User experience work has expanded fast in the last few years. In 2026, UX teams still design interfaces, flows, and content structures - but they also shape how systems behave in real time: search results, recommendations, onboarding logic, and AI-powered assistance.
That shift changes what “good UX” means. It’s not only about clean screens and usable journeys. It’s also about trust, accessibility, and measurable responsiveness across devices and contexts. For example, web responsiveness is now commonly discussed through Core Web Vitals with Interaction to Next Paint (INP) as a key metric.
This article keeps the same core idea: strong UX comes from a few foundational disciplines working together. We’ll focus on four practical pillars - User Research, Information Architecture, Experience Strategy, and Interaction Design - and show how they connect in modern product teams.
UX Design Disciplines
Understanding User Needs
Comprehending user expectations is a fundamental step in the sequence of steps in UX design. This entails multidisciplinary approaches aimed at understanding users' behaviors, needs, and motivations to enhance design.
User research is essential in this procedure; it applies different methods like interviews, surveys, usability testing, and contextual inquiry to collect helpful information.
User research plays a big part in defining the user persona, journeys, and flows, which are crucial to user-centered design. Products that match each user's expectations can only be made through information about user requirements and needs.
One such example is a UX designer creating a mobile app who then has to ask users questions about issues related to them. The team uses this information to develop appropriate features for the app that users will find easy to use.
User Research
User research keeps teams from designing for themselves by uncovering real motivations, constraints, language, and usage context.
In 2026, it runs as a mixed model: qualitative methods explain the “why,” while quantitative data shows how often issues happen and what to prioritize.
AI can speed up ops (transcription, clustering, summaries), but insights must stay auditable with a clear chain from insight → evidence → decision.
Research is increasingly “always on,” using lightweight loops tied to milestones, in-product feedback, and periodic validation as the product changes.
Key Components of UX Research
Additional resources
Books:
- "Observing the User Experience: A Practitioner's Guide to User Research" by Mike Kuniavsky: This book provides a comprehensive guide to the various methods of user research, with real-world examples and practical advice.
- "Just Enough Research" by Erika Hall: A concise and direct guide to conducting effective user research without data overwhelm.
Websites and Articles:
- Usability.gov - Managed by the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, this site contains resources on user-centered design and research strategies.
Information Architecture (IA)
Information architecture is how you make content and features findable. It covers organization, labeling, navigation, and search - but in 2026, IA has expanded beyond menus and sitemaps.
Many products now rely on:
- robust search with filters and facets,
- dynamic navigation that adapts to user context,
- and “help me find it” flows where the system guides discovery.
That means IA is often tightly linked to content modeling and metadata quality. If labels are inconsistent, categories overlap, or content isn’t structured well, no amount of UI polish will make the experience feel clear.
A modern IA approach also treats search as part of UX strategy. Users may arrive through search first, not navigation first. So IA needs to support both: quick scanning and deep exploration, with clear paths back to orientation.
Finally, IA now intersects more directly with compliance and risk. If you operate in markets with accessibility requirements that apply from 28 June 2025, the structure and labeling of journeys matter not just for usability, but also for legal exposure and customer trust.
Information Architecture
Additional resources
Books:
- "Information Architecture: For the Web and Beyond" by Louis Rosenfeld, Peter Morville, and Jorge Arango
Websites:
Experience Strategy (ExS)
Experience strategy turns UX work into a coherent, scalable system by defining shared value, aligning teams across functions, and making trade-offs explicit so the experience doesn’t fragment.
In 2026, it also has to be trust- and constraint-aware as AI features expand, because regulatory timelines can shape what “responsible UX” looks like (for example, the EU AI Act applies obligations for general-purpose AI models from August 2, 2025, with broader applicability from August 2, 2026).
Finally, it connects UX decisions to a small set of meaningful outcome metrics, so improvements accumulate instead of becoming disconnected optimizations.
User Experience (UX) as the Intersection of User Needs, Business Goals, and Information
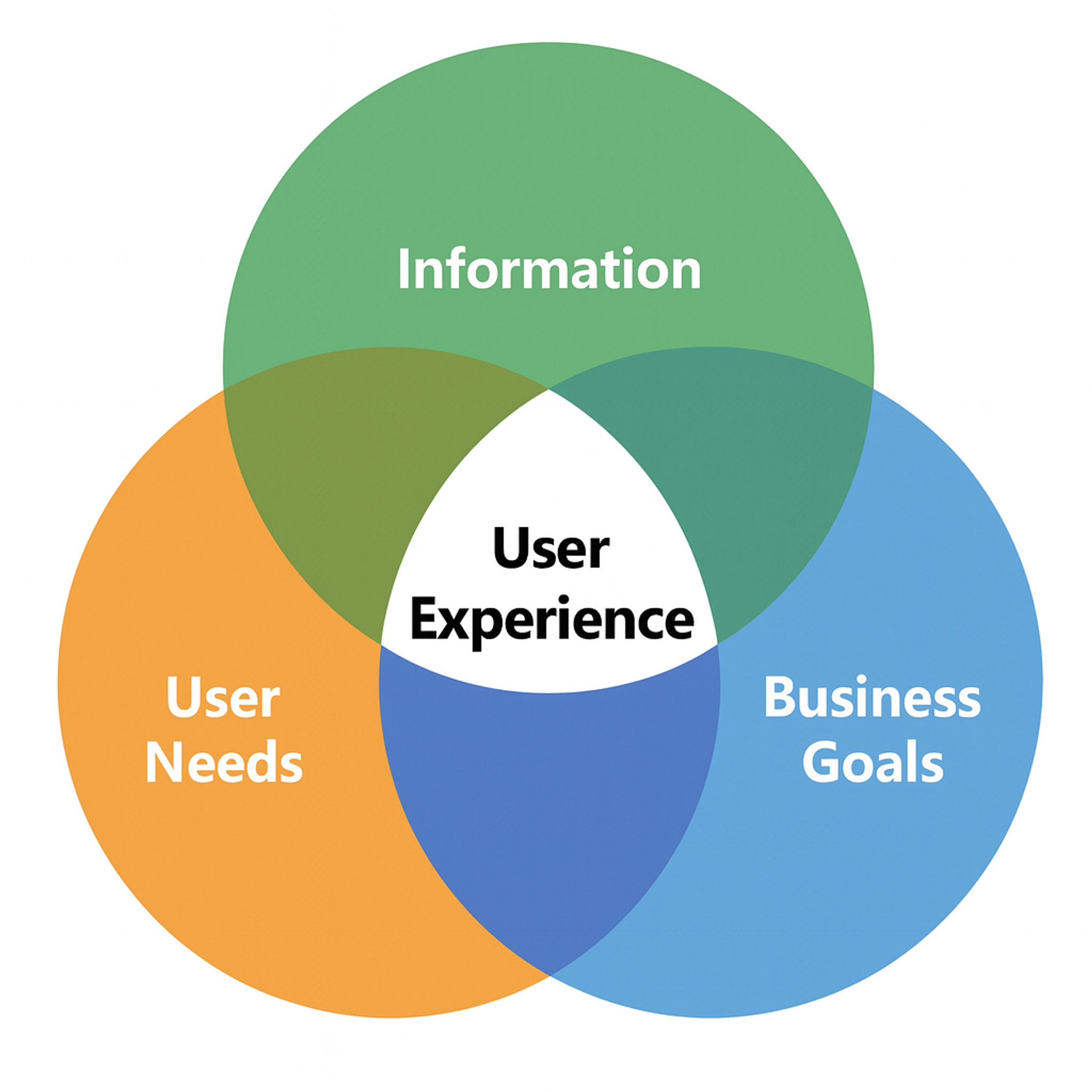
Additional resources
Books
- "This Is Service Design Doing" by Marc Stickdorn, Markus Edgar Hormess, Adam Lawrence, and Jakob Schneider
Websites
- Service Design Network: A platform offering articles, case studies, and insights into service design as a strategic experience enabler.
- UX Matters: A valuable resource for trends, techniques, and best practices in UX and experience strategy.
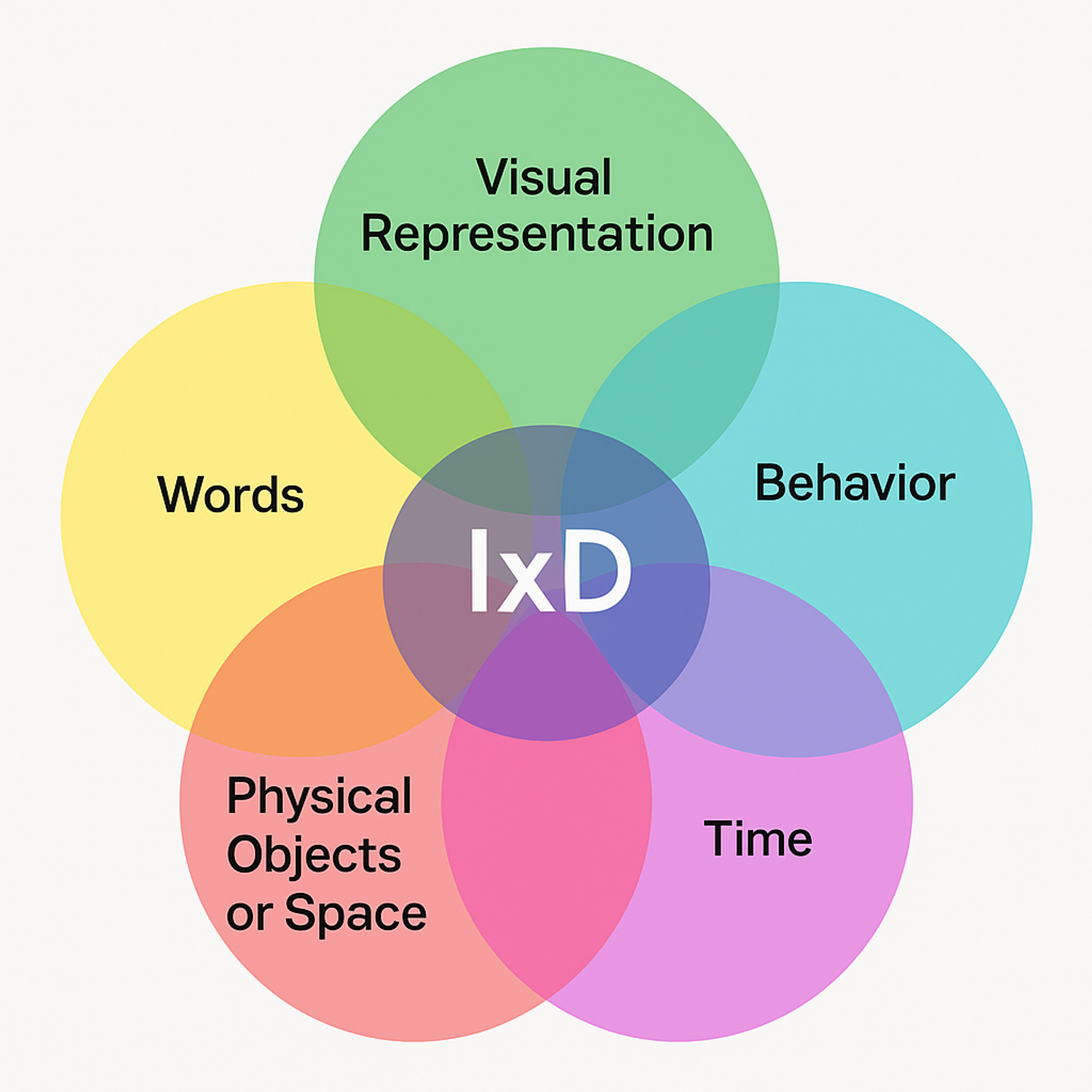
Interaction Design
Interaction design defines how users complete tasks through flows, states, feedback, and the overall “feel” of the system. In 2026, the challenge is the growing number of states and the need for strong recovery.
With personalization, real-time updates, multi-device continuity, and AI assistance, users face more uncertainty. They need clear signals about what happened, what happens next, and how to fix or reverse a wrong outcome.
Good interaction design now focuses on resilient flows (retry, undo, resume without losing progress), transparent feedback (not just “done,” but what changed), and responsiveness as UX. On the web, interaction responsiveness is commonly evaluated with INP, which replaced FID as a Core Web Vital.
Interaction Design (IxD)
Additional resources
Books:
- "Designing Interactions" by Bill Moggridge
- "About Face: The Essentials of Interaction Design" by Alan Cooper, Robert Reimann, and David Cronin
Websites:
Continuous Learning and Improvement
UX maturity in 2026 is less about knowing the “right process” and more about building a repeatable improvement loop.
That loop usually combines:
- ongoing research and feedback,
- quality monitoring (including performance and accessibility),
- and a system for turning insights into shipped changes.
If you treat UX as a one-time phase, you’ll fall behind. Products evolve, expectations rise, and constraints change. Continuous learning is how teams keep up without constant rework.
FAQ
What Are the Four Key UX Design Disciplines?
Research, Information Architecture (IA), Interaction Design, and Visual Design. Together they make products clearer, easier, and more engaging.
How Do These Disciplines Work Together?
Research finds user needs, IA organizes content, Interaction Design shapes behavior and flows, Visual Design communicates hierarchy and brand.
What’s the Difference Between UX Research and Usability Testing?
UX Research explores needs and problems (surveys, interviews, field studies). Usability testing evaluates a design’s ease of use with real tasks.
Read more:
Conclusion
Strong UX rarely comes from one discipline. It comes from a system: evidence about users, a structure that supports finding and understanding, a strategy that aligns decisions, and interactions that feel reliable in real life.
Updating this article for 2026 doesn’t require reinventing the foundations. It requires acknowledging the reality modern teams work in: faster cycles, higher expectations, stronger constraints, and more dynamic systems.
When you treat research, IA, experience strategy, and interaction design as one connected practice, you build experiences that stay clear - even as the product scales.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more


