UI/UX design creates digital products that feel natural and useful.
UI (user interface) handles the look and touch: layouts, buttons, color, type, spacing, and micro-interactions so each screen is clear and consistent.
UX (user experience) covers the end-to-end journey: how easily people find value, move through tasks, and how satisfied they feel overall.
The design process ties UI and UX together. It starts with research to understand users and goals, forms personas and problem statements, maps user flows, and sets requirements. Wireframes define structure. Prototypes show interactions. Usability testing exposes friction, and iteration refines the solution. The outcome: a product that solves the right problem and is a pleasure to use.
Understanding UI/UX Design
UI/UX design combines technology, creativity, and human psychology to create digital experiences that feel natural. UI design focuses on what users see and touch directly.
UI vs UX by Clay
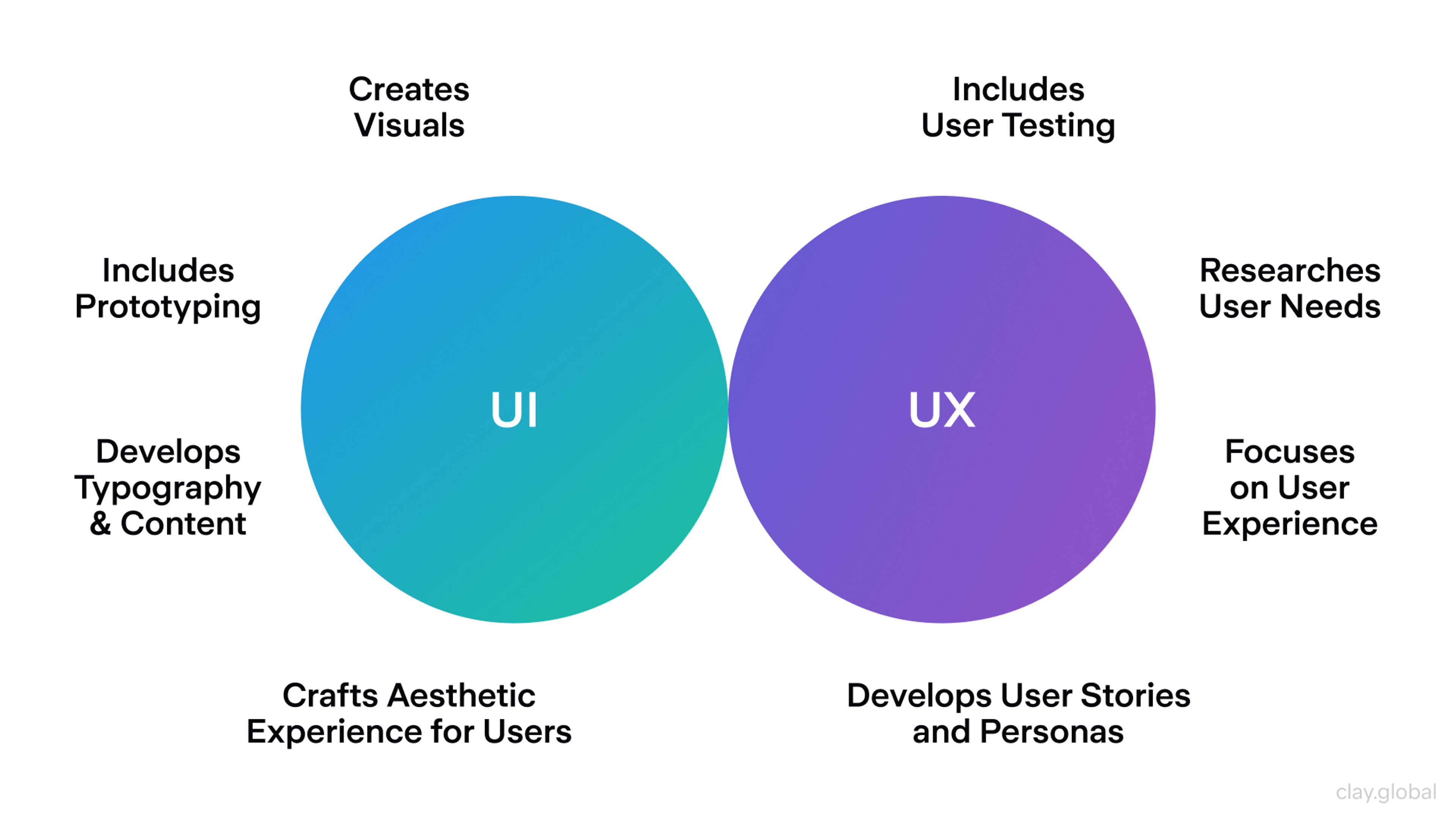
The user interface is composed of visual elements, including buttons, colors, and layout, which are crucial to the appearance and interactivity of a digital product. UX design encompasses the entire user experience, including how users feel and think while interacting with your product.
Good design starts with understanding that every user brings expectations, mental limits, and emotional needs to your product. User research and the creation of user personas enable designers to empathize with their target audience, ensuring the product is user-centered. The best designs work with human psychology instead of fighting against it.
The goal of the UX design process is to create user-centered products that are effective and enjoyable to use.
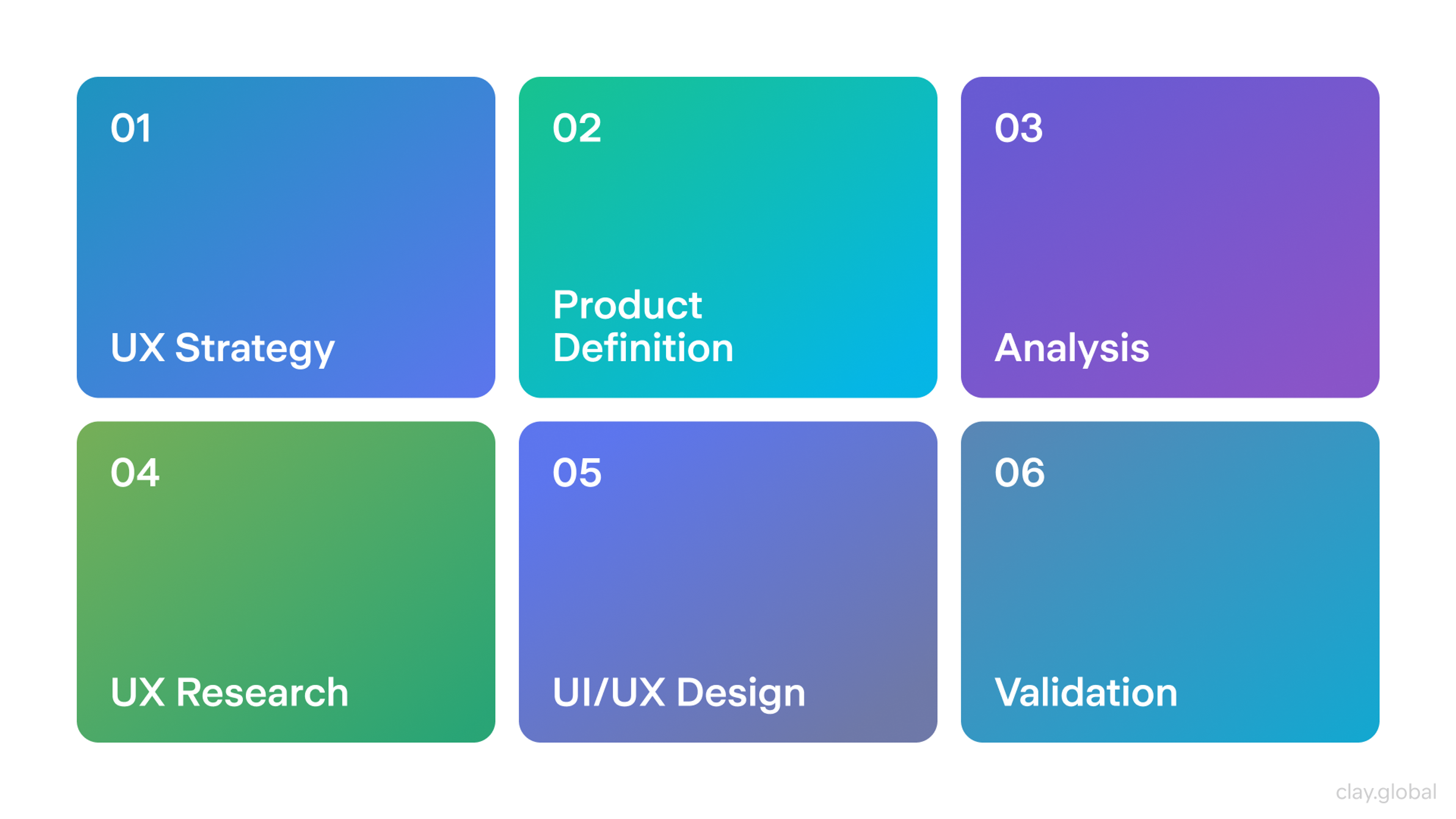
5 Steps of the UX Design Process
Here is the complete UX design process:
UX Design Process by Clay
1. Empathize and Conduct User Research to Understand the Context
The first stage of the UX design process involves defining the problem that needs to be solved. The second stage is the research phase, where research is conducted to understand user needs and behaviors.
Start by understanding users, tasks, and context across every relevant touchpoint, including digital and physical moments. Use interviews, surveys, user interviews, focus groups, field observation, diary studies, service walkthroughs, and other UX research methods as part of conducting user research during the research stage.
In addition to user research, conduct market research to analyze industry standards, understand market trends, and assess the competitive landscape. This provides valuable context for creating user-centered products.
During the research phase, create user personas and user journey maps to represent the target audience, align teams on a single problem statement, and visualize user paths.
User personas help designers empathize with users by providing detailed, research-based representations of the target audience, while journey maps highlight user behaviors and guide optimization efforts.
Develop user stories to articulate user needs and guide the design process, ensuring that requirements are translated into actionable plans.
Put yourself in users' shoes to better empathize with user behaviors and pain points, which is essential for creating effective, user-centered solutions.
AI can assist in early synthesis by transcribing sessions, clustering themes, or drafting summaries. Treat outputs as hypotheses, then confirm patterns with direct evidence from the research.
In the Discover case study, we used user personas and journey maps to optimize the app’s design. Based on real data, user personas represented different user types, ensuring the design catered to diverse needs.
Journey maps visualize the user’s experience, identifying pain points and opportunities for enhancement. This approach enabled us to align the product with user requirements and business objectives, balancing usability and strategic goals.
Discover Website & Mobile App by Clay

2. Define the Challenge and Strategy
Synthesize findings into a clear problem definition. Convert raw data into user needs, pain points, and opportunities, and prioritize a set of scenarios that address these needs and opportunities. Create user personas and journey maps to align teams on a single problem statement and visualize user paths.
Develop information architecture to organize and structure content, ensuring everyone stays on the same page. Use problem statements and "How might we…?" questions to keep the team aligned.
Define success criteria early. Focus on outcomes that can be measured and observed, such as task success, error reduction, time-to-value, or satisfaction trends. Set the scope across channels and contexts to ensure the experience remains coherent across devices and environments.
Establish design principles that guide tradeoffs. Principles often cover clarity, inclusivity, feedback, and resilience under stress. Add explicit guardrails for AI features, including transparency, user control, and safe failure modes.
Document design specs to communicate visual design elements, user journeys, and information architecture from the UX/UI team to developers, ensuring proper implementation and visual consistency. Emphasize effective communication and collaboration among team members to enhance the UX design process.
Visual Design Elements by Clay
Document constraints and requirements, especially accessibility and privacy, so compliance is designed in rather than patched later. The output is a brief that aligns user needs, business goals, constraints, and evaluation criteria.
3. Ideate and Prototype Solutions
Generate multiple solution directions before committing to one. The Ideate stage focuses on brainstorming diverse solutions and exploring a wide range of possibilities.
Combine individual ideation with group critique, utilizing methods such as sketching, storyboarding, role-playing, or service blueprinting for cross-channel journeys.
Generative AI can accelerate exploration by producing draft variants of content, flows, or interaction patterns. The value is speed and breadth, not correctness. All AI-generated concepts should be reviewed for accuracy, bias, and fit with the research.
Prototype early and often. The prototyping phase encompasses both low-fidelity wireframes and high-fidelity prototypes, enabling the testing of interactions at a lower cost.
Wireframes serve as simplified representations of a page interface, defining layout and essential elements, and often utilize reusable components and UI components to ensure consistency and efficiency.
Use low-fidelity artifacts to test structure and flow, then move to interactive prototypes for key moments.
Prototyping tools enable designers to create interactive, high-fidelity prototypes for usability testing, allowing them to gather feedback and validate design decisions.
For service and multi-touchpoint experiences, prototypes can include scripts, mock communications, and staged walkthroughs, in addition to screens.
Benefits of Prototyping by Clay
4. Conduct Usability Tests, Validate, and Refine
During the testing phase of the UX design process, prototypes are evaluated with real users through usability tests. UX designers test these prototypes to gather direct feedback and valuable feedback, ensuring that insights from real users are incorporated into the design.
This process helps gather input and user feedback to identify usability issues and enhance the product's user-friendliness.
Testing should also be conducted in real-world scenarios to ensure the design works effectively outside controlled environments. Testing is a critical stage in the UX design process, and usability testing is essential for identifying areas of improvement before final development.
7 Steps to Usability Testing by Clay
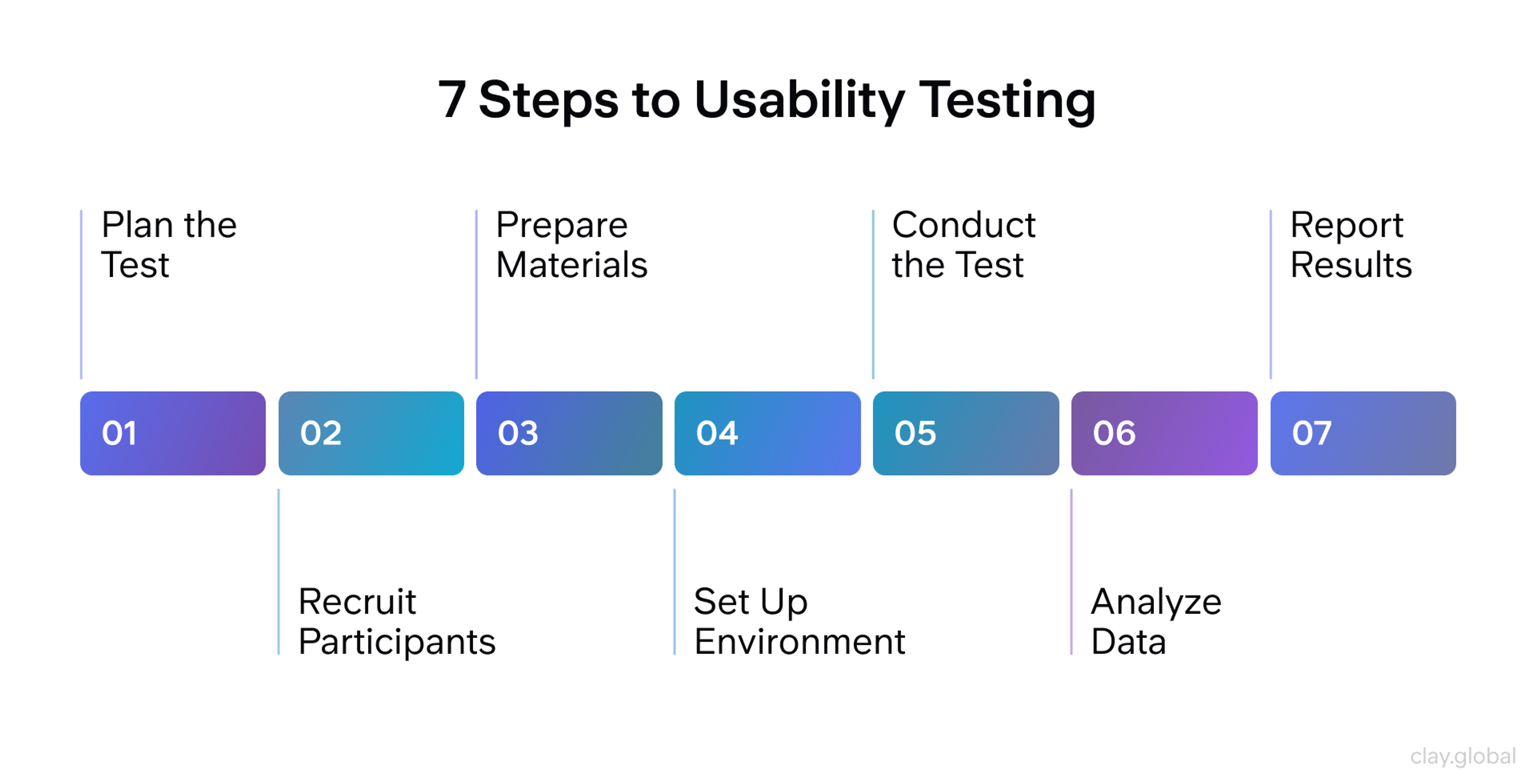
Continuous user feedback and iterative design are crucial for enhancing usability and ensuring the final product meets user needs.
Test prototypes with representative users and realistic tasks to ensure they are practical and usable. Observe behavior, collect feedback, and track basic metrics such as task completion, time on task, and error rates. Run tests across relevant platforms and modalities when the experience spans devices or channels.
Evaluate accessibility explicitly through audits and inclusive testing. Address issues in structure, navigation, focus states, contrast, motion, and language clarity.
For AI-driven features, test trust and comprehension. Check whether people understand what the system is doing, why it is doing it, and how to correct it. Add explanations, undo actions, and clear boundaries where automation could cause harm or confusion.
5. Implement, Launch, Monitor, and Iterate
Implementation is a crucial part of the UX design process, involving close collaboration between the design team and development team to ensure the final design is accurately realized.
The design handoff to developers includes these specifications to ensure the vision is accurately translated into the live product. Using a design system - a collection of reusable components - helps maintain consistency across digital products and can significantly reduce time to market.
AI tools are increasingly used to rapidly synthesize user data, enabling designers to make informed decisions and root the design in real human needs. After launch, it is essential to collect data on how users interact with the digital product by tracking key metrics, including funnels, retention signals, support volume, and qualitative feedback from reviews and research follow-ups.
This ongoing process of iteration - refining the product based on user feedback - enables designers to create products that better meet user needs and enhance overall value over time. The UX design cycle continues post-launch by monitoring live user behavior and making ongoing refinements.
UX Design by Clay
Reduced risk is achieved through early research and testing, minimizing the chances of product failure. Effective communication and collaboration among team members further enhance the UX design process, ensuring that all perspectives are considered and the result aligns with both user needs and technical feasibility.
Optimization and Continuous Improvement
Improving Experiences Systematically
Experience optimization systematically enhances user experiences by leveraging data and research to inform and improve them. This ongoing process requires measurement, analysis, and iterative improvement.
Conversion rate optimization focuses on enhancing specific user actions, such as making a purchase or signing up. User experience optimization takes a broader view of overall satisfaction and engagement, encompassing both the user's perspective and the system's performance.
Performance optimization affects user experience directly. Page load speed, responsiveness, and reliability all impact user satisfaction and task completion rates.
Engineering Better Usability
Usability engineering applies systematic methods to ensure products meet usability standards. This discipline combines engineering rigor with user experience design.
Usability requirements define specific, measurable goals for user experience. Examples include task completion rates, error rates, and satisfaction scores.
Usability inspection methods, such as expert review, identify problems without requiring user testing. Expert reviews catch issues early in the design process.
Advanced Analytics and User Behavior
Advanced analytics reveal patterns in user behavior that inform design decisions. Segmentation analysis shows how different user groups behave differently.
What Is Behavioral Data
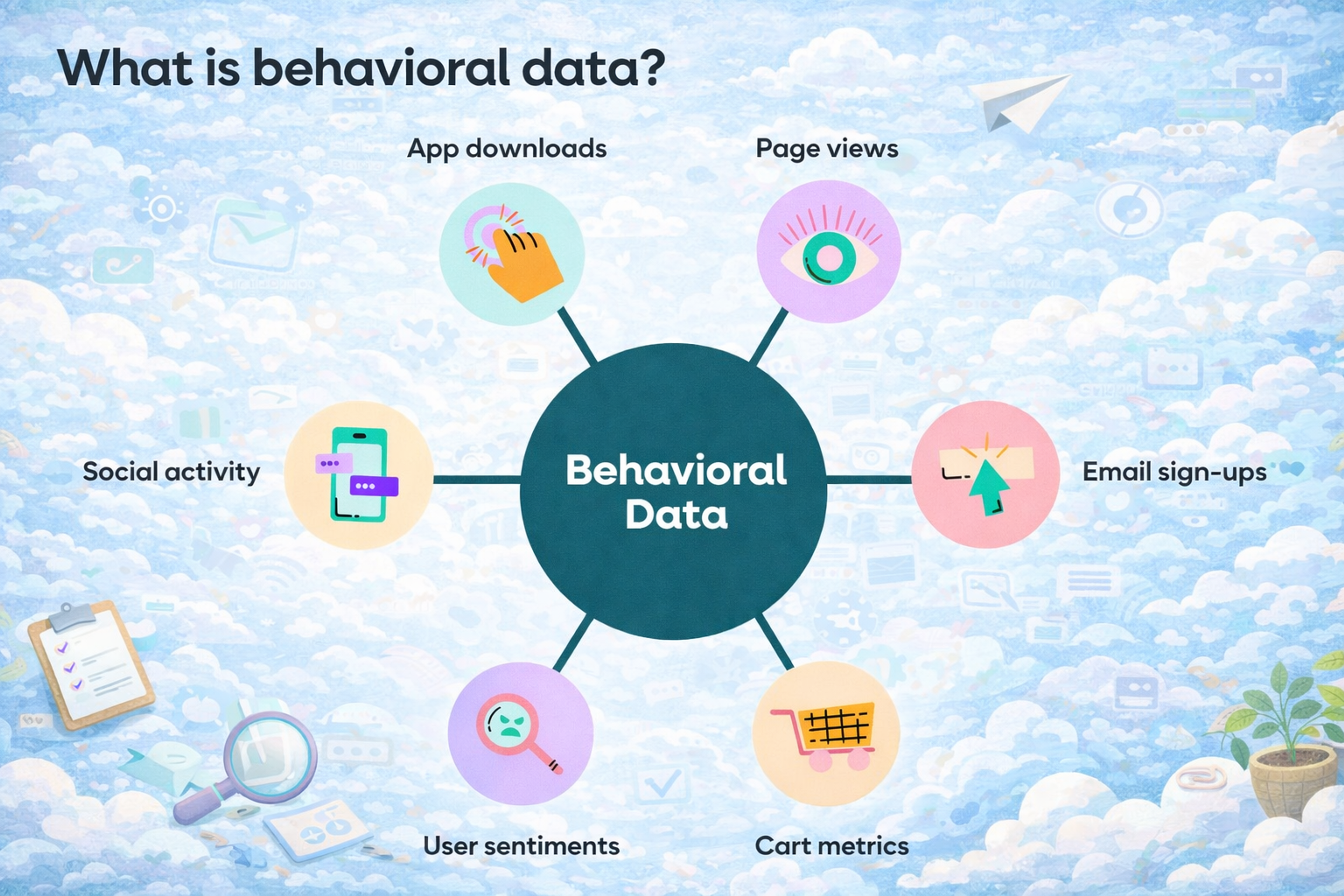
Cohort analysis tracks user behavior changes over time. Funnel analysis identifies where users drop out of important processes. Heat mapping and session recording provide detailed interaction data.
Machine learning applications can predict user needs and personalize experiences. Recommendation systems and adaptive interfaces respond to individual user patterns.
FAQ
What Are The 5 Steps Of The Design Process?
The 5 steps of the design process are Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test. This framework helps designers understand user needs, brainstorm creative solutions, create prototypes, and refine them based on feedback before launch.
What Are The 5 Steps Of UX Design Process?
The 5 steps of the UX design process are Research, Define, Design, Test, and Implement. It starts with understanding user behavior, moves to creating wireframes and prototypes, and ends with testing and delivering the final product.
What Are The 5 Elements Of UX Design?
The 5 elements of UX design are Strategy, Scope, Structure, Skeleton, and Surface. These layers guide the process from defining business goals and user needs to creating a visually appealing and functional interface.
What Is The 5D Process In UX?
The 5D process in UX stands for Discover, Define, Design, Develop, and Deploy. It is a structured approach that begins with research and problem definition, continues with design and development, and finishes with launching the product.
What Are Different UX Design Processes?
Different UX design processes vary by team or project but often include Design Thinking, Lean UX, Agile UX, and Double Diamond. Each process focuses on understanding users, iterative design, and continuous improvement to create better user experiences.
Read More
Conclusion
These five steps maintain a structured process while accommodating modern realities, such as AI-assisted design, multimodal interaction, and heightened expectations regarding trust.
The details evolve, but the core remains consistent: understand real needs, define the right problem, explore options, validate with users, and improve continuously.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more


