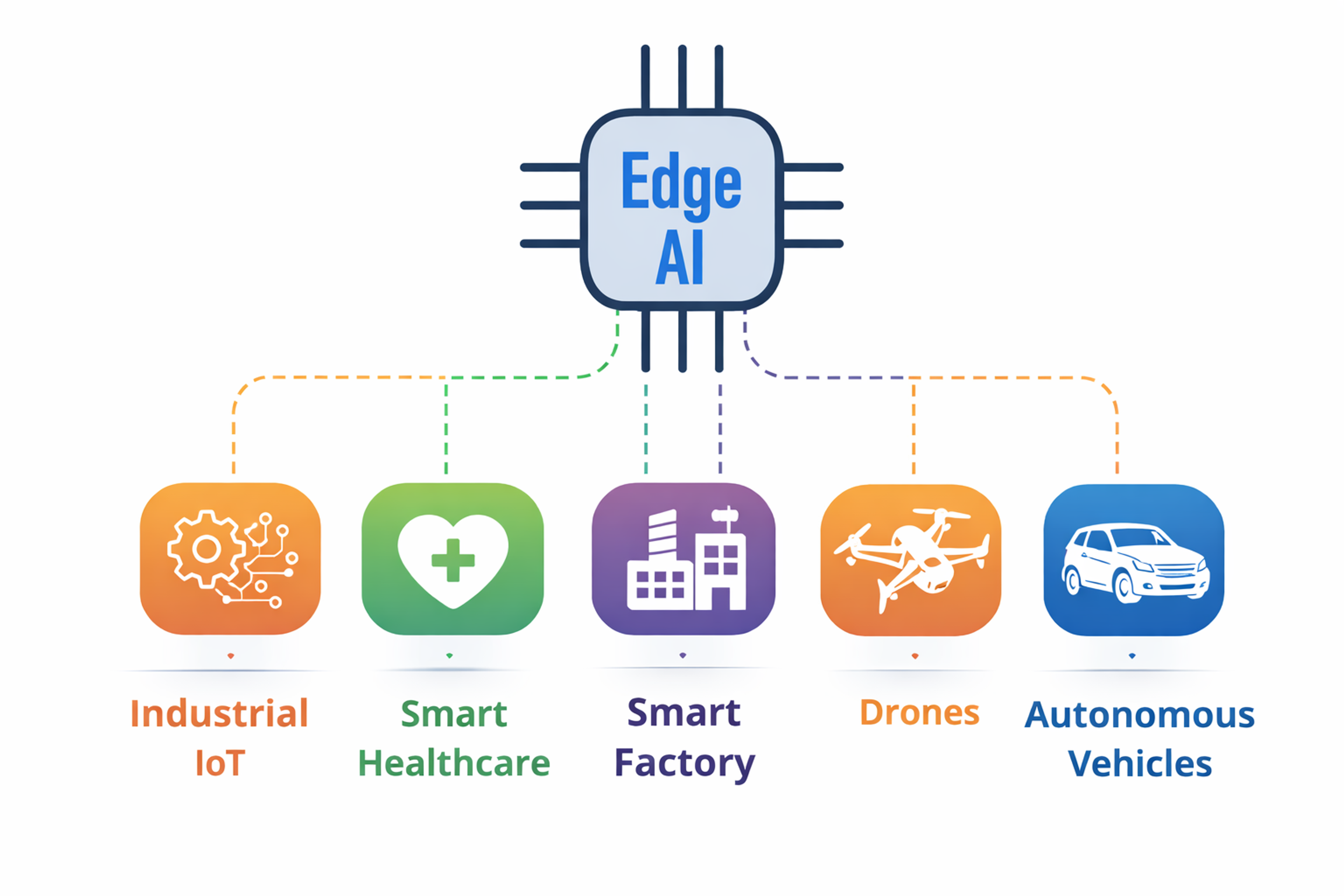
Modern AI in Practice
Federated Learning
This trains AI models across distributed devices or organizations without centralizing data. Each participant trains locally and only shares model updates, preserving privacy while enabling collaboration.
Use cases include healthcare research across hospitals, smartphone keyboard improvement, and financial fraud detection across banks.
Human-AI Collaboration
These systems augment human capabilities rather than replace them. The AI handles routine tasks, such as virtual assistants pattern detection, and information processing while humans provide judgment, creativity, and oversight.
The success pattern shows that AI plus human expertise consistently outperforms either alone in complex areas like medical diagnosis and financial analysis.
Multi-Agent Systems
Multiple AI agents work together, each with specialized roles and capabilities. They coordinate, negotiate, and collaborate to solve complex problems no single agent could handle.
Applications include supply chain optimization, traffic management, and distributed problem-solving.
Multi-Agent Systems
Choosing the Right Approach
Define Success First
Are you generating content, predicting outcomes, classifying data, or taking actions? Different goals need different AI types.
Consider Your Constraints
Need explainability? Lean toward symbolic or hybrid approaches with clear reasoning methods. Have regulatory requirements? Ensure bias testing and audit trails are built in.
Working with privacy-sensitive data? Consider federated learning or edge AI. Making high-stakes decisions? Plan for human oversight and fail-safes.
Match Your Data Reality
Lots of labeled data works well with supervised learning approaches. Mostly unlabeled text or images suit self-supervised foundation models with fine-tuning.
Interactive environments call for reinforcement learning or multi-agent systems. Distributed data needs federated learning approaches.
Plan for the Full Lifecycle
Start narrow and expand carefully. Build reliable focused AI for core tasks, then add capabilities thoughtfully. Build in monitoring for data drift, performance problems, and bias detection.
Design for updates because models need retraining and rules need updating. Plan human oversight to keep humans involved in high-stakes decisions.
FAQ
What Are The 2 Types Of AI (Weak AI Vs. Strong AI)?
Weak AI (Narrow AI) is built to do specific tasks well, like search, translation, or recommendations. Strong AI (General AI) would understand and learn any task like a human, across domains, without being limited to one narrow purpose.
General AI Vs Narrow AI
Narrow AI is specialized and common today. General AI would be flexible, transferable, and able to reason across many unrelated tasks. Today’s systems are still Narrow AI, even if they feel versatile.
What Are The Different Types Of AI?
You’ll usually see AI grouped in a few simple ways:
By capability: Narrow AI, General AI, and Superintelligent AI (theoretical).
By functionality: Reactive Machines, Limited Memory, Theory Of Mind, Self Aware (the last two are not real in practice today).
By approach: Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Rule Based Systems.
How Many AI Models Are There?
There’s no single fixed number. There are thousands of models across labs, companies, and open source. A practical way to think about it is by model families and use cases: large language models, vision models, speech models, recommendation models, and forecasting models.
What Is the Most Common Type of AI Used Today?
The most common AI is narrow AI (or weak AI), which powers tools like voice assistants, chatbots, search engines, and recommendation systems.
What Is the Most Common Type of AI Used Today?
The most common AI is narrow AI (or weak AI), which powers tools like voice assistants, chatbots, search engines, and recommendation systems.
What Is the Simplest Form of AI?
Rule-based AI is the simplest form. It follows “if-then” instructions without learning, often used in basic automation or decision trees.
What Is the Most Advanced Type of AI?
The most advanced AI today is generative AI and large language models. They can create human-like text, images, audio, and code, showing reasoning skills within specific limits.
What Is the AI App Everyone Is Using?
Popular AI apps include ChatGPT, Google Gemini, and Microsoft Copilot. Millions use them for writing, research, coding, and daily productivity.
What Is AI in a Smartphone?
AI in smartphones powers features like voice recognition, predictive text, camera scene optimization, face unlock, and real-time translation.
Read more:
Conclusion
There's no single correct way to categorize AI types because different systems reveal different truths. By capability, most current systems remain narrow but increasingly powerful. By learning approach, self-supervised and transfer methods lead the field. By architecture, transformers have revolutionized everything. By application, hybrid systems that combine strengths work best in practice.
Use these frameworks to evaluate any AI system you encounter. Understand what problem it's solving, how it was trained, what architecture it uses, and how its decisions can be understood and trusted.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more