Understanding real user needs through data turns personas from static posters into a working system. This guide shows how to build reliable, ethical, and actionable personas.
How to validate and apply them and how to scale the capability across teams. You’ll leave with a practical flow (create → validate → apply), an organizational blueprint (skills, infrastructure, leadership), and an operating cadence with clear metrics.
Personas: What They Are, Why They Matter, Where They Fail
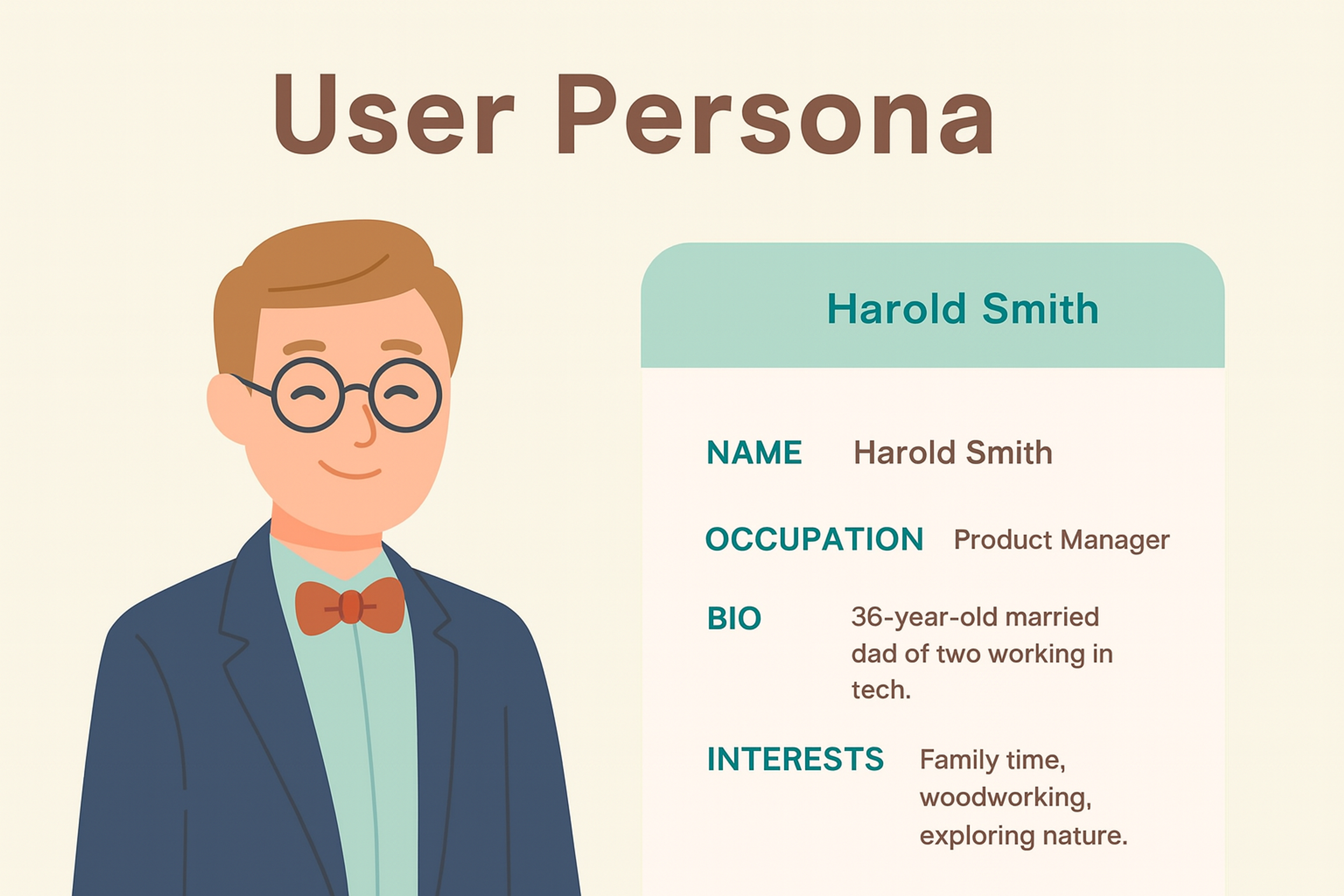
Personas are evidence-based archetypes of meaningful user segments. They capture behaviors, needs, motivations, and constraints that shape product and marketing decisions. Done well, personas align teams, sharpen scope, and improve both usability and business outcomes.
Common failure modes are predictable: generic “everyone” personas. Stereotypes and anecdotes standing in for evidence. Artifacts that never get updated and long demographic sections that don’t influence decisions. Good personas stay specific, behavior-led, and tied to measurable outcomes.
User Persona Example
Data Foundations: Sources, Methods, and Quality
Personas are only as strong as their data. Combine quantitative signals — behavioral analytics, funnels, cohort trends, retention patterns, search and usage data, survey statistics — with qualitative depth from interviews, diary studies, contextual inquiry, and support conversations. Connect product usage, feedback, and commercial metrics to see both what users do and why they do it.
Benefits of Data-Driven Personas
Quality matters. Check freshness, coverage, bias, and completeness before analysis. Standardize definitions and events, document assumptions, and make your process reproducible so future teams can trust and extend the work.
Privacy, Ethics, and Compliance
Earn trust by collecting only what is necessary, minimizing identifiers, and applying anonymization or pseudonymization where possible. Obtain clear consent, respect regional laws at a principle level (e.g., GDPR/CCPA), and define retention and deletion paths. Provide simple guidance on what data different roles may access and how to use it responsibly. Personas should never enable re-identification of individuals.
The Practical Flow
Create. Start with the data you have. Map behaviors, jobs-to-be-done, goals, and constraints. Use clustering or clear segmentation rules to identify candidate groups. Write concise persona narratives backed by evidence: behaviors, tasks, barriers, triggers, preferred value, and success markers. Keep only attributes that change product or go-to-market decisions.
Validate. Check whether persona-based predictions hold. Do users in Persona A convert on concept X more than Persona B? Do their paths, errors, or time-to-value match expectations? Use A/B tests, behavioral checks, and follow-up interviews to confirm or revise.
Apply. Wire personas into daily work. PRDs and user stories name the target persona and link to supporting evidence. Design reviews include a “persona fit” check.
Marketing briefs state the segment hypothesis and desired behavior change. Support playbooks adapt tone and guidance. Keep access easy — dashboards, quick cards, and living docs — so teams use personas, not just admire them.
User Persona Example by Clay

Organizational Capabilities
Skills. Raise baseline data literacy across roles so people read charts correctly, distinguish correlation from causation, and spot sampling issues. Teach data storytelling so insights translate into crisp narratives for executives, PMs, designers, engineers, and customer teams.
Infrastructure. Provide governed, self-serve access to persona-relevant data and artifacts: a source-of-truth dashboard, templated reports, and reproducible queries. Automate pipelines that refresh inputs and flag drift so personas don’t decay between releases.
Leadership & Culture. Set standards for data quality and ethical use. Fund the capability like a product — with owners, a roadmap, and SLAs. Encourage psychological safety: when evidence shifts, teams should update personas rather than defend them.
Operating Cadence & Metrics
Treat personas as a living system with rhythm and measurement.
Cadence.
- Weekly: track active experiments and where personas influenced decisions; log learnings and contradictions.
- Monthly: review performance by persona (conversion, activation, retention, satisfaction); update quick cards; retire stale claims.
- Quarterly: refresh segmentation inputs; revalidate assumptions; split, merge, or archive personas as behavior and market conditions change.
Metrics.
- Adoption: share of PRDs/tickets that name a target persona and link to evidence; number of design reviews with a persona fit check.
- Coverage: percent of meaningful traffic/revenue represented by current personas; explicit plan for uncovered segments.
- Impact: uplift on key outcomes for persona-targeted bets (e.g., increase in activation for “Time-Pressed Newcomer” after onboarding changes).
- Freshness SLA: days since last evidence update per persona; target ≤90 days in fast-moving products.
- Quality guardrails: completeness of critical events; survey response reliability; diversity of interview samples.
Case Studies and Examples
To illustrate the effective use of data-driven personas in product development and marketing, consider the following case studies:
Spotify
Spotify employs personas to refine its music recommendation algorithms. By understanding user behaviors and preferences - such as the social listener versus the solo artist enthusiast - Spotify optimizes playlists and features like Discover Weekly. This data-driven approach fosters user engagement and boosts the platform's overall streaming hours.
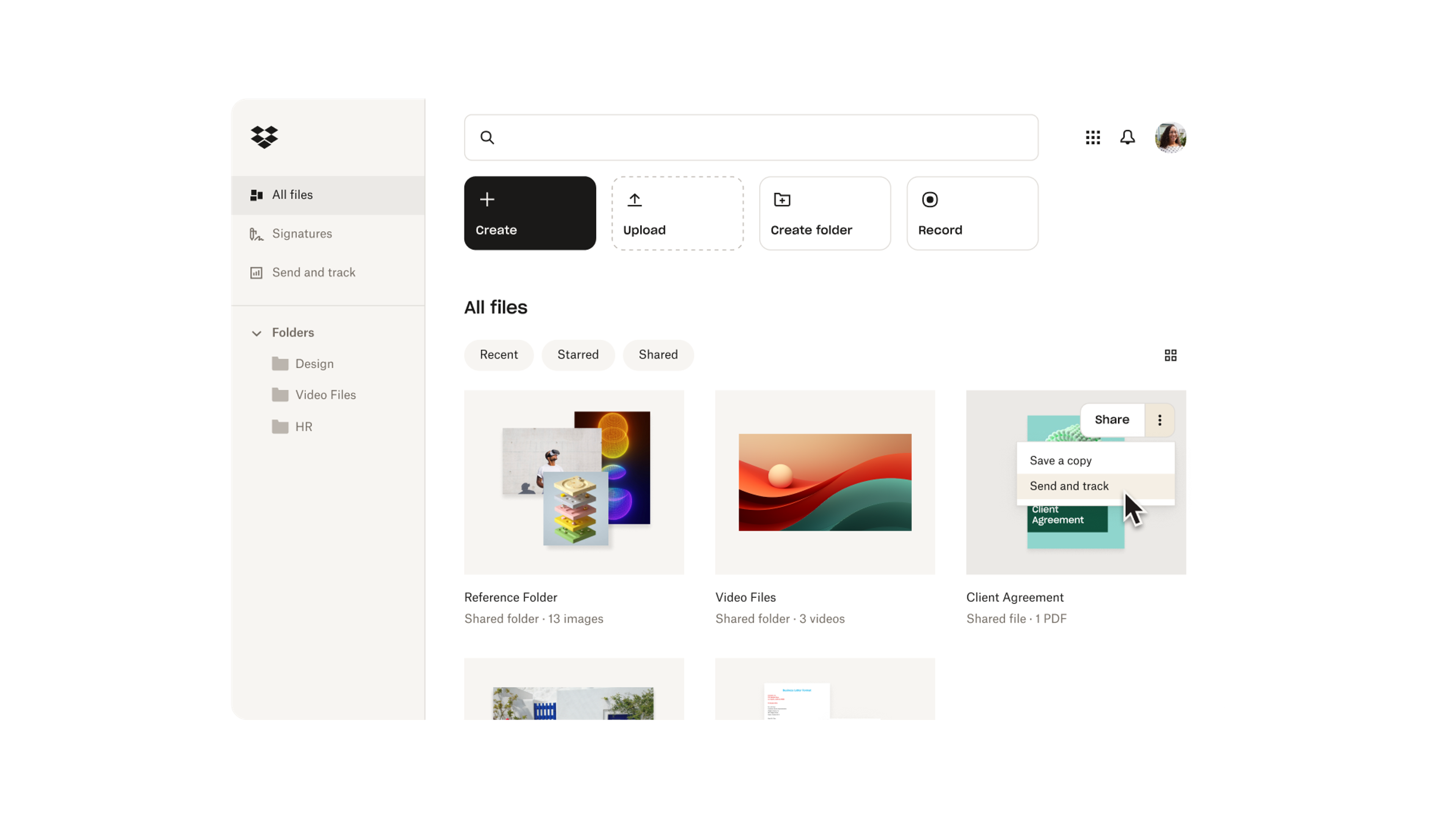
Dropbox
In its early days, Dropbox relied heavily on creating user personas, to identify individual users' and businesses needs. This differentiation enabled Dropbox to tailor its marketing strategies and product features accordingly. The focus on user-centric design led to a significant increase in sign-ups as it effectively addressed the unique pain points of both user groups.
These case studies underline the transformative power of using data-driven personas to understand user needs, drive product innovation, and enhance marketing efforts existing customers in diverse industries.
Source: Dropbox
FAQ
What Is a Data-Driven Persona?
A data-driven persona is an evidence-based archetype of a user segment built from quantitative behavior (events, funnels, cohorts) and qualitative insight (interviews, support logs). It exists to guide product and go-to-market decisions and is refreshed on a set cadence.
How Is It Different From a “Traditional” Persona?
Traditional personas rely on anecdotes and static demographics. Data-driven personas are grounded in real usage data, validated with research and experiments, tied to measurable outcomes, and maintained as living documents.
How Do We Validate Personas?
Validate personas by making falsifiable predictions, testing them (A/B tests, cohort/behavior checks), triangulating with follow-up interviews, and tracking effect sizes. Revise or retire personas that don’t predict behavior.
How Do We Apply Personas Day-to-Day?
Name the target persona in PRDs and design reviews, link the supporting evidence, tailor onboarding/UX and messaging to that persona, and track impact in dashboards. Use “persona fit” as a gate in planning and QA.
What Metrics Prove Personas Are Working?
Key metrics: Adoption (share of PRDs/reviews referencing personas), Coverage (percent of traffic/revenue represented), Impact (lift in conversion/activation/retention for persona-targeted bets), Freshness SLA (days since last update), and Data Quality (event completeness, sample diversity).
Read more:
Conclusion
In an increasingly competitive landscape, the effective use of data-driven personas can be a game changer for organizations seeking to enhance their product development and marketing strategies.
By integrating personas throughout the design process, teams can cultivate a deeper understanding of users, ensuring that solutions are functional and resonate with real-world needs and preferences.
Organizations can establish a culture focused on user-centric practices by fostering collaboration across departments, maintaining open feedback channels, and prioritizing user insights.
Ultimately, aligning design and marketing efforts around well-researched personas paves the way for innovative products and services that connect with their audience, reinforcing the importance of keeping the user's voice at the heart of decision-making.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more