Companies using UX prototyping reduce development costs by up to 60%. This powerful design method helps teams test ideas quickly before building the full product. In today's fast-moving digital world, rapid prototyping techniques separate successful products from failed ones.
This guide covers everything you need to know about UX prototyping. You'll learn different prototype types, essential tools, and proven strategies. We'll also show you how prototyping methods improve user experience and streamline your design workflow.
What Is Prototyping in UX Design?
A prototype shows an early version of your product before you build it. Think of it as a test model that lets you explore ideas and gather user feedback. UX teams create user interface prototypes to simulate how the final product will work.
Designers build prototypes to test concepts and learn from real users. This approach saves time and money by catching problems early.
As Don Norman, author of "The Design of Everyday Things," explains: "Good design is actually a lot harder to notice than poor design." Prototyping helps you spot both.
Prototypes range from simple sketches to complex interactive models. Early prototypes focus on basic structure and flow. Later versions add visual design and realistic interactions.
The prototype design process follows a clear path. Teams start with low-fidelity wireframes, then build high-fidelity interactive models. This progression helps validate ideas at each stage.
User interface prototyping serves multiple purposes. It tests usability, explores design options, and communicates ideas to stakeholders. Most importantly, it keeps users at the center of your design process.
Mockup vs Wireframe vs Prototype by Clay

Advantages of Prototyping
Prototyping brings many benefits to the design process. It helps teams test ideas quickly without spending too much time or money up front.
Here’s how prototyping helps:
- Validates ideas early: Designers can check if a concept works before full development begins. Many teams implement rapid prototyping approaches to accelerate this phase.
- Saves time and money: Catching problems early means fewer changes later.
- Improves usability: User feedback during testing helps make products easier to use.
- Supports team collaboration: Prototypes give all team members a visual tool to share feedback and ideas.
- Boosts communication: Everyone stays on the same page throughout the design process.
- Keeps users in focus: Testing with real people helps make sure the product meets user needs.
- Speeds up iteration: Tools like Figma and Adobe XD apply prototyping techniques to refine designs quickly.
- Leads to better UX: With fast feedback and continuous improvement, the final product is more polished and user-friendly.
Benefits of Prototyping by Clay
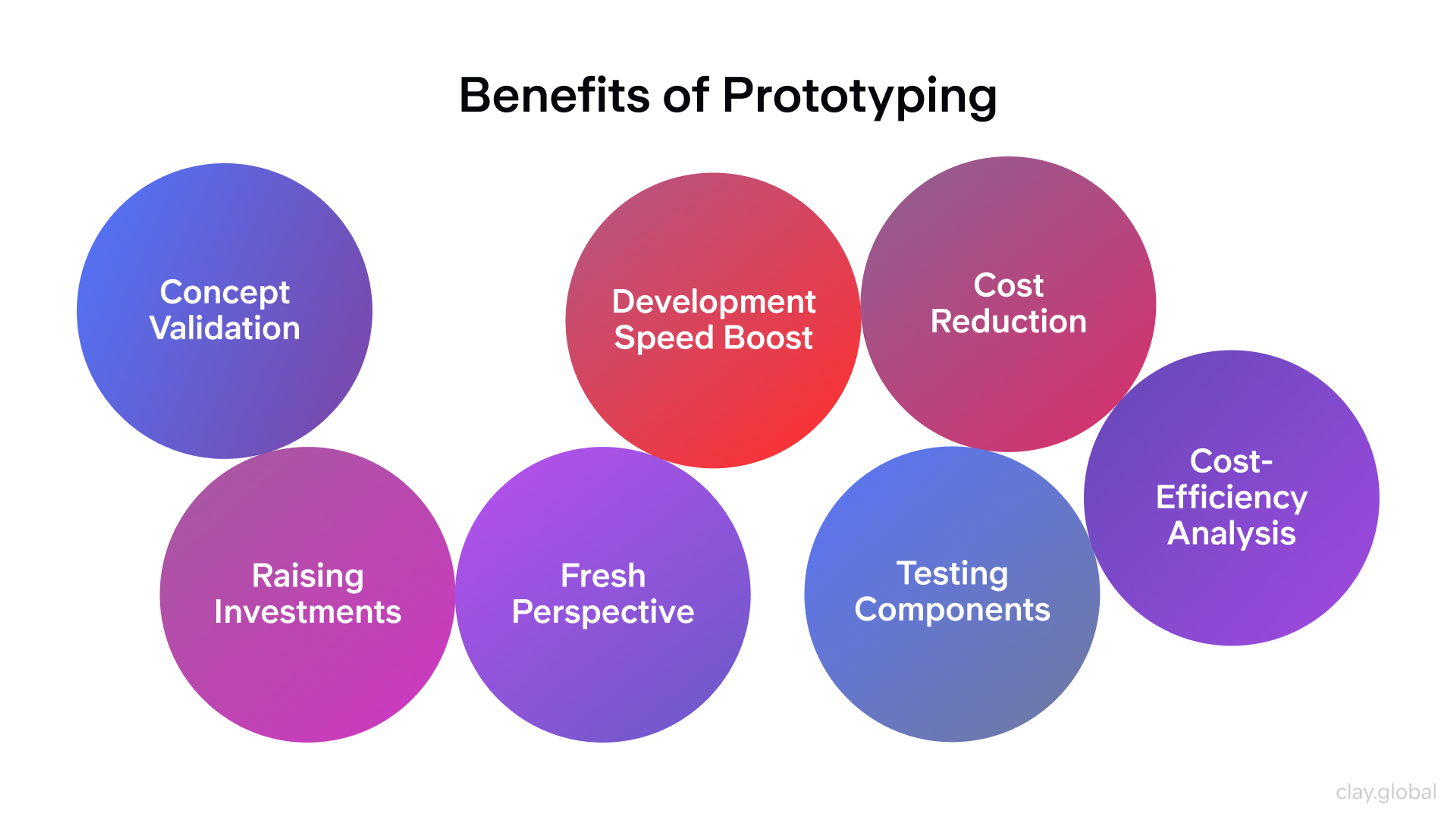
In short, prototyping strategies help teams explore ideas faster, build smarter, and deliver better products that meet user expectations.
Clay is widely recognized in the Bay Area for its leadership in rapid prototyping and user testing. Focusing on iterative UX validation and high-fidelity models, Clay has delivered research-driven designs for major clients like Google and Coinbase.
Types of Prototypes
Low-Fidelity Prototypes
Low-fidelity prototypes work best early in your design process. These simple models test basic ideas without heavy time investment. They help you explore structure and flow before committing to detailed design work.
Common low-fidelity formats include:
- Paper Prototypes - Quick sketches let you test ideas immediately. Graphic and web designers can draw, test, and revise concepts in minutes rather than hours.
- Wireframes - Digital outlines show layout and structure. These user interface prototypes demonstrate functionality without visual distractions.
- Flowcharts - Process diagrams map user journeys. They reveal potential problems in your interaction flow.
- Storyboards - Visual narratives show how users interact with your product. They help teams understand context and user goals.
Steve Krug, usability expert and author of "Don't Make Me Think," advocates for quick, informal testing with low-fidelity prototypes. This approach finds major problems before you invest in complex features.
Low-Fidelity Wireframe by Clay
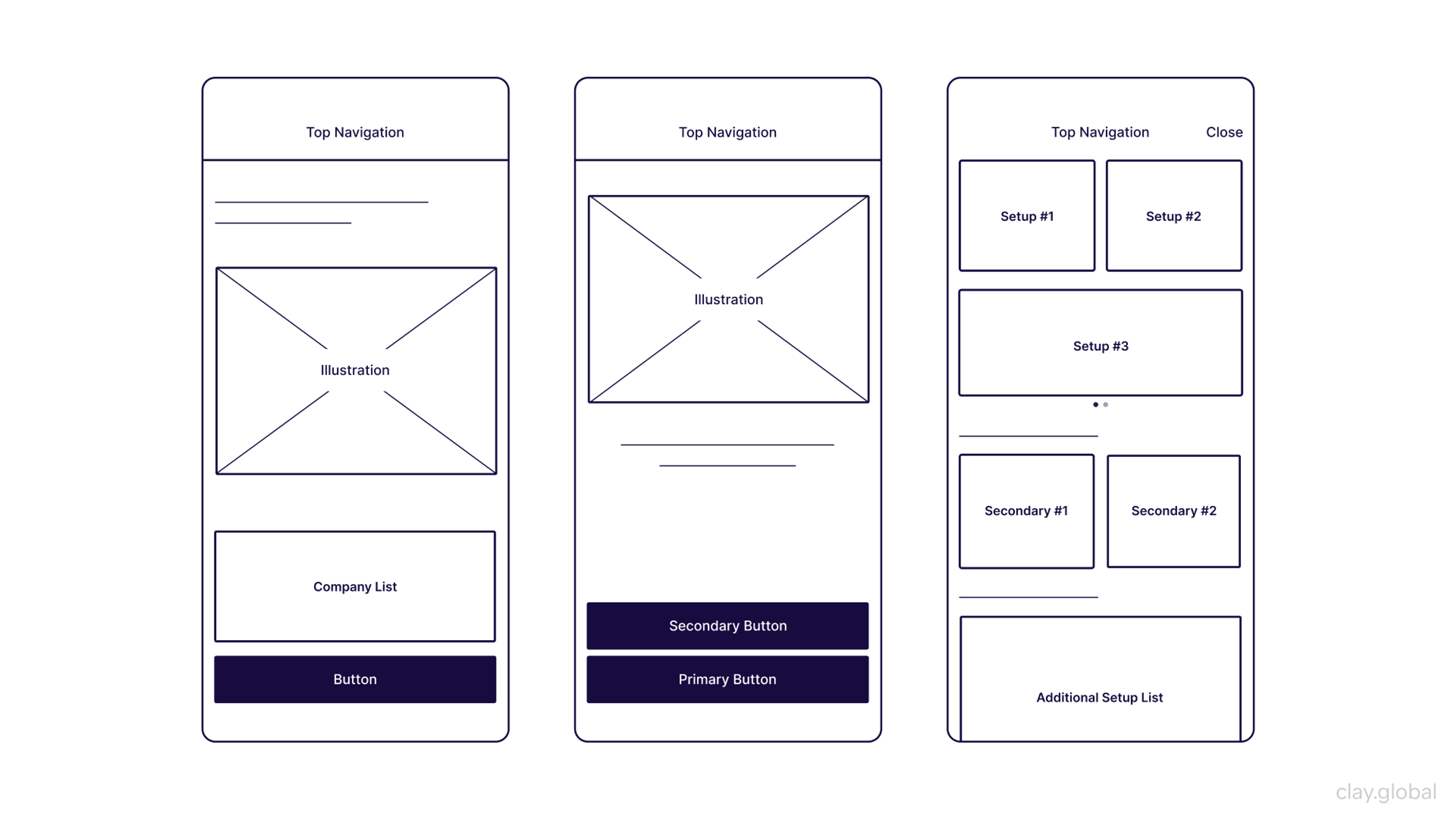
High-Fidelity Prototypes
High-fidelity prototypes look and feel like real products. These detailed models include actual content, visual design, and interactive elements. They're perfect for testing specific interactions and gathering detailed user feedback.
Key features of high-fidelity prototypes:
- Realistic Content - Real text and images instead of placeholder content. This helps users understand your product's true purpose.
- Interactive Elements - Clickable buttons, working forms, and navigation systems. Users can experience your product naturally.
- Visual Design - Actual colors, fonts, and styling. This helps stakeholders visualize the final product.
- Device-Specific Design - Mobile, tablet, and desktop versions that work on real devices.
Interactive Prototypes
Creating interactive prototypes for mobile apps requires special attention to touch interactions and device constraints. Modern rapid prototyping techniques help teams simulate real mobile experiences.
Essential mobile prototype elements:
- Touch Gestures - Swipe, pinch, and tap interactions that feel natural on mobile devices.
- Screen Transitions - Smooth animations between app screens that match user expectations.
- Device Features - Camera access, GPS, and other mobile-specific functionality.
- Performance Testing - Prototypes that reveal potential speed issues on actual devices.
Netflix uses interactive mobile prototypes to test streaming interfaces. Their A/B testing through prototypes optimizes video discovery and improves user engagement.

Horizontal Prototypes
Horizontal prototypes focus on the overall layout and breadth of your interface. These models show many screens and surface-level features without diving into back-end logic or deep interactions. They’re ideal for testing navigation patterns and evaluating visual consistency across a product.
Common uses for horizontal prototypes include:
- Navigation Flow – Users can click through menus and screens to test how easily they move around your product.
- Information Architecture – Teams can validate whether categories, labels, and groupings make sense from the user’s perspective.
- Layout Consistency – Designers can explore how visual components are reused and aligned across multiple screens.
Horizontal Prototype by Clay
Horizontal prototypes help uncover confusion in screen hierarchy and guide improvements in structure. They're often used during stakeholder reviews to show the big-picture experience before refining specific features.
Vertical Prototypes
Vertical prototypes dive deep into one specific feature or user flow. These detailed models simulate full functionality for a single task—from input to output. They help teams validate logic, interaction timing, and user decision paths in depth.
Common uses for vertical prototypes include:
- Feature Validation – Teams can simulate an end-to-end task, like booking a ticket or submitting a form, to test its effectiveness.
- Behavior Testing – Designers can study how users respond to feedback elements like loading states, error messages, and confirmations.
- Performance Insight – Even without live data, vertical prototypes can hint at potential speed, complexity, or friction in interactions.
Vertical Prototyping by Clay
Vertical prototypes are ideal for testing scenarios that require realism and accuracy. While they don’t cover the entire product, they offer valuable insights into how a core feature performs under user pressure.
The Prototyping Methodology
Research-Driven Design Process
Effective UX prototyping starts with user research. Teams must understand their audience before building anything. This research-driven approach reduces guesswork and increases success rates.
User Interviews reveal pain points and goals. Jakob Nielsen, usability expert, recommends testing with five users to find 85% of usability problems.
Competitive Analysis shows industry standards. Teams can identify opportunities to differentiate their products.
Analytics Review provides data about existing user behavior. This quantitative insight guides prototype priorities.
Creating User Personas
User personas represent your target audience. These detailed profiles help designers make user-centered decisions throughout the prototyping process.
Alan Cooper pioneered persona development in "About Face." His methodology creates realistic character profiles based on research data. Effective personas include demographics, goals, frustrations, and technology comfort levels.
User Persona Example by Clay

Teams should create 3-5 primary personas maximum. Too many personas dilute focus and complicate design decisions. Each persona should represent a distinct user segment with unique needs.
Persona validation requires ongoing research. Teams must update personas based on new user insights and changing market conditions.
Defining Clear Requirements
Prototype requirements guide the design process. Clear objectives prevent scope creep and ensure team alignment. Requirements should connect directly to business goals and user needs.
Functional Requirements specify what the product must do. These technical constraints shape prototype capabilities.
Performance Requirements set speed and reliability expectations. Mobile prototypes especially need performance considerations.
Usability Requirements define success metrics. Teams can measure prototype effectiveness against these benchmarks.
Testing and Validation
User testing transforms prototypes into user-centered products. Different testing methods reveal different insights about your design.
- Moderated Testing provides deep qualitative insights. Researchers can ask follow-up questions and explore unexpected user behavior.
- Unmoderated Testing captures natural user behavior. Participants complete tasks in their own environment without the researcher's influence.
- A/B Testing compares design alternatives. Teams can test specific elements like button colors or headline copy.
- Guerrilla Testing offers quick feedback with minimal resources. Designers can test prototypes in coffee shops or public spaces.
Prototype Example

The Google HEART framework measures user experience success. It tracks Happiness, Engagement, Adoption, Retention, and Task completion metrics.
Accessibility Validation
Accessible design serves all users, including those with disabilities. Prototype testing should include accessibility validation from the beginning.
- Screen Reader Testing ensures content works with assistive technology. Many users rely on these tools for navigation.
- Keyboard Navigation lets users complete tasks without a mouse. This feature helps users with motor disabilities.
- Color Contrast Testing makes content readable for users with visual impairments. WCAG guidelines provide specific contrast ratios.
- Cognitive Load Assessment evaluates the mental effort required to use your product. Simple, clear interfaces reduce user frustration.
Best Prototyping Tools for UX Designers
Here are some of the best prototyping tools for UX designers:
1.
Figma: A cloud-based design tool that allows for real-time collaboration and feedback. Figma is known for its ease of use and powerful features, making it a favorite among many UX designers.2.
Sketch: A digital design platform that allows for the creation of static designs and prototypes. Sketch is highly regarded for its vector editing capabilities and extensive plugin ecosystem.3.
Adobe XD: A user experience design software that allows for the creation and prototyping of digital products. Adobe XD offers a seamless integration with other Adobe Creative Cloud tools, making it a versatile choice for designers.4.
InVision: A design platform that allows for the creation, prototyping, and testing of digital products. InVision is known for its robust collaboration features and interactive prototyping capabilities.5.
ProtoPie: A prototyping tool that allows for the creation of interactive prototypes with a low learning curve. ProtoPie is ideal for designers who want to create complex interactions without writing code.6.
UXPin: A design tool that allows for the creation, prototyping, and testing of digital products. UXPin offers advanced features like design systems and code components, making it suitable for large-scale projects.7.
Marvel: A design tool that allows for creating, prototyping, and testing digital products. Marvel is user-friendly and offers a range of features for both beginners and experienced designers.8.
MockPlus: A prototyping tool that allows for creating interactive prototypes with a low learning curve. MockPlus is known for its simplicity and speed, making it a great choice for rapid prototyping.
Prototyping Programs
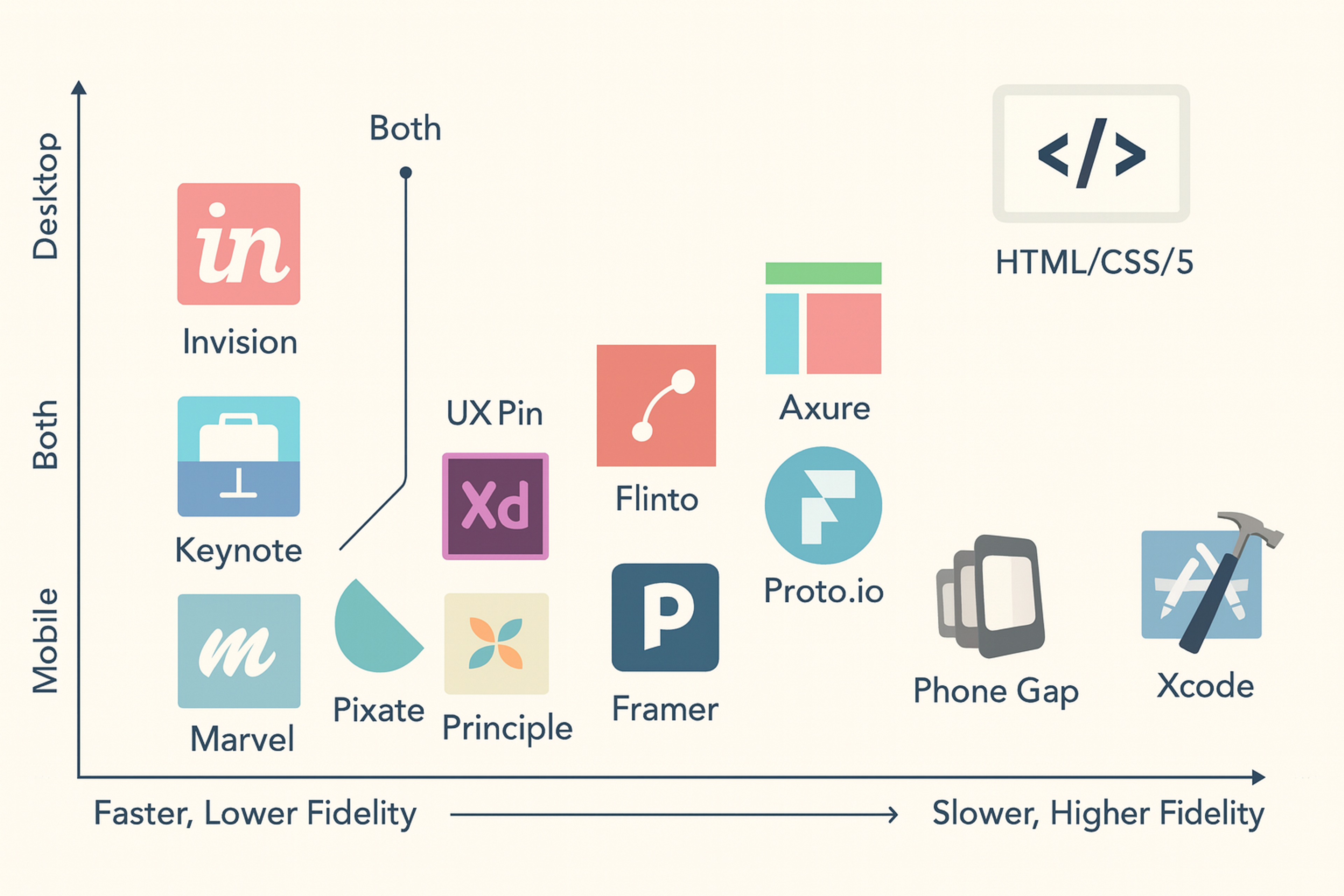
UX Prototype Examples
Aircall (Interactive Call Center Dashboard)
Aircall teamed up with Geckoboard to build interactive, real-time dashboards that give customer support teams clear visibility into call activity and performance. These prototypes allowed them to experiment with different dashboard layouts and interactions, directly improving how their teams handle incoming calls and manage productivity. You can explore their approach on Geckoboard's website.
Ledger (Crypto Hardware Wallet App)
Ledger's development team used advanced prototyping techniques while building their crypto wallet application. They created realistic, high-fidelity interactive mockups to ensure secure and intuitive user experiences, especially around onboarding and security verification processes. Ledger openly shares their prototyping guidelines and examples in their Developer Portal.
Source: Ledger

Notion (Collaborative Workspace Tool)
Notion emphasizes rapid experimentation through sketches and basic wireframes to quickly test new ideas. Although detailed public case studies are limited, various interviews and discussions within the design community reveal that Notion's iterative prototyping approach helps them continually align the platform with user needs and expectations.
Getting Started with Your First Prototype
Planning Your Prototype Strategy
Start small and iterate quickly. Your first prototype should test one key assumption about your design. Don't try to build everything at once.
1.
Choose Your Fidelity Level based on what you need to learn. Use low-fidelity for early concept testing and high-fidelity for detailed interaction validation.2.
Set Clear Success Metrics before you start building. What will tell you if your prototype works? Define these criteria upfront.3.
Plan Your Testing Approach early in the process. Who will you test with? What questions do you need answered?
Building Your First Prototype
1.
Start with User Flows - Map the key paths users will take through your product. Focus on the most important user goals first.2.
Create Lo-Fi Wireframes - Sketch the basic structure and navigation. Don't worry about visual design yet.3.
Add Interactivity Gradually - Begin with simple click-through prototypes. Add complexity as you validate basic concepts.4.
Test Early and Often - Don't wait for perfection. Get feedback as soon as you have something testable.
Remember Eric Ries's Lean Startup principle: "Build, Measure, Learn." This cycle applies perfectly to prototype development.
Common Prototyping Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-Designing Too Early - Don't spend time on visual polish before validating core concepts. Users care more about functionality than appearance in early testing.
- Skipping User Testing - Internal reviews can't replace real user feedback. Even informal testing provides valuable insights.
- Ignoring Technical Constraints - Work with developers to understand what's possible. Unrealistic prototypes create false expectations.
- Testing Only Happy Paths - Design for edge cases and error states. Real users don't follow perfect scenarios.
- Forgetting Mobile Context - Test mobile prototypes on actual devices. Desktop testing misses important usability issues.
The Future of Prototyping in UX Design
The future of prototyping in UX design is exciting, with new tools and technologies emerging all the time. Here are some trends to watch:
1.
AI-Powered Prototyping: AI-powered prototyping tools are emerging, allowing for faster and more accurate prototyping. These tools can automate repetitive tasks and provide intelligent suggestions, enhancing the efficiency of the design process.2.
Virtual and Augmented Reality: Virtual and augmented reality are becoming more prevalent in UX design, allowing for more immersive and interactive prototypes. These technologies enable designers to create realistic simulations and test user interactions in a virtual environment.3.
Design Systems: Design systems are becoming more popular, allowing for consistency across products and teams. Design systems provide a set of standards and guidelines that help maintain a cohesive look and feel throughout the design.4.
Collaboration Tools: Collaboration tools are emerging, allowing for real-time feedback and iteration. These tools facilitate communication and collaboration among team members, ensuring that everyone is aligned and working towards the same goals.
By staying informed about these trends and incorporating new tools and technologies into your design process, you can create innovative and user-centric products that meet the evolving needs of your users.
Read more
Conclusion
UX prototyping transforms ideas into successful products. The companies that embrace rapid prototyping techniques build better experiences and achieve stronger business results.
Most importantly, keep users at the center of your process. As Don Norman reminds us, "Design is really an act of communication." Prototypes help you communicate more effectively with both users and stakeholders.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more


