Design better, smarter, and faster. Learn how to utilize customer journey maps to design experiences that users will remember and recommend.
Your user opens your app. Within seconds, confusion sets in. They abandon it forever. This scenario happens more often than you think. Customer Journey Maps transform frustrated users into loyal advocates.
Research shows that businesses using journey mapping grow faster. Companies that excel at customer experience grow revenue 4-8% above their market. Organizations with strong multi-channel strategies keep 89% of customers.
Companies like Airbnb and Spotify have built their success on understanding every step of their users’ journeys. Are you ready to join them?
What Is a Customer Journey Map?
A Customer Journey Map visualizes every user interaction with your product or service. It tracks from initial awareness to long-term loyalty. Think of it as a detailed roadmap.
A customer journey map is a visual representation of the user's experience, illustrating each touchpoint and interaction along the way. It shows not just what users do, but how they feel while doing it. Users progress through various stages, from awareness to loyalty.
According to Hanover Research, 76% of companies say that journey mapping has increased ROI on business investments and made them more customer-centric.
Key Elements of Every Customer Journey Map
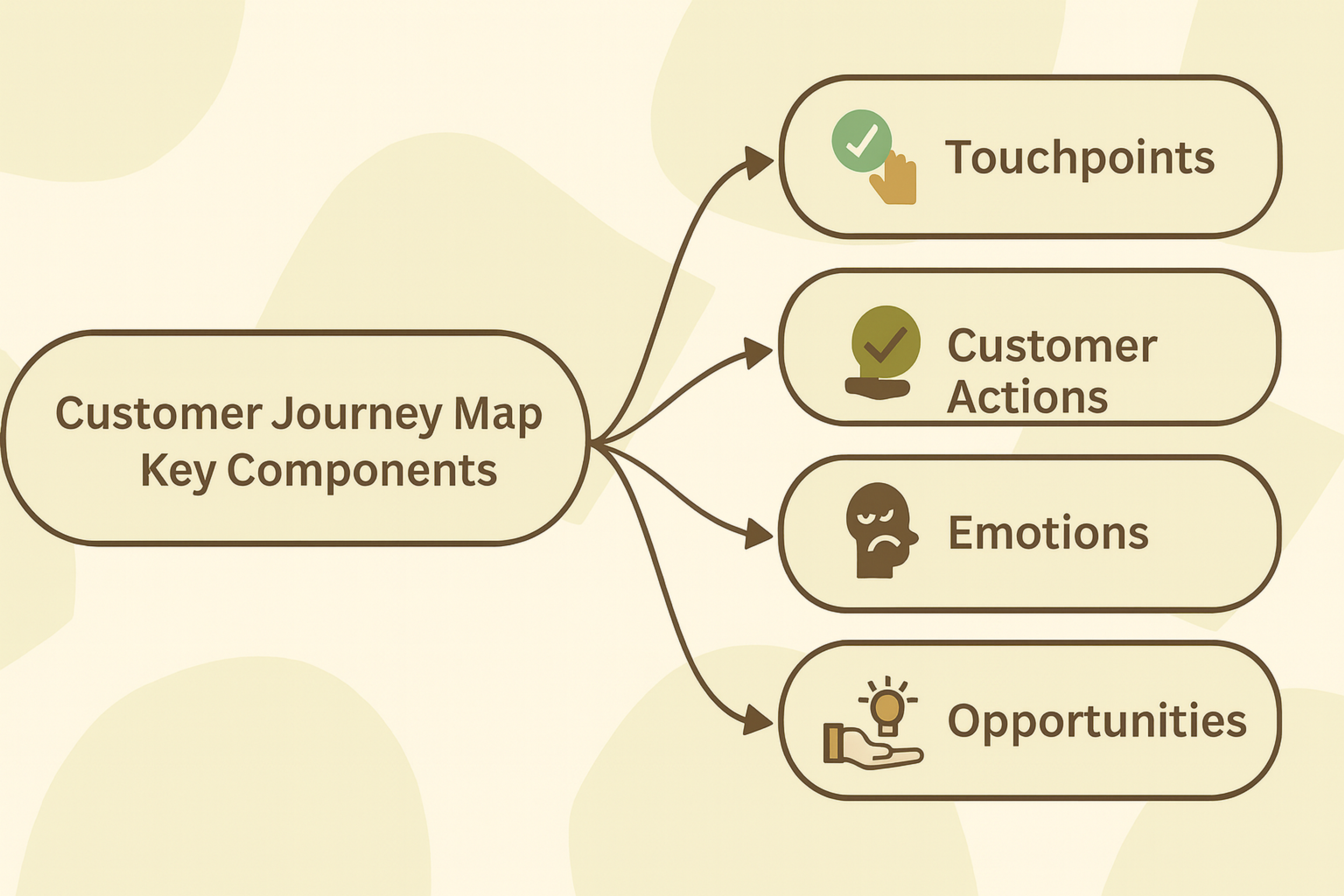
- Key Touchpoints: These are the critical moments of interaction between the user and the product. Website visits, app opens, and customer service calls represent typical touchpoints. These help identify gaps and optimize the overall experience.
- Personas: Detailed profiles of your target users based on real research data. Teams should create customer personas to understand better their target audience, including demographics, behaviors, motivations, and pain points. These profiles guide every design decision.
- Phases: The distinct stages users move through. The journey typically follows Awareness, Consideration, Purchase, and Retention stages.
- Emotions: How users feel at each stage matters deeply. Users experience a range of emotions, including frustration, excitement, confusion, and satisfaction.
- User Actions: Specific behaviors users take at each key touchpoint. They browse, compare, purchase, and share.
- Opportunities: Moments where you can improve the experience or add value. These represent your biggest wins.
Key Elements of Every Customer Journey Map
Is Customer Journey Mapping Important?
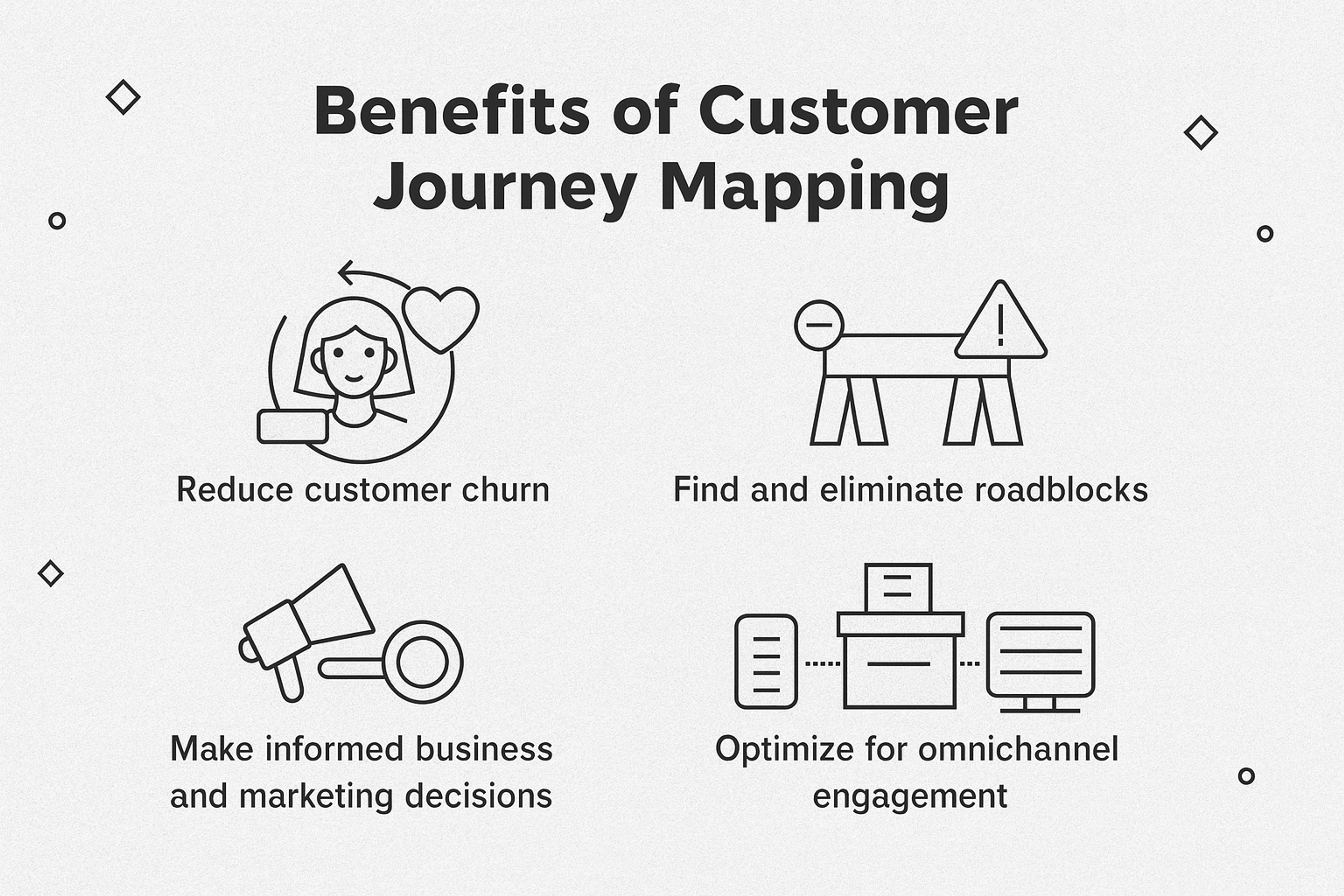
Customer Journey Maps deliver measurable value for both users and businesses.
Benefits for Users
Enhanced experiences through better-designed touchpoints, reduced friction in key processes, and more personalized interactions that actually solve real problems.
Benefits for Business
Journey mapping fosters a more profound empathy within teams. This leads to products that truly serve user needs. You identify hidden pain points that cost you customers. You discover untapped growth opportunities. You build stronger customer relationships that drive long-term retention.
Customer Journey Mapping Benefits
When teams understand the entire customer journey, they make more informed decisions. Marketing creates more relevant campaigns. Product teams prioritize features that matter. Support teams anticipate user needs before problems arise. Journey mapping enables proactive support by helping teams address issues before they impact customers.
Understanding the Customer Journey
Understanding the customer journey enables you to deliver exceptional experiences. The customer journey encompasses multiple interconnected stages. It starts when a customer learns about you.
From there, they move through considering and buying your product. The journey continues into after-sales interactions and loyalty.
Each stage brings unique chances and challenges. Mapping the entire customer journey reveals all points where the customer interacts with your brand. This includes both direct and indirect touchpoints.
Creating a customer journey map helps your business see these stages clearly from the customer's perspective.
How UX Designers Use Customer Journey Maps
UX designers leverage customer journey maps to create better experiences. These maps do more than provide diagrams. They help designers clearly see what users need, feel, and expect at each step.
Creating a user story for each stage further clarifies user needs and guides design decisions. Additionally, ux journey mapping is a powerful tool for visualizing and improving the user experience.
Understand Users Clearly
UX designers use journey maps to visualize users' experiences. The maps show designers exactly where users get confused or frustrated. Google Analytics flow reports and Hotjar heatmaps validate these observations. Tracking user visits to key pages, such as repeated visits to the pricing page, helps identify where users engage most or where they tend to drop off.
Spot Design Opportunities
Journey maps highlight problems clearly. Designers utilize these insights to enhance their designs. They make products easier and more enjoyable to use.
Check Designs with Real Users
UX designers test ideas using journey maps. They verify whether new features effectively address user issues. Mixpanel event tracking confirms whether solutions truly help people. Customer interviews provide direct feedback on new features, assisting teams to understand user needs and refine their approach.
Work Better with Other Teams
Journey maps make communication easier. Designers, developers, marketers, and product managers use them to gain a clear understanding of the user's perspective. Everyone stays focused on improving the user experience.
Keep Users at the Center
Journey maps remind designers that real people use their products. Designers regularly check the maps. They stay connected to user needs and feelings.
Using customer journey maps helps UX designers build products people love. These maps ensure every design decision is valuable and meaningful for users.
Types of Customer Journey Maps
Current State Journey Maps
These maps document how users currently interact with your product. They show actions, thoughts, and emotions at each stage. This includes all the imperfections.
They help you understand the experiences of existing customers. You identify and improve touchpoints for current clients. These touchpoints include renewals, upgrades, or resolving issues.
Current state maps work perfectly for identifying immediate problems and quick wins. Use them when you need to understand existing pain points. They also help onboard new team members to user reality.
Pros: Based on real user behavior. Reveals actual problems. Guides immediate improvements.
Cons: Can be overwhelmed with too much detail. May focus too heavily on problems.
Future State Journey Maps
These envision the ideal user experience you want to create. Future state maps guide product roadmaps and help align teams around a shared vision of what's possible.
When to use: Planning major redesigns, setting long-term product strategy, or communicating vision to stakeholders.
Day-in-the-Life Maps
These capture how your product fits into users' broader daily routines. By mapping the customer's life, you gain insight into their overall routines and experiences. This helps you understand the role your product plays beyond isolated interactions.
They reveal context that single-interaction maps miss. They show when and why users actually need your solution.
Day-in-the-life Journey Map Template

Use cases: Understanding usage patterns, identifying new feature opportunities, or designing for specific user contexts.
Service Blueprints
Service blueprints resemble journey maps, but they also incorporate backend processes and systems. They show what happens behind the scenes to deliver each user experience moment. This includes the actions of service teams and customer service representatives.
Service Blueprints Example
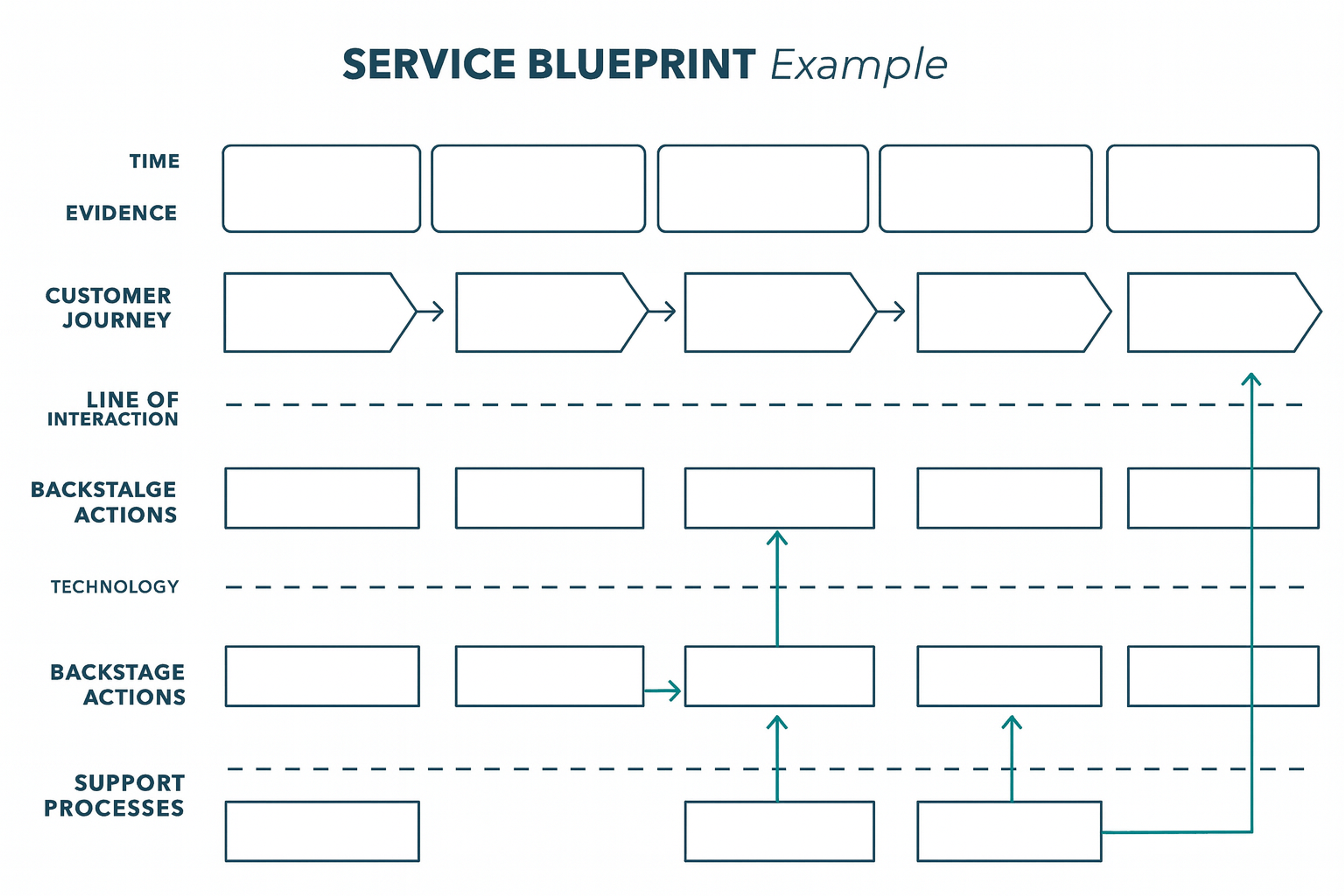
Key difference: Journey maps focus on user experience. Service blueprints include operational processes, staff actions, and system requirements.
Use journey maps for UX improvements. Use service blueprints for operational optimization. Assigning internal ownership of specific processes ensures accountability for implementing improvements.
Industry-Specific Journey Mapping
Different industries have unique customer journey patterns. Understanding these differences helps you create more accurate maps. When mapping, it's essential to consider the various customer segments unique to each industry, as each group may interact with your brand in distinct ways.
B2B Customer Journey Mapping
Business customers have longer, more complex journeys. Multiple people influence buying decisions. The journey can take anywhere from months to years.
In B2B contexts, distinguish between the buyer's journey and the broader customer journey. The buyer's journey tracks the specific process from initial awareness to purchase decision, mapping the stages a potential customer goes through to make a purchasing decision.
Key differences in B2B journeys:
- Multiple stakeholders and decision-makers
- Longer consideration periods
- Higher-value transactions
- More complex approval processes
Salesforce demonstrates how B2B companies map complex, multi-stakeholder journeys. Their approach takes into account different decision-makers at each stage. They track how technical evaluators, financial approvers, and end users each interact with the product differently.
SaaS Customer Journey Mapping
Software-as-a-Service companies focus on subscription retention. Their journeys emphasize onboarding, activation, and ongoing value delivery. Monitoring customer churn at each stage enables SaaS companies to identify and address retention challenges, ultimately leading to a better customer experience and increased loyalty.
Critical SaaS journey stages:
- Free trial or freemium signup
- Product activation and first value
- Feature adoption and expansion
- Renewal and upgrade decisions
E-commerce Customer Journey Mapping
Online retailers track detailed shopping behaviors. They focus on conversion optimization and reducing cart abandonment.
Customer Journey Mapping for Ecommerce

Essential e-commerce touchpoints:
- Product discovery and search
- Product page interactions
- Shopping cart and checkout
- Post-purchase experience
Healthcare Customer Journey Mapping
Healthcare journeys involve emotional and physical experiences. They require special attention to privacy and accessibility.
Healthcare journey considerations:
- Regulatory compliance requirements
- Emotional support needs
- Accessibility requirements
- Privacy and security concerns
- Users' emotional state and its impact on healthcare experiences
Step-by-Step Guide: Creating Your Own UX Customer Journey
Step 1: Define Clear User Personas and Scenarios
Start with research, not assumptions. Define your target customer base first by identifying your target audience and creating detailed customer personas. Then interview real users and conduct customer interviews to gather in-depth insights. Analyze support tickets, review analytics data, and survey customers to further inform your understanding.
Create a customer persona for each primary user type, focusing on 2-3 target customer personas to ensure your journey map is relevant.
Avoid using too many personas: concentrating on a few key personas is more effective and provides clarity.
User Persona Template
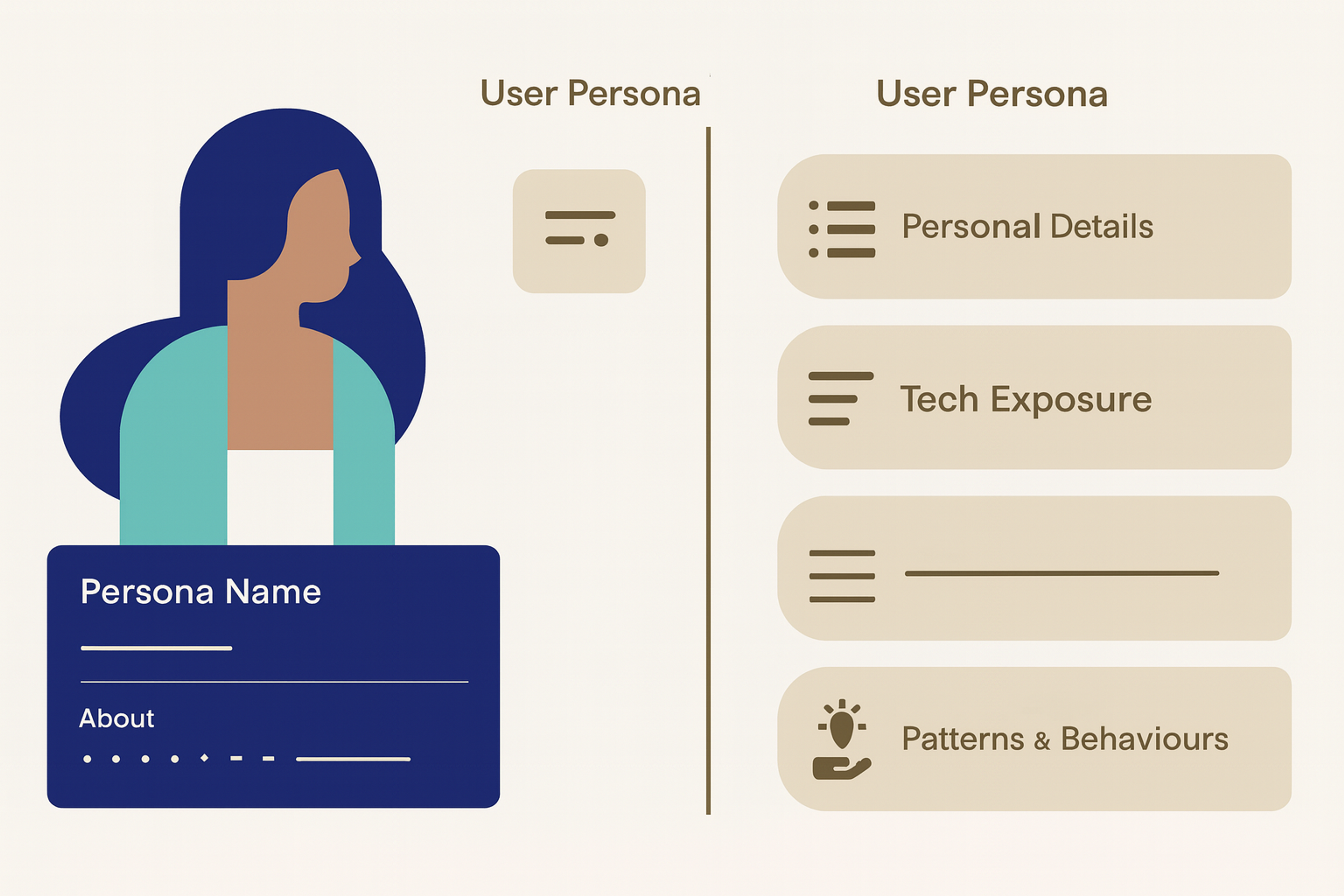
Best practice: When developing personas, consider the average customer to capture common traits. Include demographic details, goals, pain points, preferred communication channels, and technology comfort levels. Give each persona a name and photo to make them feel real to your team.
Example scenario: “Sarah, a busy marketing manager, needs to create a presentation for tomorrow’s client meeting while commuting home on the train.”
Step 2: Identify Stages and Touchpoints
Map out every interaction point by chronologically mapping the customer journey stages and touchpoints. Don’t just focus on your product: include social media, word-of-mouth, competitor research, and post-purchase experiences.
Understanding where and how customers interact with your brand across different channels is important for gaining a complete picture of their experience.
Mapping the buying journey and buying process helps clarify user actions and motivations, especially for potential customers and their interactions at each stage.
Practical tip: Use the “moments that matter” framework. Identify 5-7 key stages, starting with the awareness stage as the initial phase, and listing 3-5 key touchpoints per stage. Quality over quantity - too many touchpoints create confusion. A quick Google search can help you identify online customer touchpoints and mentions of your brand.
Step 3: Map Customer Thoughts, Emotions, and Actions
For each touchpoint, document three layers:
- Thoughts: What’s going through their mind? (“Is this secure?”, “Will this work?”)
- Emotions: Map both customer emotions and customers’ emotions at each stage - how do they feel? (Excited, frustrated, confident, overwhelmed)
- Actions: Document customer behaviors and the specific steps a customer takes at each stage - what do they actually do? (Click, scroll, call, abandon).
Use real quotes from user research whenever possible. Assumptions kill good journey maps.
Step 4: Highlight Pain Points and Opportunities
Customer pain points are moments where users struggle. They get frustrated or consider leaving. Mark each pain point clearly on the map with red indicators or frowning faces. You can also use color coding to group similar ideas, making it easier to organize and analyze related pain points.
Customer Pain Points
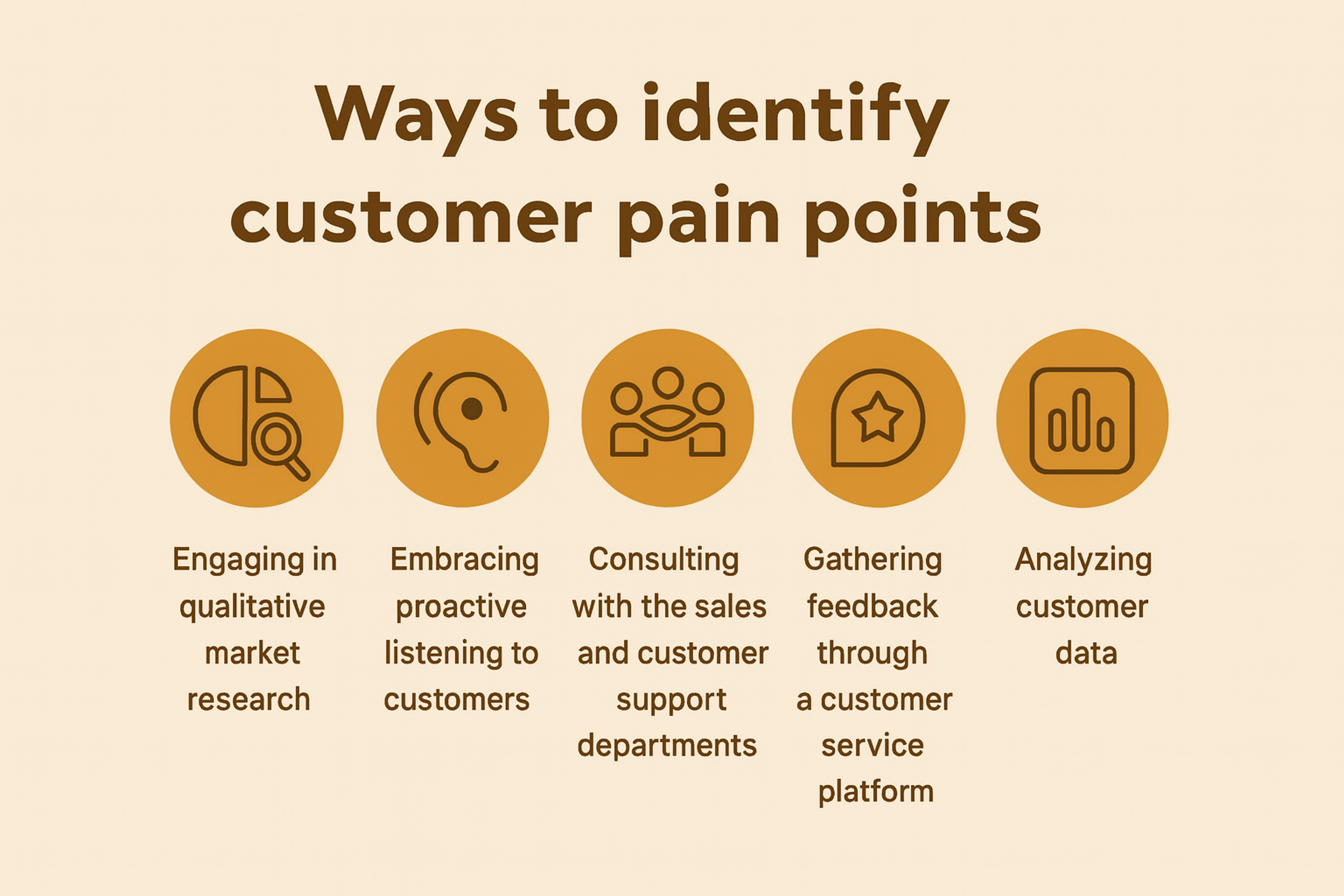
Opportunities are moments where you could add value. You could reduce friction or create delight. These might include:
- Gaps between touchpoints where users need support
- Moments of high emotion where minor improvements have a significant impact
- Points where users make critical decisions
Step 5: Analyze and Validate Your Journey Map
Test your map against real user behavior. Use analytics data and operational data to validate assumptions, identify areas for improvement, conduct usability testing to confirm pain points, and survey users (including existing customers) about emotional responses and their experiences.
Validation criteria: Does this match user feedback? Do analytics and operational data support the flow? Can team members easily understand and act on insights? Does the map help create more satisfied customers and retain customers over time?
Common Customer Journey Mapping Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Mistake 1: Lack of User Research
Creating journey maps based on internal assumptions rather than real user data leads to fantasy maps. These don't reflect reality. Not involving key stakeholders, such as the sales team, means missing valuable insights from direct customer interactions.
Solution: Always start with user research. Interview at least 8-12 users per persona. Analyze support tickets. Review session recordings before mapping anything. Analyze online reviews to gather additional user feedback and identify emotional signals and pain points. Include your sales team in the process. They capture frontline experience with customers.
Mistake 2: Too Much Assumption, Not Enough Validation
Teams often map what they think happens rather than what actually happens.
Solution: Validate every assumption with data. Use Google Analytics, Hotjar heatmaps, and Mixpanel event tracking. Conduct user testing. Run surveys to confirm each step of your journey map.
Customer Journey Map Mistakes

Mistake 3: Ignoring Emotional Factors
Focusing only on actions while ignoring how users feel misses crucial insights. You lose understanding of user motivation and decision-making.
Solution: Always include emotional data. Ask users how they felt during key interactions. Use tools like emotion mapping to capture feelings alongside actions.
Mistake 4: Failing to Update Journey Maps Regularly
Journey maps become outdated quickly as products evolve and user behavior changes.
Solution: Review and update journey maps on a quarterly basis. Regularly revisiting the customer's journey ensures your maps reflect the latest changes in products, services, or customer behaviors. Set calendar reminders. Assign ownership for keeping maps current.
Practical Examples & Real-World Use Cases
How Airbnb Uses Customer Journey Maps
Airbnb's journey maps revealed that users felt most anxious during the period between booking and arrival. Three weeks of minimal communication created uncertainty.
This insight led to the development of Airbnb's automated messaging system. The system provides booking confirmations, local recommendations, and check-in reminders.
Key insight: The emotional journey extends far beyond the product interface. Airbnb now maps the entire customer experience. From initial dreaming to post-trip memories, they focus on every stage of the customer's experience.
Spotify's Personalization and User Journey Maps
Spotify maps multiple customer journey maps for distinct journey types. Discovery-focused listeners, background music users, and active music explorers each get different treatment.
By mapping these different customer journeys, Spotify tailors each experience to the individual. They provide tailored interface elements and recommendation algorithms.
Key insight: One size doesn't fit all. Mapping different customer journeys enables the delivery of unique customer experiences at the same touchpoints.
Implementation: Discovery users see prominent "Discover Weekly" features. Background listeners get easy playlist controls and minimal interruption.
Discover: Clay's Approach
We collaborated with Discover to enhance their mobile app, improving user experience through refined onboarding processes, card activation flows, and new feature discovery.
By mapping customer journeys, we created an effective customer journey map that helped identify pain points and optimize the app’s design, making it more user-friendly.
This involved creating detailed flow diagrams, multiple UX prototypes for testing, and implementing a comprehensive design system with custom icons and illustrations, ensuring a cohesive brand experience across all platforms.
Discover Wireframes by Clay
Advanced Tips & Best Practices for Effective Customer Journey Maps
Combining Journey Maps with Other UX Tools
Journey maps work best in conjunction with other research artifacts. Use empathy maps to gain a deeper understanding of user emotions. Combine with service blueprints to identify operational improvements. Reference user personas to ensure journey accuracy.
During collaborative mapping workshops, use sticky notes to organize journey stages and touchpoints on whiteboards or virtual boards. This helps teams visualize the process and identify key insights together.
Create a "tool stack" approach: Start with personas. Add empathy maps. Build journey maps. Then layer in service blueprints for complex interactions.
Integrating Data Analytics with Journey Maps
Modern journey mapping combines qualitative insights with quantitative data. Utilize Hotjar heatmaps to determine where users spend their time. Analyze conversion funnels with Google Analytics to identify drop-off points.
Track emotional sentiment through surveys and feedback tools, and incorporate customer feedback from surveys and reviews to gain a deeper understanding of user experiences.
Pro tip: Create "data layers" in your journey maps. Include user quotes for qualitative insights. Add Google Analytics data for behavioral validation. Incorporate business metrics to measure success.
Measuring the Impact of Customer Journey Mapping
Measuring the impact of customer journey mapping can help you improve user experience and business results. Start by setting clear goals for your journey maps.
For example, you might aim to boost customer satisfaction, keep more customers, or reduce user frustrations.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Customer satisfaction scores
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- Customer Effort Score (CES)
- Conversion rates at each stage
- Customer lifetime value
- Churn rates and retention metrics
- ROI Calculation Methods
Journey mapping isn't a one-time project. Regularly update your maps based on new data and changing customer behaviors. This creates experience mapping that evolves with your business.
Tools & Journey Map Templates to Get Started Fast
Free Downloadable Templates
UXPressia offers a large library of over 100 free templates. These include customer journey maps, service blueprints, persona profiles, and impact maps. You can choose templates for general use or specific industries like healthcare, transport, and telecom. The library includes pre-filled B2B and B2C examples that save time and guide structure.
User Interviews features a curated selection of high-quality journey map templates and real-world examples. They emphasize user research-driven designs. You’ll find current‑state maps, future‑state layouts, emotion curves, and persona-based grids. Most of these are free to download as PDFs.
Smaply provides structured templates focused on journey mapping and service design. Its resources support multi-persona maps, stakeholder maps, integrated emotion tracking, and backstage processes. It helps teams design rich, actionable maps tied to personas and opportunities.
The Interaction‑Design Foundation guides you toward free and professional templates, too. They offer customer journey map documents and tools shaped by best practices from the field. Their coverage spans both design and cross-functional business use.
Software Platform Reviews
Miro (Free - $16/month): Excellent collaboration features, extensive template library, integrates with popular design tools. Best for remote teams.
UXPressia ($16 - $29/month): Purpose-built for journey mapping, includes persona tools, offers presentation mode. Best for dedicated UX teams.
Figma (Free - $15/month): Strong design integration, real-time collaboration, component libraries. Best for design-focused teams.
Read More
FAQ
What Is the Difference Between a Customer Journey Map and a Service Blueprint?
A customer journey map shows what users do, think, and feel as they interact with your product or service. A service blueprint adds the behind-the-scenes systems, workflows, and teams required to deliver that experience.
What Is the Difference Between a Customer Journey Map and a Funnel?
A customer journey map captures the full end-to-end experience, including emotions and touchpoints. A funnel focuses on measurable steps that move users toward conversion and does not reflect post-purchase or emotional context.
When Should I Create a Customer Journey Map?
Create one when launching a new product, redesigning an experience, solving user pain points, or aligning teams around how customers actually move across channels.
How Often Should I Update a Customer Journey Map?
Update it quarterly or whenever major product changes, new features, or shifts in customer behavior occur so the map stays accurate and actionable.
How Detailed Should a Customer Journey Map Be?
Keep it to five to seven stages with a few key touchpoints each. It should be detailed enough to show real issues but simple enough for teams to read and use.
Who Should Be Involved in Creating Customer Journey Maps?
Bring in UX, product, engineering, marketing, support, and customer success. Different teams provide different insights and create a more reliable map.
What Is the End-to-End Customer Journey?
It includes every interaction from first discovering your brand to onboarding, everyday use, support experiences, retention, and long-term advocacy.
What Are the Five Main Points of a Customer Journey?
The common five stages are Awareness, Consideration, Purchase, Retention, and Advocacy. These reflect how users progress from discovering your brand to recommending it.
Conclusion
Customer Journey Maps aren't just pretty diagrams. They're strategic tools that transform how you understand and serve your users.
Start small. Pick one key user persona. Map their most critical journey today. Use the templates and techniques outlined above. Validate with Google Analytics data and Hotjar insights. Watch as insights emerge that fundamentally change how your team approaches product decisions.
Every moment you delay mapping your customer's journey, you lose users to friction that could be easily fixed. Start your journey mapping practice today.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more


