The world of user experience is always moving forward, and keeping up with the latest tools, trends, and best practices can feel overwhelming. That’s exactly why we created the Ultimate UI/UX Guide 2026 — a comprehensive resource designed to help you craft digital experiences that are functional and truly meaningful for your users. It guides user experience design while offering clear direction through every phase of your project.
This guide is the result of years of research, testing, and real-world application by a team of seasoned UX professionals. It walks you through every stage of the design process, from understanding user behavior and needs to building wireframes, prototypes, and intuitive information architecture. It supports inclusive user experience by helping teams design products for a wide range of users.
Whether you’re new to UX or a seasoned designer looking for new perspectives, this guide offers practical insights to help you create digital products that are both effective and memorable. With the right UI/UX services in place, you can boost user engagement and build experiences that feel seamless, intentional, and uniquely tailored to your audience. This approach centers on user experience design to ensure usability and satisfaction.
What Is UX Design?
“Everything is designed. Few things are designed well.” — Brian Reed
UX design, short for user experience design, is all about shaping how users interact with a product or service. It goes beyond just creating beautiful interfaces — it involves crafting every aspect of the experience, from usability and accessibility to performance and responsiveness.
The goal is to make those interactions intuitive, enjoyable, and meaningful. Great UX designs user experience by putting user needs at the heart of every decision.
Studies show that users form opinions about a design in just 50 milliseconds or less. As attention spans shrink, those first impressions are more important than ever. A visually pleasing, easy-to-navigate interface can instantly grab attention and set the tone for the entire user journey. User experience optimization plays a key role in achieving this.
Excellent user experience (UX) design starts with truly understanding your users, what they want, and how they think. That information is gold, but it can’t work in a vacuum. Designers must also weave in business goals, tech limits, and a clean, on-brand look. When everything slots together, users feel the lift. Happy users stick around, spread the word, and help your business grow over the long haul.
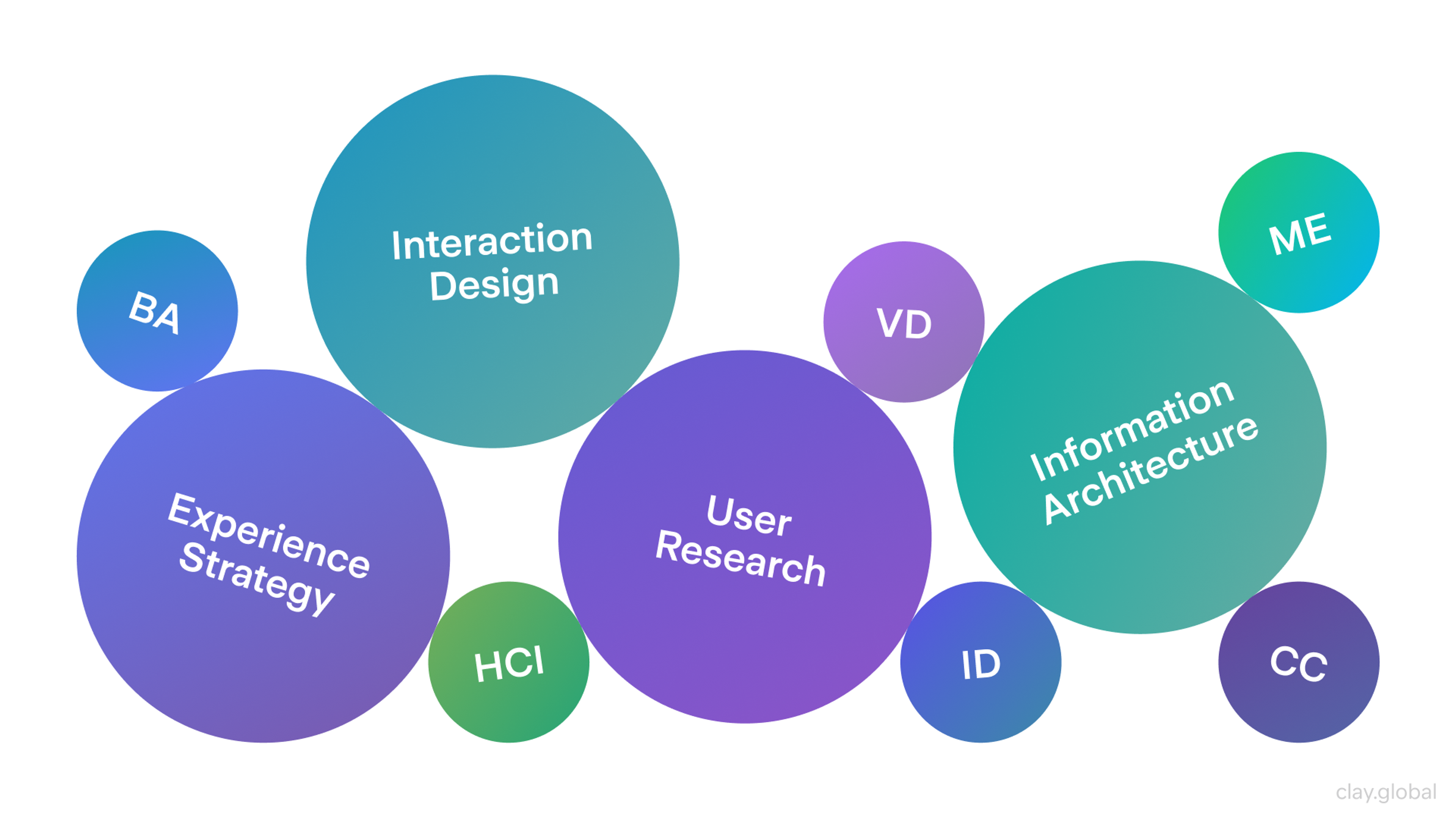
At the core of UX design best practices are four key disciplines:
- User Research (UR): Understanding what users need, want, and struggle with.
- Information Architecture (IA): Structuring content and features in a logical, user-friendly way.
- Experience Strategy (ExS): Aligning user needs with business goals to create a clear vision.
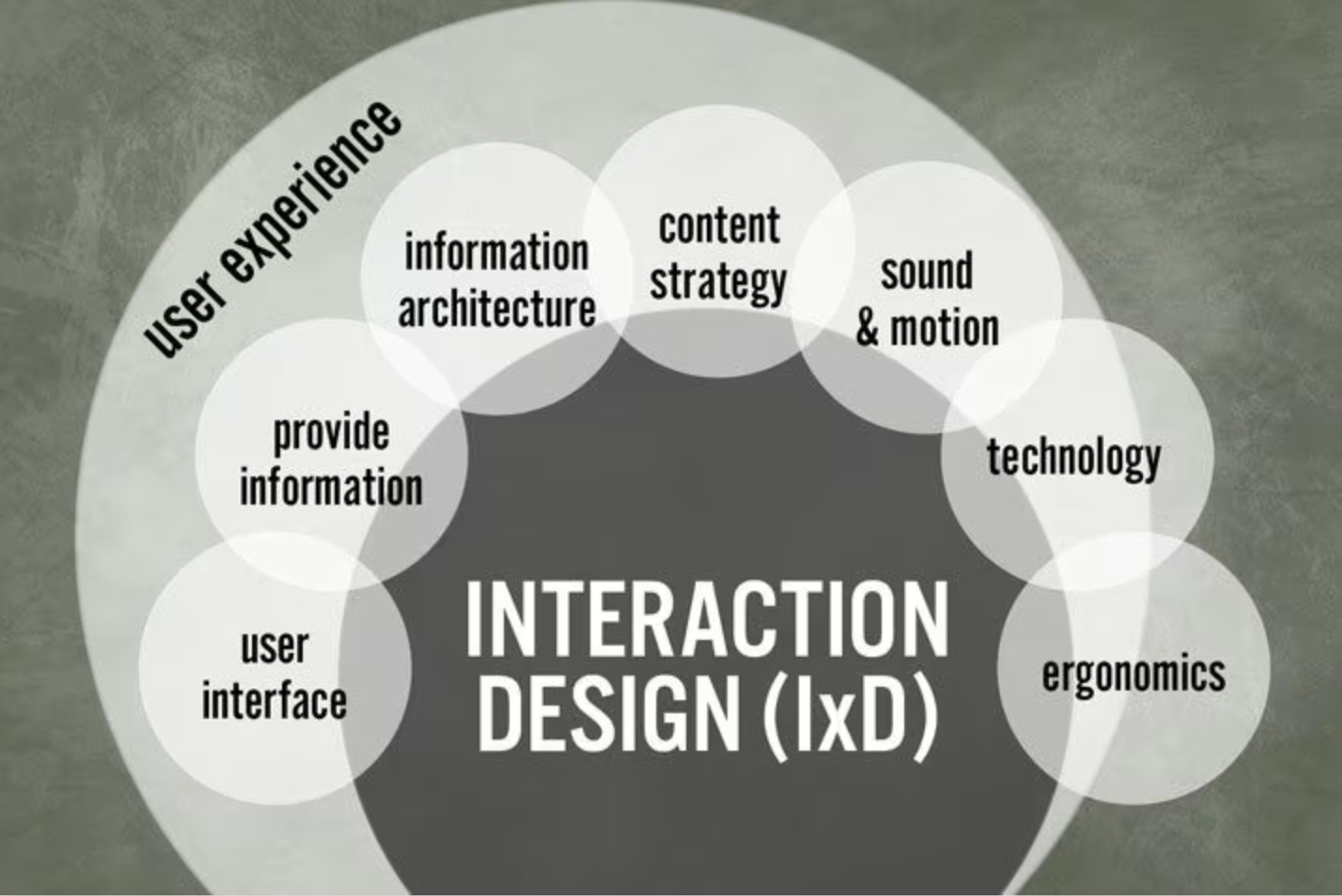
- Interaction Design (IxD): Designing how users interact with interfaces, from buttons to navigation flows.
Together, these disciplines form the foundation of any successful digital product.
4 Key UX Disciplines by Clay
User research is a foundational part of UX design. It’s all about uncovering how users think, feel, and behave by collecting real-world insights through interviews, surveys, usability tests, and other research methods. These insights reveal pain points, highlight what’s working, and support user experience design decisions that lead to better, more user-centered solutions.
Information architecture is about how content is laid out inside a digital product. Think of it as the plan that guides users to the stuff they want without fuss. When designers show how different parts connect and tuck related items together, clicking around feels smooth and straightforward.
Experience strategy takes a broader view. It’s about shaping the full journey a user has with a product or service. This discipline looks at goals, motivations, and potential roadblocks to create a strategic vision that aligns user needs with business outcomes. A thoughtful experience strategy ensures that every interaction supports user experience design and delivers meaningful results.
Interaction design brings structure and clarity to the way interfaces behave. It maps out the user journey, defines how users interact with the system, and ensures that each element supports the goal of intuitive navigation. From clickable buttons to animation cues, interaction design is what makes digital products feel smooth and responsive.
Looking ahead, UX design continues to evolve rapidly. As technology advances and user behaviors shift, designers must adapt and stay current with trends.
One of the most significant trends now is a stronger focus on accessibility and inclusivity. More than ever, designers are expected to create experiences that serve a wide range of users, including those with disabilities or specific needs. Supports inclusive user experience is no longer optional; it’s essential for modern UX practice.
Great UX design isn’t just a nice addition — it’s a key ingredient in the success of any digital product. It helps users easily move through your platform, builds trust, and leaves a positive, lasting impression.
It becomes even more important in industries like crypto and Web3, where the underlying concepts can be complex or unfamiliar. A thoughtful, intuitive interface can make all the difference, helping users feel confident as they explore decentralized technologies and blockchain-based platforms.
What Is UI Design?
“A user interface is like a joke. If you have to explain it, it’s not that good.” —Martin LeBlanc
UI design stands for user interface design and is about crafting a product or service's visual and interactive parts. When someone talks about UI, they mean things like menus, buttons, screens, and any other graphic element the user interacts with. UI design also pays attention to how something looks, including principles of design, typography, color palettes, images, and layout.
UI Elements Examples by Toptal
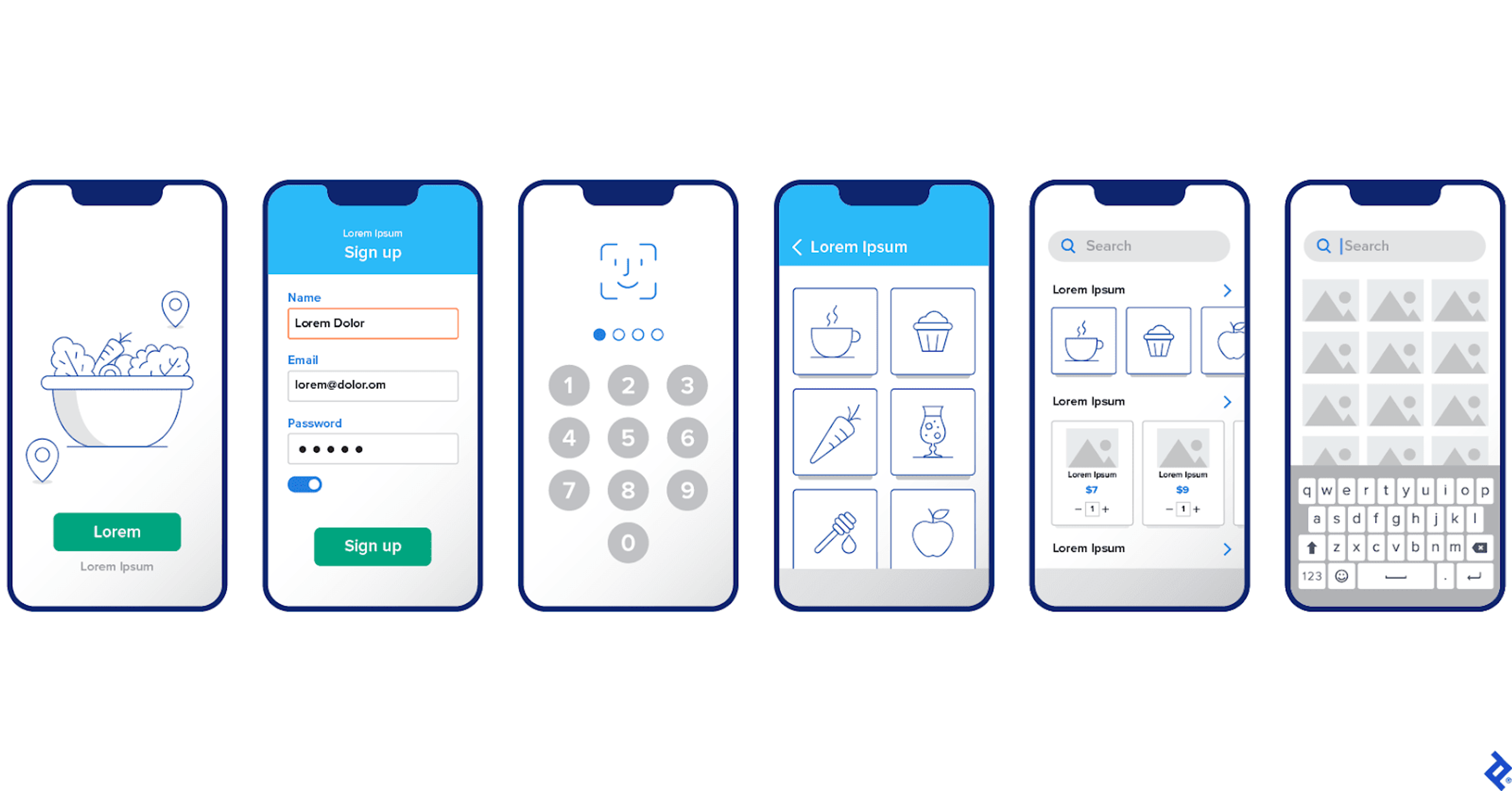
UI design is a creative job that zooms in on every tiny detail of what users see on the screen. When done well, UI design guides people using a product, thanks to smart visual hints and instant feedback. Every element should feel like it speaks directly to the user, saying, "Here's what to do next."
Using established UI patterns is essential for keeping things steady and user-friendly. When every part of a product behaves familiarly, it helps users trust the system. They can see what's happening and know what to expect, so they can focus on their task instead of figuring out how the system works.
Strong UI design isn't just about beauty. Beauty without purpose is fluff. The goal is to make every tap, swipe, and click effortless. The best UI seamlessly carries users to their goal, making the interface a reliable, invisible helper.
Good user interface design goes beyond choosing appealing fonts or colors. Designers also need to ensure that any information presented on screen offers enough contrast so that users with color blindness or low vision can read it easily. An interface that flatters the eye but ignores these guidelines can shut the door to people relying on screen readers or requiring larger text.
Logos, typefaces, and documented design rules are the silent but powerful actors that keep brand voices loud and clear across every app, website, or digital screen. Designers use these branding elements to craft an experience where every tap or click feels unmistakably part of the same story, preventing the user from drifting into an unfamiliar neighborhood.
As digital experiences keep expanding, using built-in, accessible components is no longer optional. It's expected. Take search bars, for example. Users rely on the one that hugs the top of almost every web page. When designed with clear buttons, keyboard shortcuts, and screen-reader-friendly labels, rivals fade away and help desk calls dwindle, creating one smooth path to the answer people came for.
UX vs. UI
UX design and UI design are two distinct disciplines. While often used interchangeably, they refer to different focus areas and have distinct roles in development.
UX design primarily focuses on user experience and involves understanding user needs and behaviors to create an enjoyable, efficient, and effective interaction with a product or service. UX designers research user needs, develop user stories and personas, conduct usability testing, and create design wireframes.
UI vs UX by Clay
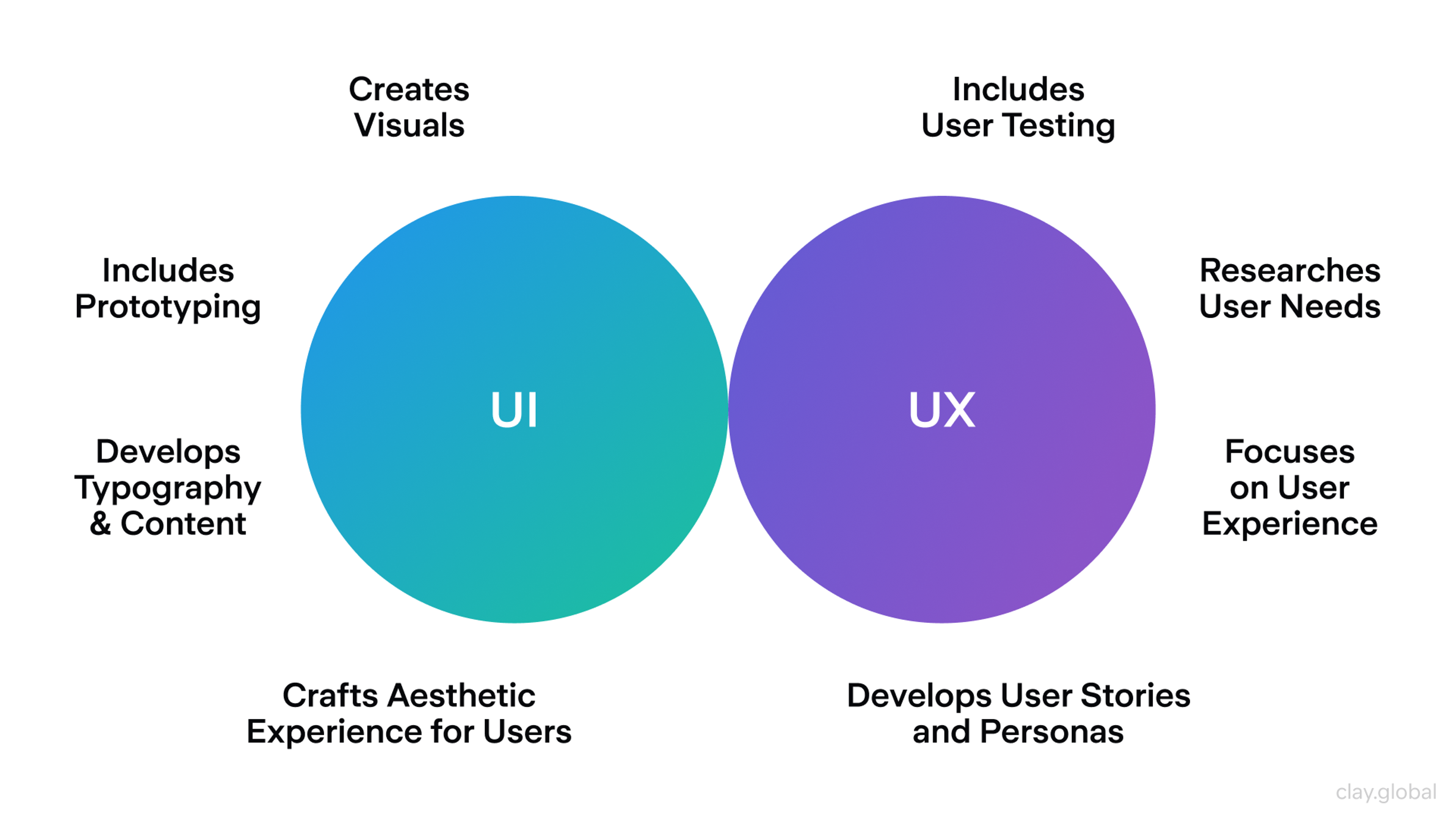
A design system helps maintain consistency in both UX and UI design by providing comprehensive documentation and guidelines for UI patterns and components, ensuring alignment throughout the design and development process. It is crucial to remain consistent in both UX and UI design to avoid user confusion and ensure a seamless experience.
UX design covers a broader range of elements than UI design, encompassing areas such as research and user testing. On the other hand, UI design primarily concerns enhancing the interface’s visual appeal and optimizing its communication with users through clear and effective error messages.
While both play crucial roles in delivering exceptional products or services, they serve distinct purposes during the development process and must be considered when crafting any offering.
Researchers have found that improvements in the user interface can increase conversion rates by 200%. User experience improvements can increase conversion rates by up to 400%. (Forrester Research)
What Do UI/UX Designers Do?
UI/UX designers shape how easy, attractive, and functional a website or app feels to everyone who visits. With a mix of design expertise and regular talks with actual users, they build interfaces that look good and are still a snap to use.
Great interfaces result from a strong grasp of design basics like font choices, color use, layouts, images, easy-to-find links, and how people naturally interact with screens. Designers keep everything feeling natural so users stay on a single page and complete their tasks quickly and successfully.
Design groups use tools like UXPin Merge to ensure that every mockup stays on the same page with the actual app code. When designers and developers collaborate this closely, prototypes accurately reflect every little interaction, and the finished product feels polished and consistent. Saving time and boosting quality become part of every release.
Designers don’t stop at beauty and ease. They study every primary accessibility guideline so interfaces can serve people with visual, hearing, or motor challenges as effectively as anyone else.
Prototyping tools are the workshop. Instead of handing over a paper mockup, designers can turn paintings into movable mockups that click, swipe, and react like an app. With programs like InVision and UXPin, team members and users can walk through screens before they’re built. Feedback from actual people sharpens ideas and snags tiny problems before steps start feeling like real work.
A great user experience starts with designers who can focus on the big picture while remembering the tiniest details. Spotting possible errors before users encounter them is another, often underappreciated, part of the job. During each round of testing, the goal is to catch issues early so people move smoothly through the interface without unnecessary roadblocks.
Understanding real user needs and the behaviors that flow from them is just half the job. To balance that knowledge with what the business needs, designers have to step into the users’ shoes — in personal terms, that means listening, observing, and sometimes imagining what a user’s day looks like. The team can only craft a solution that works for real people and the bottom line.
Finally, designing an interface is only one part of the process. Excellent designers can sketch a wireframe and, just as importantly, talk through it with developers, product owners, and marketers. Sharing a clear vision and keeping everyone organized is necessary so that the final product feels cohesive and valuable to every kind of user, from the goal-driven shopper to the curious newcomer.
Source: Budka Damdinsuren on Unsplash

By creating designs that meet both technical requirements and user needs while keeping aesthetics in mind, UI/UX designers help build products or services that are enjoyable and efficient for users while meeting business goals.
The Importance of UX Design
The importance of UX design cannot be overstated. As technology evolves, so do user expectations, making UX design increasingly important for providing users with meaningful experiences that meet their needs. A strong UX strategy is crucial in aligning UX design with business objectives, defining accountability within the UX team, and demonstrating the value of their work to stakeholders.
Consumers don’t have the patience for bad experiences — even when they’ve been long-time, loyal users. A global survey found that 32% would stop buying from a brand after one bad experience. (PwC)
Increase Brand Loyalty
When done well, UX design can help increase brand loyalty. By understanding user needs and behaviors, a product or service can be designed to create an enjoyable and efficient user experience. A positive experience will encourage users to return, and this fosters brand loyalty. UX designers can also increase brand loyalty through personalization, trustworthiness, and consistency.
In the case of Joe & The Juice, we incorporated a vibrant visual identity and engaging features in the mobile app design to enhance user experience. The app included a gamified loyalty program with 3D elements, digital gift cards, and an entertaining order-tracking system with animations. These elements not only streamlined the ordering process but also created a memorable and enjoyable user experience, thus fostering increased brand loyalty.
Joe & The Juice Identity by Clay
Build and Strengthen the Company’s Reputation
A well-designed product or service creates trust and loyalty between the user and the brand, increasing customer satisfaction. By focusing on user needs and behaviors, a UX Designer can create an enjoyable and efficient experience that ultimately helps build a company's reputation.
80% of UX teams that consistently do user research to optimize products say it positively affects customer satisfaction. 76% say that it also positively impacts brand perception. This is opposed to those that don’t do research or don’t do it consistently. Only 50% see satisfied customers, and 45% see improved brand perceptions. (UserZoom)
Reduce Future Costs
Source: Kylie Jane Willis on Medium
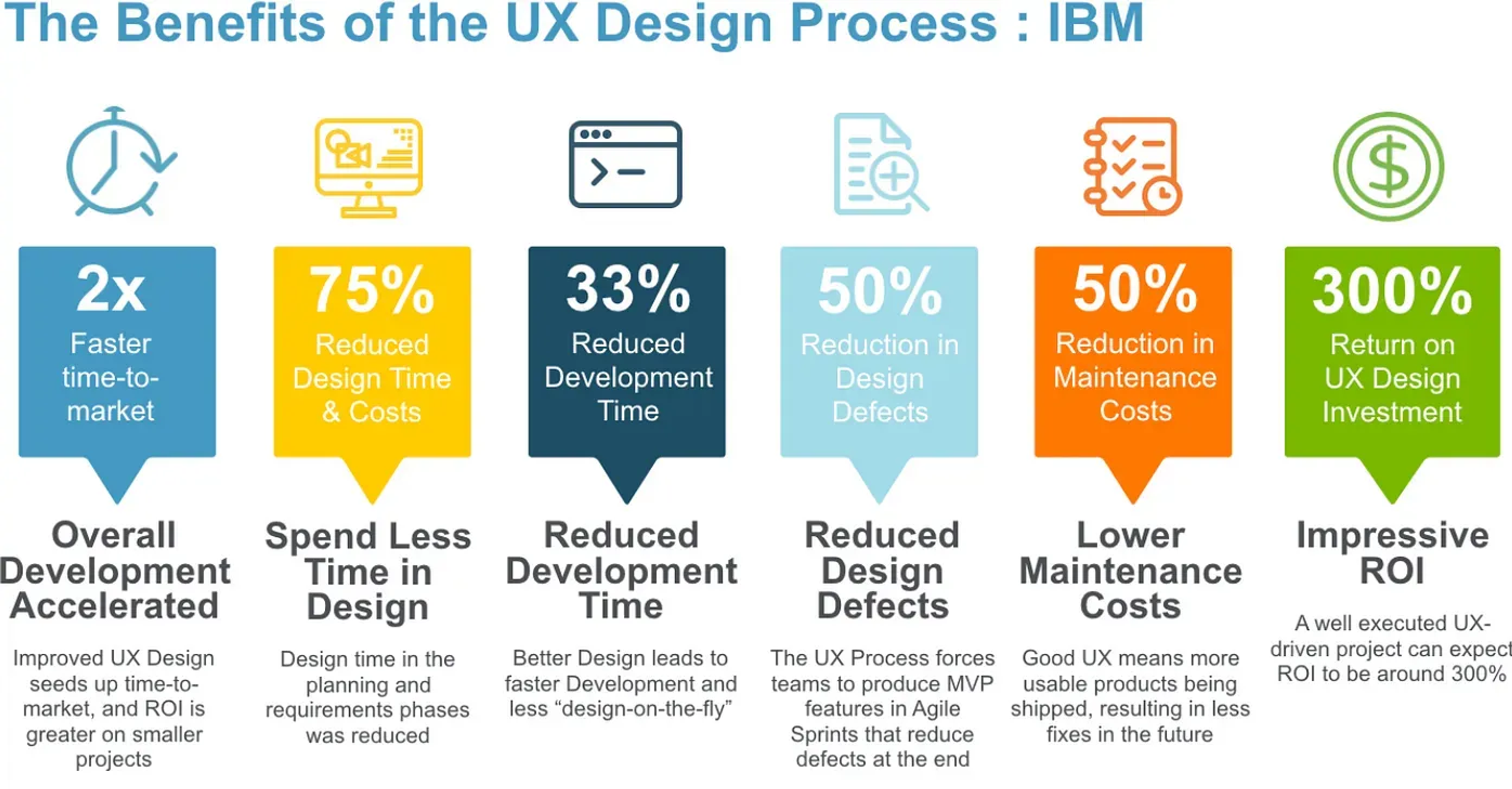
UX designers can also help reduce development costs by creating effective designs that consider usability, efficiency, scalability, accessibility standards, and more. By taking a holistic approach to design, UX designers can create interfaces that are easier to develop while meeting user needs. This helps eliminate unnecessary features or functions requiring more development time and resources.
"For every $1 invested in user experience design, businesses can expect a return of $100." (Forrester Research)
Psychology in UX Design
Psychology in UX design investigates why people see, feel, and think in ways that shape their online journeys. Designers use cognitive psychology ideas — like attention, memory, and habit formation — to build screens that seem natural and touch people's feelings.
Guiding theories, like Hick's Law (which trims choices to keep focus), the Von Restorff effect (using bold colors to make one item stand out), and affordances (letting shapes naturally show their use), steer users across an app without friction. Emotion is key, too. Knowing how to soften frustration, lift delight, and earn confidence can change the tone of an interface.
Psychological nudges make screens both easy to use and more persuasive. Progress bars on a long form show small strides, cutting the drop-off. Social proof — like ratings and reviews — positions a product as trusted, and the principle of reciprocity (offering small freebies) drives users to click "buy." Smartly managing cognitive load prevents info overload, opting for tidy hierarchies and bite-sized details instead.
By weaving psychology into UX, designers serve up experiences that work on the surface and sync with people's real, messy brains.
UI/UX Design Process
“Good design is about process, not product.” – Jared Sinclair
The UI/UX design process requires careful planning and execution to ensure optimal results, from initial ideation to the final product launch. In UI/UX design, ideation involves brainstorming and sketching out potential solutions to a given problem. By understanding each step in the UI/UX design process, you can create effective designs that will engage your target audience and drive success. Achieving great UX requires consistent design and ongoing user testing to meet user needs across different platforms.
A well-structured product development process enhances collaboration between design and development teams, ensuring consistency and accountability, which ultimately leads to improved product quality and business value.
UX Design Process by Clay
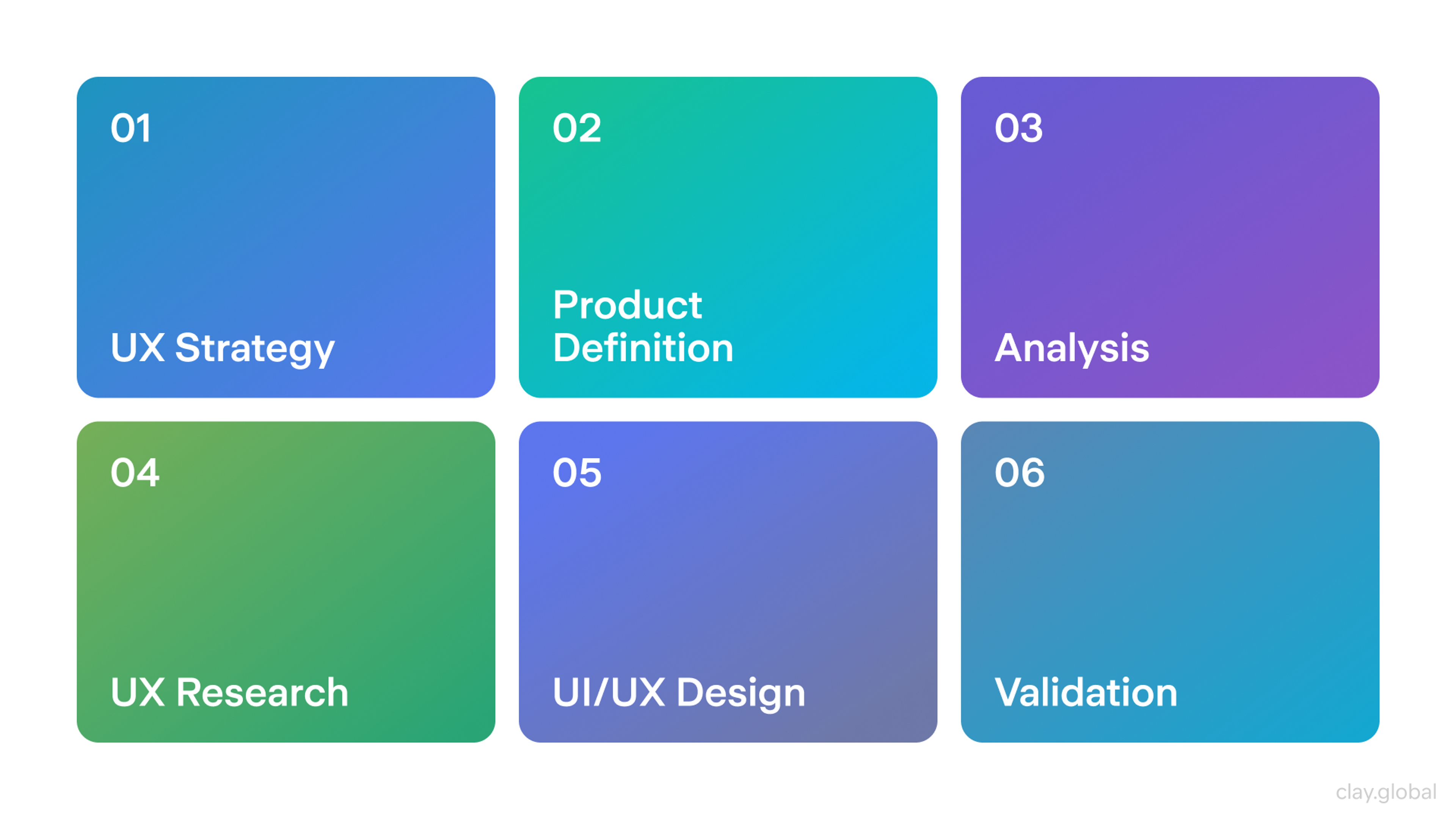
UX Strategy
UX strategy is the foundation of successful user experience design. It involves understanding users, their goals and motivations, and how they use products or services. UX strategists analyze customer data, research customer journeys, and identify pain points to create optimized user experiences for maximum engagement.
Understanding user goals is crucial in developing an effective UX strategy, as it helps in setting appropriate defaults and designing interfaces that cater to specific user objectives.
A crucial aspect of this process is conducting a competitive analysis to understand the competition’s actions, strengths, and weaknesses, which informs the development of a user experience guidelines. A key element of UX strategy is empathizing with potential customers to understand their needs and create a product that solves their problems.
Product Definition
Product definitions spell out why a product exists, what it does, what tech it requires, and who it serves, so the product actually helps the people who will use it.
Uniform design isn’t a nice extra. It’s how users see a product as a single, trustworthy thing. When every button, color, and action behaves similarly, people move confidently and feel comfortable, turning guesswork into muscle memory.
To create a product people love, market research uncovers who users really are, what’s trending, and how competitors are moving. The data keeps the design team on a path users expect rather than one they have to figure out.
During the definition stage, experts check existing experience guidelines and conduct in-field customer research. The goal is to draft a product that fixes a real issue and proves useful from the start.
A product that’s finished only in name won’t last. Definitions also map how the product scales and spell out what can and can’t be built so teams can stay nimble. Design squads use tools like UXPin Merge to show developers how, not just the why, catching consistency issues while the lines of code are still fresh.
Analysis
A thorough analysis identifies what users truly need and how they engage with products or services daily. Researchers review behavioral logs, complete journey maps, and aggregated feedback to grasp how users view offerings and where friction most commonly occurs.
To make informed design choices, nationals, or emotional, designers trace small details — like the subtle hover states of buttons or the variance of animated cursors on different tasks — to uncover what subtle cues signal intent and comfort. This intelligence reveals not just actions but shifting shapes of need.
Mapping what customers intend to do and how they behave transforms vague desires into concrete changes. By distilling this understanding into deliberate design tweaks or supportive defaults, design teams refine existing products and craft moments of delight. Users feel seamlessly synchronized with the solutions they’re offered, and conversion becomes a natural extension of the experience.
UX Research & Methods
UX research and methods are crucial to the UI/UX design process. User research and methods are used to understand user needs, motivations, behaviors, and preferences in-depth. Error prevention is a key aspect of UX research, helping to address potential issues during user testing before a product launch.
Remote usability tests are an essential part of UX research, providing a convenient way to gather insights from a diverse pool of testers and enhancing the understanding of user interactions with websites or apps.
Through user research methods and testing (include usability and desirability), design teams can identify potential problems and create designs that meet user expectations.
Qualitative Methods
Qualitative methods are a key part of user research and methods in the UI/UX design process. Through qualitative methods, designers can understand the complexities and depth of user needs, motivations, behaviors, and preferences. Qualitative methods such as interviews, focus groups, and ethnography can provide insights into why users behave the way they do and how they interact with products or services.
Qualitative Methods of UX Research Process by Clay

User Interviews
User Interviews are an important part of the UI/UX design process. They involve interviewing users to better understand their needs, motivations, behavior, and preferences.
User interviews involve conducting one-on-one sessions with users to ask questions about their experiences and preferences. This data can provide insights into what users seek in a product or service, how they interact with it, and what improvements can be made.
Focus Groups
Focus groups are valuable for gathering user feedback and insight on a particular topic or product. By bringing individuals together, focus groups aim to better understand how users interact with the product, their preferences, and potential areas for improvement.
This approach enables a deeper level of understanding when it comes to user needs. So, rather than simply relying on surveys or individual interviews, focus groups offer a more dynamic and collaborative approach to gathering feedback.
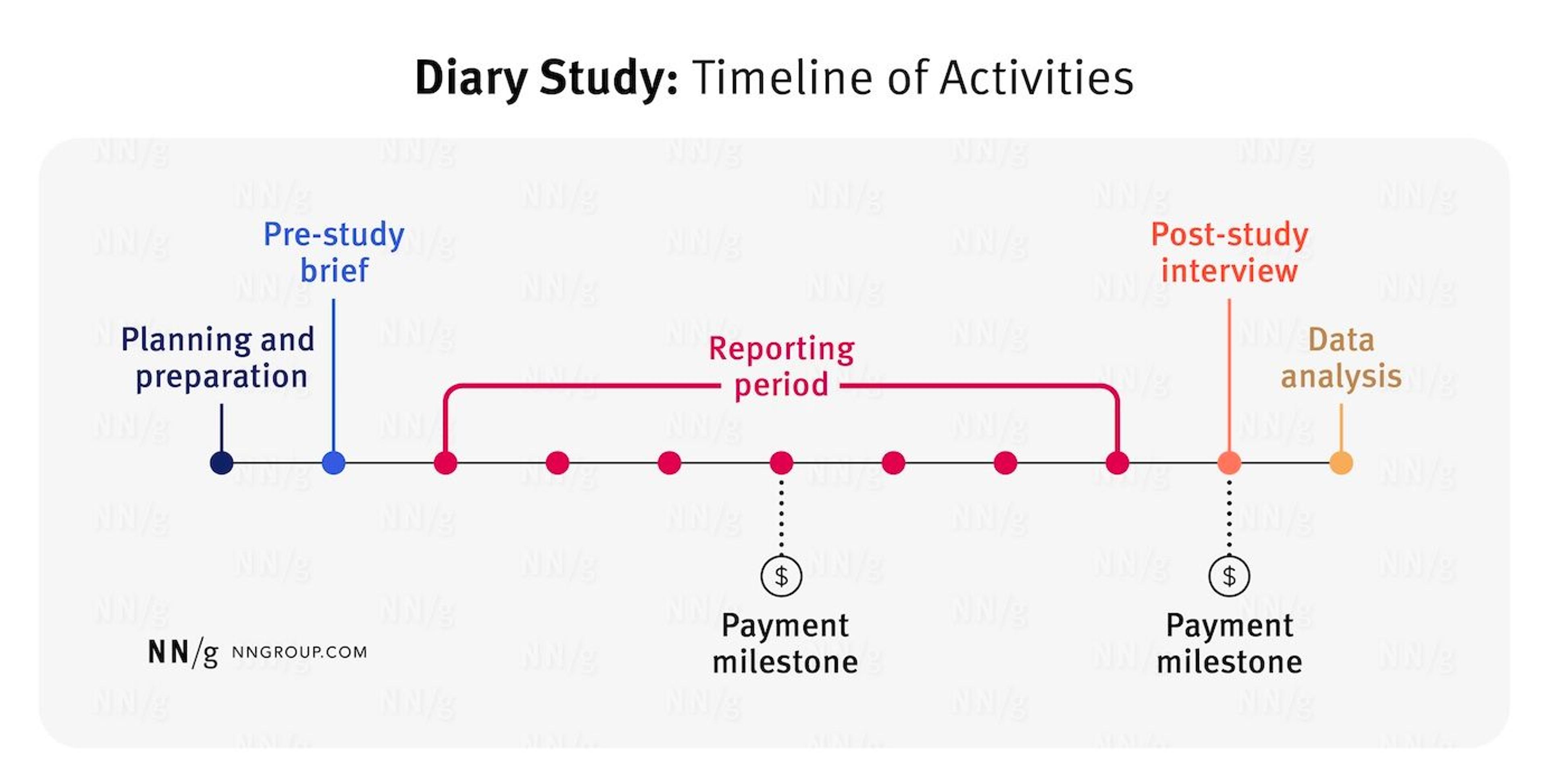
Diary Studies
are another qualitative method used in user research. These studies involve gathering user data over a period of time to better understand user needs, motivations, behaviors, and preferences.
Diary studies involve users tracking their experiences with products or services over a given period and recording their feedback in a diary. This data provides valuable insights into user behavior, which can be used to create and improve products or services.
Dairy Studies Timeline of Activities by NNGroup
Ethnography Studies
Ethnography studies is a meaningful user research tool in the UI/UX design process. It involves observing users in their natural environment to understand how they interact with products or services. This provides valuable insights into user behavior and preferences, helping designers create compelling user experiences tailored to the target audience.
Usability Testing
Usability testing is integral to user research in the UI/UX design process. It is an iterative process that involves testing user interactions with a product or service to identify any areas of improvement or potential problems. During usability testing, users are asked to interact with the product or service to detect issues or provide feedback on improving it.
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative methods involve gathering data through surveys, A/B testing, and other types of experiments to understand user needs better. Through quantitative methods, designers can collect and analyze large amounts of data to determine how users interact with products or services, what improvements can be made, and how users feel about the product or service.
Quantitative Methods of UX Research Process by Clay

Surveys & Questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are an important part of user research. They collect user data by asking about their experiences, preferences, and behavior. Surveys and questionnaires provide a structured way to ask questions, making it easy to analyze the data and make decisions.
A/B Testing
A/B testing is a noteworthy UX research tool in the UI/UX design process. It involves running experiments with two versions of a product or service (version A and version B) to determine which performs better.
Analyzing User Behavior Data
By analyzing user behavior data, designers can understand how users interact with products or services and what improvements can be made. This data can provide valuable insights into user preferences, motivations, and needs.
Tree Testing
Tree testing is a type of testing in the UX research process. It involves a user navigating through a website or product interface using a visual tree structure representing the website structure, allowing them to identify any potential navigation or information architecture issues.
UI/UX Design
“88% of online consumers are less likely to return to a website after a bad user experience.” (Hubspot)
The design phase in UI/UX design process involves creating wireframes, prototypes, and other visual design elements that will be used to create the final product or service.
During this phase, designers must consider usability, accessibility, aesthetic appeal, and user behavior when creating a design. Consistent design is crucial for creating a cohesive user experience, where UI elements are predictable and familiar to users.
It is crucial to design realistic prototypes using tools like Framer to test concepts with real users before final development, enhancing user satisfaction and improving overall design quality.
Design Sprint
A design sprint is a structured, five-day sprint that turns a complex product or design challenge into a tested solution overnight. Built on hands-on, step-by-step activities, the sprint forces us to move at the speed of a prototype rather than a plan.
From Monday morning to Friday, designers, product leads, engineers, and key stakeholders work side-by-side. Instead of long conversations, we draw, map, and prototype ideas to find the best path. When we wrap the week, we have a tested prototype and a firm decision on whether to build, refine, or discard the idea.
The week itself has tight checkpoints. Monday is all about understanding the challenge and mapping the user journey. Tuesday, we quickly sketch a range of ideas. The team selects the strongest concept by Wednesday, creating a realistic prototype on Thursday. We put that prototype before real users on Friday morning to gather feedback — measured, time-boxed, and real.
Sprints shine in three cases: exploring a one-line idea that could become a product, pivoting an existing product that needs a fresh direction, or confirming a top-line feature before the team writes the first line of code. It turns guesswork into tested proof, letting the team move in the right direction rather than the wrong one.
Beyond the final prototype, a design sprint cultivates a shared mindset. By focusing on users and sketching rather than debating, we clear misunderstandings, reveal hidden expertise across disciplines, and quickly build momentum on the idea we took into the week.
Sketching
Sketching plays a vital role in the UI/UX design process. It involves creating quick preliminary wireframes and designs for a product or service. This helps designers visualize their ideas in a low-fidelity form and experiment with different options before moving on to more time-consuming tasks like coding.
Using UI templates during the sketching phase can help standardize the layout and features, streamlining the design process and ensuring consistency. Sketching can be used to create simple mockups for user testing and feedback.
Wireframing
Wireframing is an essential part of the UI/UX design process. It is the process of creating a visual guide for the structure and layout of a product or service. Maintaining consistency in wireframing is crucial as it ensures uniformity across user interfaces, enhancing the overall user experience.
Wireframing helps designers visualize different user interface elements, such as buttons, text, images, and navigation. It provides a blueprint for how users interact with a product or service.
Prototypes
Prototyping involves creating interactive prototypes that simulate how a product or service will function in its final form. Prototypes are useful for testing user interactions, validating design decisions, and collecting user feedback before investing resources into implementation.
Direct feedback from users during usability testing and while sharing prototypes with stakeholders is crucial for understanding user experiences and identifying areas for improvement in product design.
They can help ensure that the product or service meets user needs and expectations by providing an interactive environment to test and refine ideas.
In the case of the Discover mobile app, we created detailed flow diagrams during the UX phase to explore all potential use cases for receiving and activating a credit card. Multiple iterations of these prototypes were tested on iOS and Android to find the most user-friendly approach, ensuring an optimal onboarding experience and user feature discovery.
Discover Mobile App by Clay
Mockups
Mockups are static visual designs that test user interactions, validate design decisions, show user flow, and collect user feedback. They provide a concrete representation of how a product or service will look and function in its final form. Mockups help designers understand how users interact with a product or service.
Wireframe vs Mockup vs Prototype by Clay

UI Design Process
UI design is an important part of the UX design process. It is a process for creating interactive and intuitive user interfaces that are aesthetically pleasing and easy to use. UI design involves creating layouts, colors, typography, icons, images, and other visual elements that will help guide users through a product or service’s features and functions.
We emphasized the UI design process with a minimalistic approach for the Echo Street project, utilizing the "Echo effect" as a key visual identifier. The design incorporated layering of blocks to add depth, 3D presentations to highlight sustainable investments, and seamless transition sequences on the front page to convey the brand story fluidly. Special attention was given to ensuring a consistent mobile experience, effectively showcasing the firm's unique values and team members.
Echo Street Elements by Clay
Micro-interactions & Interface Semantics
Micro-interactions are those quiet, tiny animations you notice when using an app — like the gentle ripple when you tap a button, the small wheel spinning while you wait, or the elegant switch slide. Each move is fast and easy to overlook, yet together they turn a cold screen into an attentive partner, guiding you through a task.
These little helpers cut through doubt and give the app a tiny dose of charm. A heart that fills when you tap it or a checkmark that jumps forward when a file is sent shows you what happened. Recommended only when they elevate the journey without shouting for attention, they remind you what to do next without ever stealing the spotlight.
Interface semantics are about each icon and color's quiet agreement with the user. A trash can always promises to delete; a red banner shouts that something needs fixing. Keeping these promises builds what designers call a mental model — a shared map that lets the brain navigate without wondering what a shape means or what a shade decides.
When the visuals are consistent and the tiny animations add just the right personality, they take the guesswork out of using the app. The result is a calmer, more trusting experience. Users know why that button just reacted that way, and their decision feels supported, not startled.
Validation
Validation ensures that a product or service meets user needs and expectations by testing it with real users in its intended environment. Validation allows designers to gain user feedback on how effectively the product or service functions and whether any improvements can be made.
Considering the user’s point during validation is crucial, as it helps to pinpoint areas for improvement, ensuring that the final product meets user needs effectively.
This feedback can be used to refine and improve the design before launching it to the public. Error prevention is also a key aspect of validation, as addressing potential errors during user testing can significantly enhance the user experience.
Collaboration between design and development teams is essential during validation. This collaboration allows for accurate prototyping and maintaining consistency throughout the product development process, ultimately leading to improved user experience and efficiency.
Final Testing & Corrections
The final user testing guarantees the product or service satisfies user requirements and expectations, it is when adjustments are made to enhance areas requiring improvement.
This testing involves real users interacting with the product or service in its intended environment, allowing designers to gain valuable feedback on improving the design. The feedback can refine the product or service before it is released to the public.
Launch
The launch phase of the UI/UX design process is when the product or service is made available to users. It involves preparing promotional materials, setting up marketing campaigns, and meeting all user needs and expectations.
This is an important step, as it is the first time users can interact with the product or service in its final form. In this phase, designers must ensure that all user feedback has been considered to create a successful launch.
How to Measure UX?
Measuring UX assesses a product or service’s effectiveness in providing a positive user experience. UX metrics can help designers identify areas that need improvement, monitor performance over time, and optimize their designs for peak results.
Understanding user goals is crucial in measuring UX, as it helps in setting appropriate defaults and designing interfaces that cater to specific user objectives.
An analytics tool can be invaluable in this process, offering features like session replays and heatmaps to analyze visitor behavior, identify usability issues, and gather qualitative feedback.
UX Metrics (Behavioural and Attitudinal) by Clay

Common UX metrics include user satisfaction, task success rate, engagement time, and conversion rate. By closely monitoring these metrics, designers can identify areas that need improvement and refine the product or service to provide the best user experience possible.
These are just some steps in the UI/UX design process. From creating prototypes to launching a product or service, designers must consider all aspects of the user experience to ensure that their products or services meet user needs and expectations. By measuring UX metrics, designers can optimize their designs for the best user experience possible for potential customers.
UI/UX Deliverables
UI/UX deliverables refer to designing and developing user interfaces and experiences that ensure an efficient, effective, and enjoyable interaction between a user and a product. Consistent design is crucial for creating a cohesive user experience, where UI elements are predictable and familiar to users.
Product teams play a crucial role in shaping the UX vision and executing the design process in a dynamic and responsive manner. Design teams are essential in creating cohesive and functional user interfaces by leveraging tools like UXPin Merge, ensuring collaboration between design and development teams.
It involves researching the target users and audience, understanding their needs and motivations, designing interfaces that meet the requirements of the user’s journey, creating prototypes, and testing them to gather feedback.
Design Systems & Pattern Libraries
Design systems are more than significant documents — they're playbooks that tell your team how colors, buttons, fonts, and spacing should work together every time. Inside these frameworks, you'll find all the rules and ready-made pieces that keep your website, app, or software looking and acting the same, whether on a phone, tablet, or desktop.
Unlike dated PDFs, a sound design system grows with the product. Designers and developers keep adding new patterns, rules, or tokens, so the system keeps the product appearing cohesive — without freezing it in stone. Think of it as a carpentry framework: the walls can change without toppling over as long as the beams are solid.
Housed inside, pattern libraries serve as the curated MVC — most valuable collection — of buttons, checkboxes, scrollbars, and such. You'll find the same checkbox design used on the web, iOS, and Android, always framed with clear guidance on when and how to use it.
The design system sets colors, row heights, and hover timings (the rulish tokens). The pattern library shows the same sitemap button rendered in three versions, evaluated, tested, and ready.
This connection between intention and use powers everyone from the UX intern to the veteran code wizard, allowing teams to squeeze time out of the process, share the same terms, and keep user experiences smooth, no matter how fast the team grows.
UI/UX Research Document
A UI/UX research document serves as the research team's final report, laying out what they've learned from studying both the user and the overall experience.
Grasping how real people currently interact with the product is vital. That understanding acts as the bedrock for a successful user experience (UX) strategy. Recognizing user goals in these reports is equally essential, as it helps ensure that every design move is laser-focused on what users are trying to get done.
The document usually lists who participated in the interviews, what patterns emerged (like user preferences and behavioral trends), the research methods employed, and suggestions for product fixes. The goal is to circulate fresh insights among team members so designers can base their improved product layouts on user behavior.
Source: UX Collective
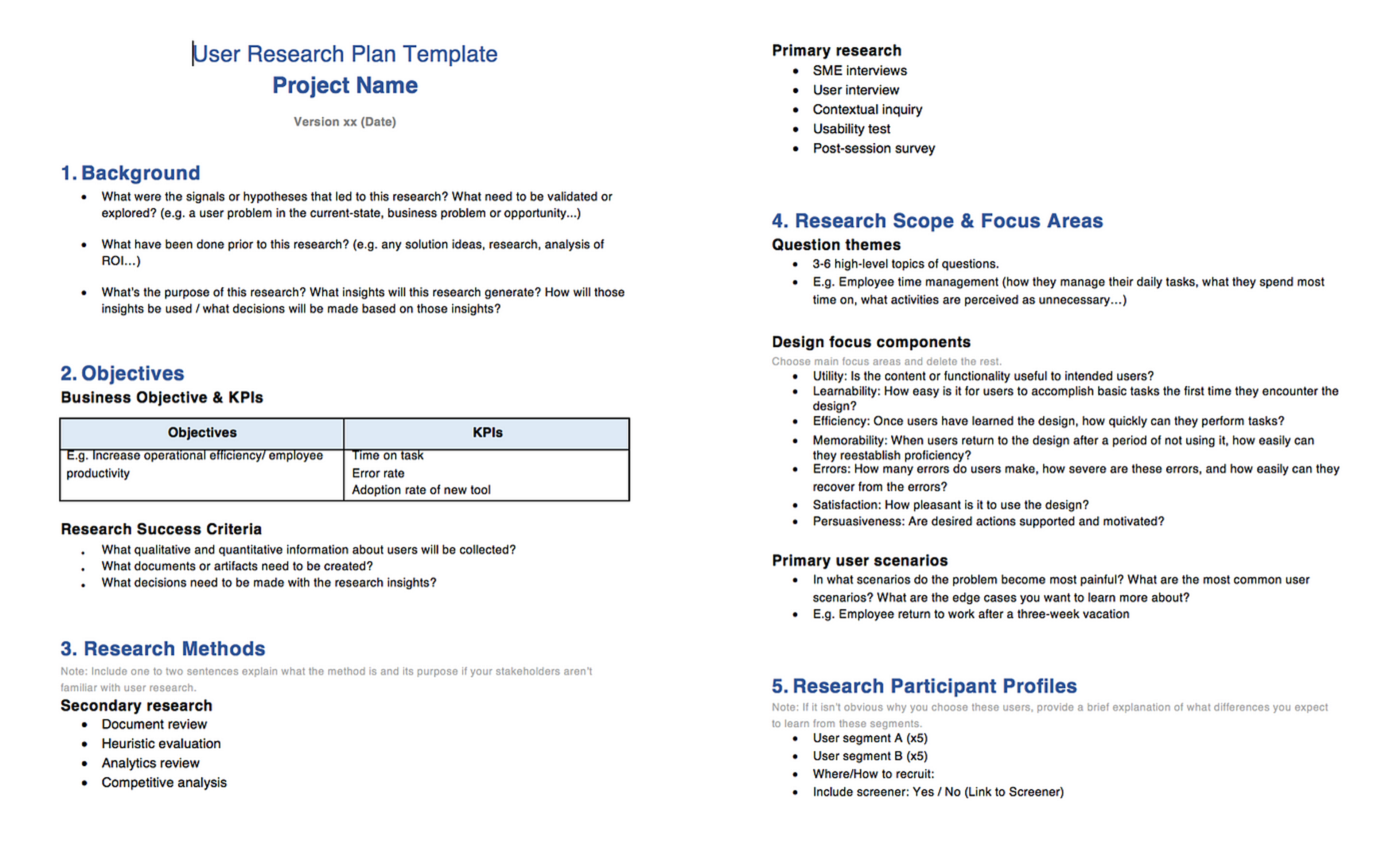
Take a study where participants repeatedly mention a desire for more straightforward navigation. The designer can quickly jump to action, trimming down the menu, moving items around, or merging similar choices to make it feel effortless. Beyond providing improvement tips, the report should also present a detailed breakdown of every task the user completed and map their journeys while testing the product.
This report gives UX designers the complex numbers and honest user feedback needed to choose the right design path. Rather than guess what looks good or assume what's easy to use, designers can see precisely how future customers click, swipe, and browse.
By combining visuals, user-session recordings, and survey insights, the report lays out the data clearly, making it easy to prioritize changes that will improve the user experience. Whether crafting a brand-new interface or polishing an already live product, designers can use this evidence to back every decision with solid facts, leading to smoother tools that users love.
User Research Takeaways
User research takeaways are the key insights learned during the gathering user data phase. They can be used to inform product design decisions, improve user experience and identify areas of improvement.
Understanding the feedback from end users is crucial as it helps refine the strategy to meet real user needs. Additionally, focusing on error prevention during user research can significantly enhance the final product by addressing potential issues before launch.
User research takeaways include discovering what users expect from a product, how they interact with it, their preferences when using it, and any areas of difficulty.
This data can then inform product design decisions, such as creating an improved user interface or improving the overall user experience. Design teams play a vital role in this process by leveraging tools like UXPin Merge to ensure accurate prototyping and maintaining consistency throughout the product development process.
User Flow Document
A user flow diagram or document is essential to UI/UX design and development. It details a user’s steps when using a product or website, providing insights into how they interact with it and allowing UX designers to optimize the experience.
Incorporating a user-centered approach is crucial in creating user flow documents, as it ensures the design is tailored to meet users’ needs and behaviors, enhancing usability and engagement. Additionally, maintaining a consistent design is vital for creating a cohesive user experience, where UI elements are predictable and familiar to users.
The goal of a user flow document is to create an intuitive experience that guides users through their journey without any confusion or frustration. It usually includes diagrams and text explaining each step of the user’s journey, their goals, and how they achieve them.
For Serena & Lily, we mapped the user flow to ensure a seamless and elegant shopping experience. The flow from product discovery to checkout was streamlined, eliminating unnecessary steps and simplifying navigation. This redesign enhanced the user journey, making it intuitive and enjoyable, aiming to increase conversion rates and customer satisfaction by leveraging the expertise of our design teams.
Serena & Lily by Clay
Wireframes
Wireframes are a tool designers use to represent the user interface, an idea of how it will interact. Wireframes are simple squares and rectangles representing buttons, menus, text, and images. They often illustrate navigation, page structure, and content placement.
Error prevention is crucial in wireframes, as addressing potential errors during user testing can significantly improve the final product.
By implementing reusable components in wireframing, design teams can create a unified user experience across multiple products, enhancing usability and consistency while facilitating quicker development.
Wireframes also provide an essential visual representation of the user interface before any coding or design takes place and can be used to gather feedback from users about the proposed design.
Interactive Prototype
An interactive prototype is a hands-on mock-up of a user interface that lets designers see how their designs work. It loads up with clickable features — buttons, tabs, and menus — so users can play with the app before it’s built. Keeping the design the same across the board is key; when users always see the same styles, gestures, and layouts, everything feels smooth and predictable.
These prototypes shine when designers need to build multiple apps for a similar audience. Even a quick interactive mock-up can show how all the applications come together. This was helpful for remote-learning tools during COVID, showing that the same easy, familiar experience is needed across Zoom rooms, homework trackers, and progress logs.
While users navigate a key task — like signing up for a class or uploading an assignment — designers watch to find rough edges. They see the steps users take, where they hesitate, and which buttons they miss. This real-time feedback is the fastest way to spot and fix confusing layouts. Adjustments can be pulled into the prototype, so everyone can continue testing the next day.
Production teams hang on to versions that combine code with design tools, such as UXPin Merge, to save time and design spills. This bridge means every button that gets a finishing touch in design also gets that finishing touch in code, so everyone stays in sync on spacing, colors, and interaction delay.
Because the prototype looks and feels as polished as the finished product, teams can fly through user testing, and designers can confidently hand off a consistent and carefully validated product.
User Testing Report
A user-testing report is a handy reference that sums up what testing reveals about a product or website. Within its pages, designers will spot details like how users navigate, what tasks they finish, and where extra guidance is necessary.
Having this document keeps designers grounded in reality. They see where users stumble, why they get frustrated, and what they appreciate. Focusing on preventing mistakes during the testing lets designers catch problems before they become a headache on launch day, smoothing the path for the person who’ll eventually click the buttons.
The actual users’ thoughts breathe life into the report. Their comments let teams know whether the design meets the hoped-for needs and whether using the product feels natural and enjoyable. Design teams, in turn, keep close ties with developers, sharing early and clear prototypes, and confirming that style, button placement, and tone stay on track until the final line of code is written.
Common UI Elements
“Users spend an average of 5.94 seconds looking at a website’s main image.” - Nielsen Norman Group
Common UI elements are the building blocks of user interface design. These elements include buttons, menus, text boxes, images, sliders, and more. They allow users to interact with a product intuitively and efficiently. Consistent design in these elements is crucial for creating a cohesive user experience, where UI elements are predictable and familiar to users.
UI elements should be designed to be easy to understand and use for all users. Effective UI/UX design not only attracts visitors but also keeps users engaged by fostering loyalty and long-term engagement through intuitive usability and strategic planning.
UX designers must also consider how the elements fit into the product’s visual hierarchy, style guide, and overall user experience and how they can improve user engagement. Design teams play a vital role in this process by leveraging tools like UXPin Merge to ensure accurate prototyping and maintaining consistency throughout the product development process
Grayscale UI Kit by Clay

UI Animations
UI animations are an essential part of user interface design. Animations provide visual cues that allow users to understand how a product or website works and can be used to create a more engaging user experience. Animations can also help guide users through the user flow, making completing tasks easier and more efficient.
Error prevention is crucial in UI animations, as it helps minimize user mistakes and creates a smoother user experience.
UI animations can surprise and delight users by adding unexpected design elements or animations that enhance the overall user experience.
When used correctly, visual design and animations can be powerful tools for creating an engaging and intuitive user experience. UX designers must understand the principles of animation to ensure that their designs are effective and add value to the user experience.
We employed motion design for Cornerstone to enhance the visual identity and user experience. Custom brand characters and objects were strategically placed and animated to create a friendly and memorable first impression.
These animations help categorize information, guide users, and reinforce the brand’s modern image, making the web experience more dynamic and engaging. Design teams play a crucial role in this process, ensuring accurate prototyping and maintaining consistency throughout the product development.
Cornerstone 3D Animations by Clay
UX Design Methods
User experience (UX) design methods are a set of processes and techniques used to create digital products that provide an enjoyable, intuitive, and useful experience for the user. UX designers use various tools and methods to ensure that their products meet the needs of the target user group while also being appealing and engaging. Consistent design is crucial for creating a cohesive user experience, where UI elements are predictable and familiar to users.
Integrating business strategy within UX design is crucial for aligning product development with organizational goals, setting expectations, addressing constraints, and facilitating stakeholder discussions to enhance user experience while meeting business objectives.
Design teams play a vital role in this process by leveraging tools like UXPin Merge to ensure accurate prototyping and maintaining consistency throughout the product development process.
Value Proposition
Crafting a value proposition statement that outlines the essential elements of your product – its purpose, target audience, and use cases – is critical to ensuring that everyone on the team can agree upon what it will deliver.
Understanding user goals is essential in crafting a compelling value proposition, as it helps align the product's features with the specific objectives of the users.
Keeping teams on the same page is crucial for creating a value proposition, as it ensures that all stakeholders and team members have a unified understanding of the design guidelines, pattern libraries, and UX strategies. This alignment is vital for optimizing interactions with potential customers and enhancing their overall experience.
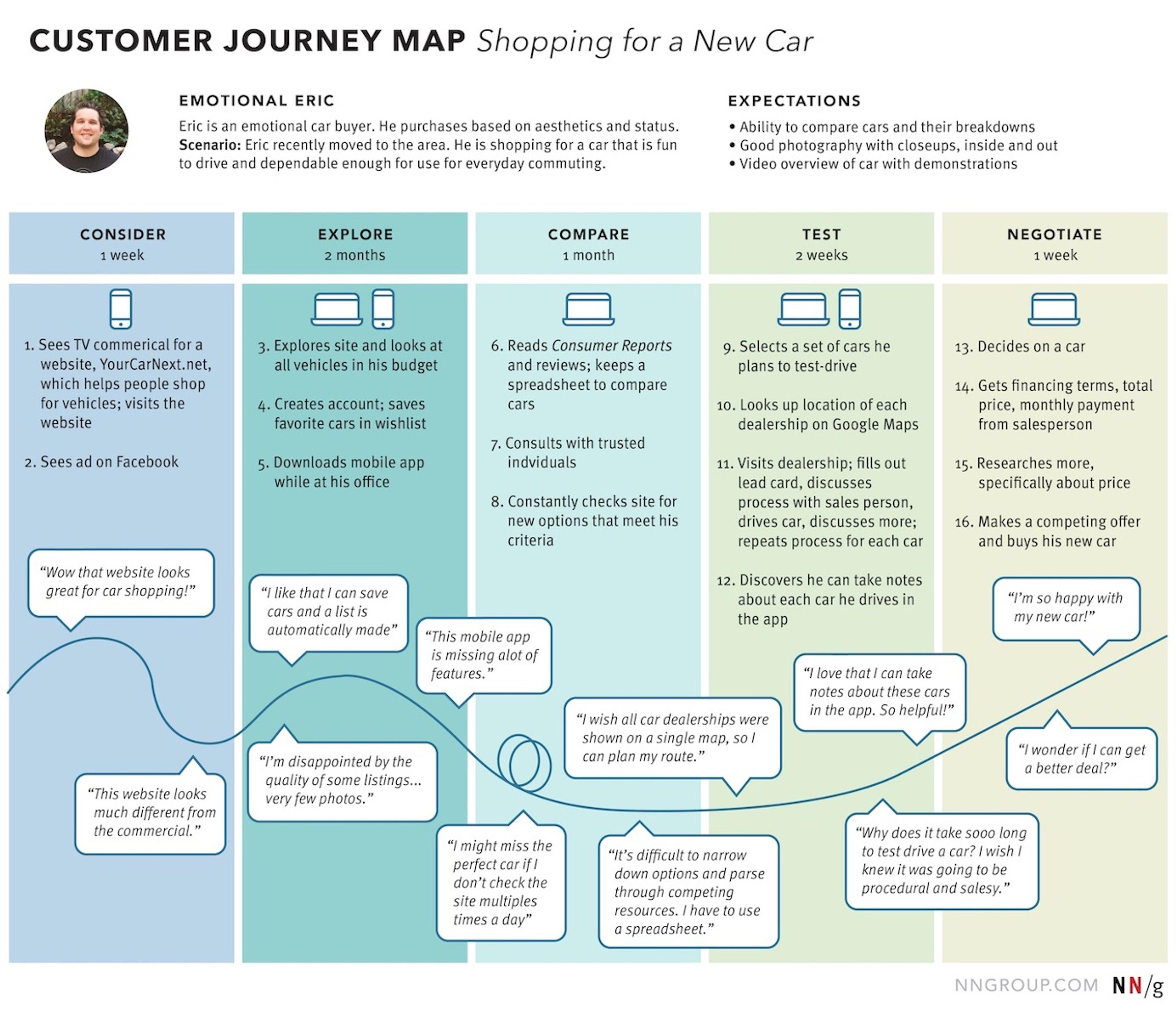
Customer Journey Maps
Customer journey maps visually represent a user’s journey when interacting with a product or service. It is useful for helping designers better understand the entire customer experience and identify areas where they can improve their product or service. By mapping out the entire customer experience, designers can better understand what users seek and how they interact with their products or services.
Error prevention is crucial in customer journey maps to ensure a smooth and error-free user experience.
It is crucial to consider the entire process when creating customer journey maps to ensure consistency and a comprehensive understanding of the user experience.
Customer journey maps help designers identify pain points, opportunities, and solutions to improve the user’s experience. For example, by identifying common problems that users encounter while using a product or service, designers can create solutions to make the experience more enjoyable and intuitive.
Design teams can also use customer journey maps to spot potential areas to make improvements to provide users with a more personalized experience that caters to their specific needs.
Example of CJM by NNGroup
User Personas
User personas are a powerful tool used in UX design to create in-depth profiles of potential clients that help designers better understand the needs and motivations of their target audience. Consistent design is crucial in user personas as it ensures a cohesive user experience, making UI elements predictable and familiar to users.
User personas help in understanding the user’s experience by capturing their needs, frustrations, and behaviors, ensuring that every aspect of the user journey is considered.
Personas help designers develop an understanding of the behaviors, points, and needs of different groups. They also allow designers to think beyond demographics to create products and services tailored to the individual user. Personas can help designers develop more meaningful products and create experiences that users can easily relate to.
User personas are also helpful when testing new designs or features. Designers can use personas to test prototypes with different types of users, get feedback on how their product performs, and make necessary adjustments. Design teams play a crucial role in this process by collaborating closely to ensure accurate prototyping and maintaining consistency throughout the product development.
Heuristic Evaluation
Heuristic Evaluation is a handy UX design method for checking how easy a website or app is to use. The process reviews the product’s design to see if it meets smart rules for good usability. An expert will go through key screens, checking buttons, links, and layouts to spot issues that could confuse users. Before users ever touch the product, we focus on stopping little mistakes that keep them from completing their goals.
In this process, UI and UX designers are the eyes that see where a design can trip users. They report the bumps and then brainstorm fixes to straighten the path. No design tool is too big or too small — platforms like UXPin Merge can wire-frame to the final pixel, ensuring the tweaks stay intact from idea to live launch.
Heuristic evaluations are goal-oriented. An example might be a hard-to-read button; the evaluator may recommend making it bolder for clarity. Another might be the search experience, where a feature that remembers past queries could simplify the journey. When a team acts on these findings, they wrap up the rough edges and give users a smoother ride, all before the big reveal.
Product Roadmap
A product roadmap is an essential tool in UX design that outlines the plan for improving a product or service. It helps designers visualize and prioritize their short-term to long-term objectives. The product roadmap provides a comprehensive plan for developing a product and its various features, including user interface elements and interactions. Consistent design is crucial for creating a cohesive user experience, where UI elements are predictable and familiar to users.
A product roadmap outlines the product development stage, detailing each phase from initial concept to final release, including prototyping as a crucial phase to test functionality and refine designs.
Source: LinkedIn
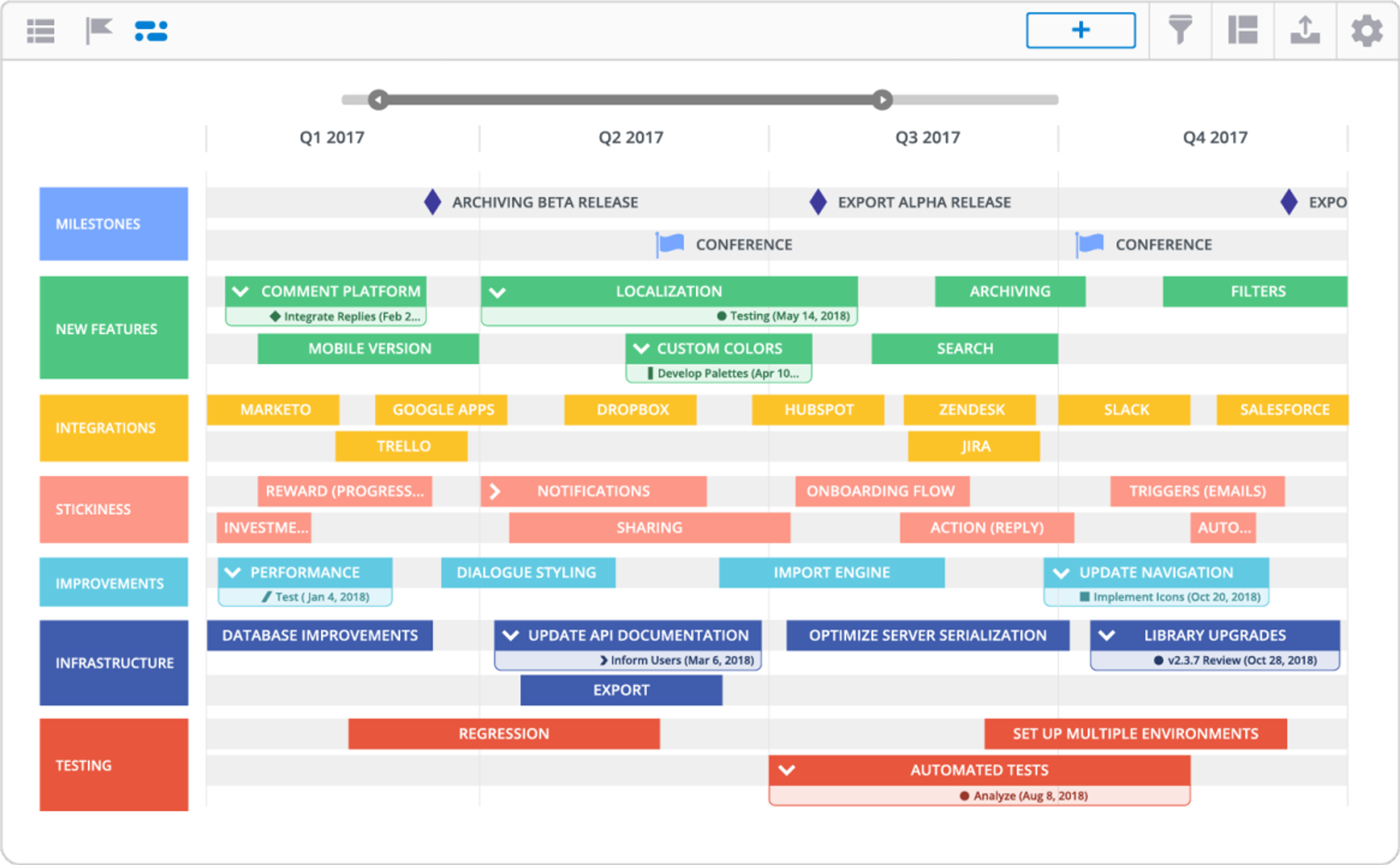
Designers use product roadmaps to determine the most critical areas of their product or service that need improvement or redesign. They can also identify areas where they may want to develop new features or create more user-friendly interfaces. Design teams play a vital role in this process by leveraging tools like UXPin Merge to ensure accurate prototyping and maintaining consistency throughout the product development process.
Usability Testing
“Usability answers the question, ‘Can the user accomplish their goal?” - Joyce Lee
Usability testing is a process in UX design that evaluates the usability of a product or service by having users interact with it. It involves observing users as they interact with a product or service to identify any usability issues, determine user preferences, and uncover opportunities for improvement. Usability testing can include focus groups, surveys, interviews, and user experience testing sessions.
Error prevention is crucial in usability testing, as it helps designers address potential errors during user testing before a product launch.
A user-centered approach is crucial in usability testing as it focuses on understanding users’ needs and behaviors through research, leading to tailored designs that enhance usability and engagement.
Usability testing allows designers to gain valuable insights into how users interact with their product or service. This feedback can refine a product or service and ensure it meets user needs. It also helps design teams develop solutions that make it easier for users to use the product or service.
Guerrilla Testing
Guerrilla testing speeds up usability research, keeps costs down, and makes testing feel less formal. Designers bring prototypes or live products into natural, bustling environments — think of an outdoor park or a corner cafe — and then watch people use the system as they would at home. Uniform appearance across the interface is a must. When buttons, colors, and gestures behave the same whether the context is mobile, sticky kiosk screen, or promo page, users trust the system and keep moving — always a win.
Data collected during these mini sessions turns into actionable insights almost right away. One group of users might spend extra time tapping the fine print, another might accidentally join a confusing onboarding loop — both signals that the same touchscreen prototype needs tweaking. The designer takes live notes behind the screen or tablet, and the entire product team adjusts pixels that afternoon, not at next month's meeting. Collaborative tools like UXPin Merge let everyone — from visual leads to front-end devs — swap in the corrected component and push an updated prototype to the same guerrilla site a few blocks away.
When the crew is semi-bold enough to park outside a music festival or lift their sketches to a local Starbucks, magic happens. The interacting users' ambient noise and hesitant muscles reveal intent that the rails and personas map might miss.
Observers see the full user soundtrack — finger tracks drawing invisible routes across the map, frowns when GPS toys with the button order. Those subtle clues push the interface's last five pixels into a comfortable place. Designers list the next subtle slide or buttons larger once prototypes loop home, incrementally improving the product at the same velocity users pick up coffee.
Task Analysis
Task analysis is a complex process consisting of several interconnected steps. In this case, task analysis is a method that identifies such tasks by defining each step crucial to effectually completing the multi-step activity.
Error prevention is crucial in task analysis, as addressing potential errors during user testing can significantly enhance the user experience.
With this technique, one can address any alterations or redesigning that can improve the accuracy, effectiveness, and uniformity in the consistency of the task performance, which in return aids in clarifying processes, devising training guides, and planning.
Similar to many methods, this method finds its utility in education, usability design, and workplace improvement in that it is a toolkit for achieving set targets and increasing efficiency. Design teams play a vital role in this process by collaborating to create cohesive and functional user interfaces, ensuring accurate prototyping and maintaining consistency throughout product development.
Essential Takeaways for UI/UX Designers
The success of any digital product hinges on how smoothly users can interact with it. That’s why UI/UX designers are key players in the building team. They need to whip up a design that’s not just pretty but also easy to use and packs the right features — all while playing by industry best practices.
Keeping UI designs fresh and evolving is a must if you want to outpace the competition. A steady look across every screen helps users feel at home, because the buttons, colors, and navigation behave the same wherever they go in the app. With that in view, here’s a list of must-remember tips for every UI/UX designer out there.
Design team efforts shine brightest when they blend art and code. Tools like UXPin Merge enable designers to work hand in hand with developers, creating prototypes that look and run like the real thing. This collaboration locks in design consistency from the first mockup, leading to a smoother user journey and a faster workflow — from the first concept to the final product.
How to Become a UI/UX Designer
To become a UI/UX designer, you must learn the right skills and gain solid knowledge. Start by studying design rules, usability testing, interface code, interaction design, and graphic design. You should also practice solving problems visually. Knowing what users want is key, too, because designs only feel right when they do what users expect and help them succeed.
You can keep your edge by joining workshops or online courses to see what's new. Read up on the practices designers swear by and spend time drafting a winning UX strategy. A focused approach makes your designs shine and ties them to your team or client's goals. That way, everyone on your team is laser-focused, too.
Once you've built your skill set, jump into the job hunt. Apply for agency roles, grab freelance gigs you spot on job boards, or use connections on platforms like LinkedIn. When you land a project, keep lines of communication open. A quick chat or update every few days builds trust and smooths problems before they start. That makes your designs not just projects, but lasting wins.
Also, tackling real client projects is a smart way for future UI/UX designers to build a real-world portfolio. They can launch a personal portfolio site, pitch in on open-source projects, or jump into hackathons to improve their skills.
Source: ConvertKit on Unsplash

A polished portfolio highlighting standout work shows future employers exactly what a designer can accomplish. It assures the designer is ready to take on challenges, making the hiring decision more straightforward.
Becoming a UI/UX designer requires hard work and dedication but offers many exciting opportunities and rewards. With a combination of honed technical skill sets, creative problem-solving abilities, collaborative working methods, and self-initiative projects, one can succeed in this highly sought-after UX/UI design field!
How Much Is a UI/UX Designer's Salary?
UI/UX designers have the opportunity to earn a very competitive salary. According to a recent survey by Glassdoor, the average annual salary in 2023 for a UI/UX designer is $95,000. This number can range significantly depending on experience and skill level, with some earning up to six figures annually.
In addition to a salary, UI/UX designers can earn bonuses and benefits. These may include healthcare plans, flexible working arrangements, additional vacation days, and professional development opportunities. One can succeed in this creative field with the right skill sets, dedication, and creative problem-solving abilities!
Skills for a UX Designer
As a UX designer, you must connect deeply with user experience so that design decisions always serve fundamental human needs. This means digging into the core areas: you’ll research design principles, run usability studies, refine user interfaces, master interaction and visual design, apply graphic design, and tackle complex problems. Spotting and fixing potential errors during testing loops is equally crucial. Catching minor faults ahead of time transforms the final experience for the better.
Following a user-centered workflow is non-negotiable. Gathering data on user goals, needs, and habits, you craft intuitive interfaces. This tailored design keeps people engaged, lowers the chances of them bailing on your product, and boosts long-term value for the business. Research today means less wasted effort tomorrow.
Outstanding UX doesn’t call only for creativity; you will also benefit from key technical skills. A grasp of HTML, CSS, and lightweight JavaScript is helpful, though you’re not expected to code like a developer. More important is solving problems creatively and collaborating effectively with product managers, developers, and other designers.
Well-coordinated design teams use tools like UXPin Merge to build high-fidelity prototypes that feel real. Syncing design elements early speeds up production and guards against inconsistency across screens and devices.
Key UX Designer Skills by Clay
Soft Skills
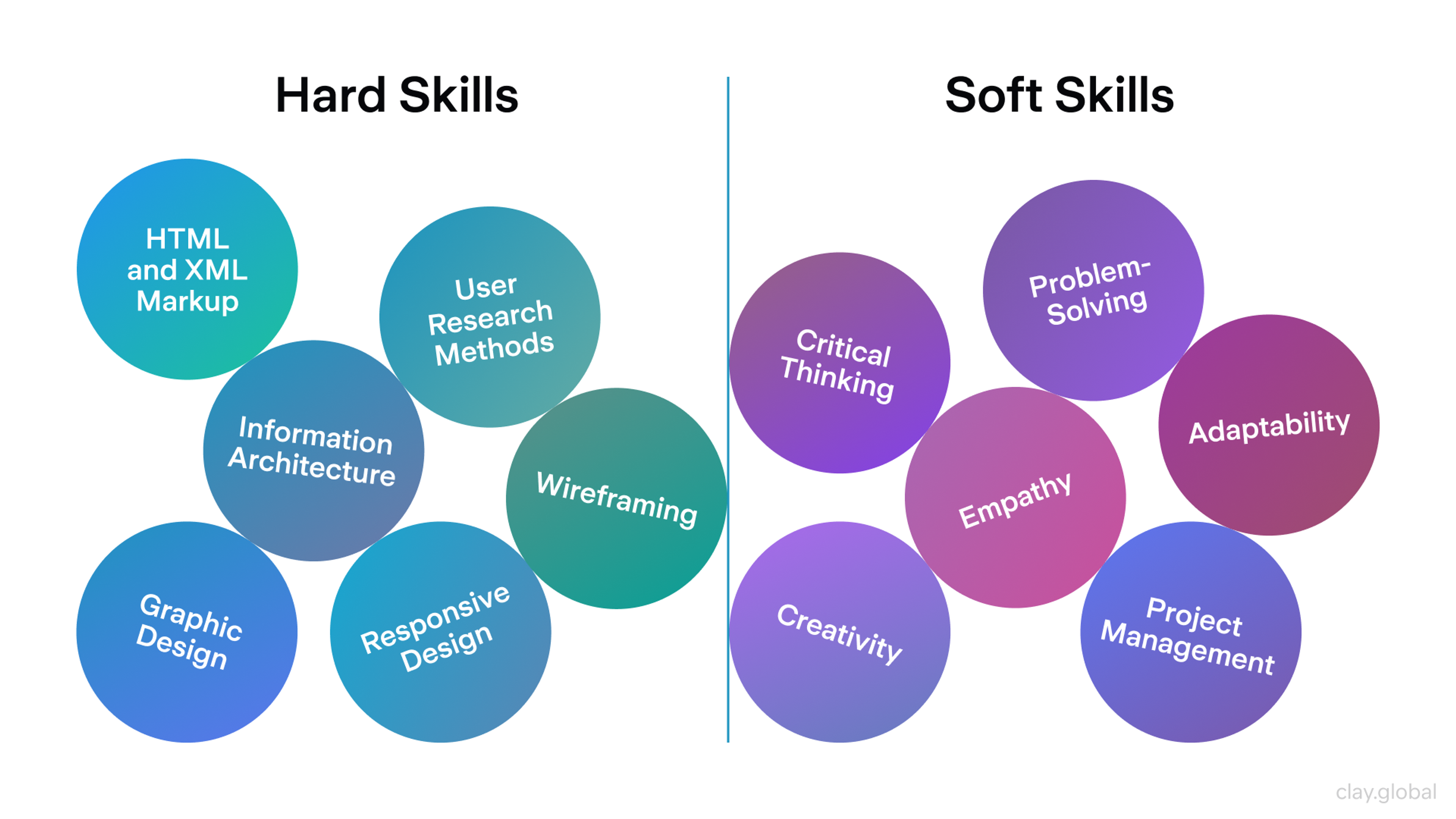
Soft design skills are personal knowledge and skills that take your work as a designer to the next level. For user experience designers, these include:
- Critical thinking
- Problem-solving
- Empathy
- Creativity
- Project management
- Organization
- Collaboration
- Curiosity
- Communication
- Adaptability
- Patience
The first three skills are especially important as they play a critical role in the design thinking process.
Hard Skills
Hard design skills are the knowledge and skills you need to perform your job duties. For user experience designers, these include:
- HTML and XML markup
- CSS
- JavaScript
- UX design principles
- User research methods
- Information architecture
- Wireframing
- Graphic design
- Interaction design
- Prototyping
- Usability testing methods
- Responsive design
- Accessible design
- Ethical design
UX writing and search engine optimization (SEO) aren’t a must, but having these skills can instantly give a designer a leg-up on the competition.
What Is a UI Designer?
A UI designer is a specialist in user interface design. They are responsible for creating the look and feel of user interfaces, from mobile apps to websites. UI designers focus on creating visual elements that make a user experience intuitive, attractive, and easy to use. This includes graphic design components like typography, color palettes, and interactive elements like menus, buttons, sliders, and forms.
What Is an Interaction Designer?
Interaction designers specialize in understanding user behavior and creating intuitive experiences. They are responsible for crafting the interactions between the user and the interface, from button triggers to gestures to text input. Interaction designers use various methods, such as research and usability testing, to understand user needs and preferences. The goal is to create an interface that is visually appealing and easy to use.
Source: Mockitt
What Is a UX Researcher?
UX researchers play an essential role in the user experience design process. They employ various methods like interviews and user testing to gain insight into users’ behaviors, needs, and preferences. This helps them to identify areas where UX design can be improved.
Market research is also crucial in this process, as it helps understand industry trends and competitive landscapes, guiding the design to align with user expectations. UX researchers are also responsible for creating personas – representations of a particular type of user – to ensure the whole user-centered design process is tailored to target users.
What Is a UX Writer?
UX writers are an integral part of the user experience design team. They specialize in creating content that helps to refine further and enhance the user experience. UX writers create all kinds of text, from product descriptions and error messages to onboarding instructions and help articles. They work closely with UX designers to ensure that the written content complements the visual design of the user interface.
Source: Nick Morrison on Unsplash

What Is a Product Designer?
Product designers are responsible for designing the overall product experience. This includes researching user needs, creating user-friendly designs and interfaces, prototyping and testing designs, and collaborating with other teams to ensure the product meets customer requirements.
Product designers must be able to think outside the box and come up with innovative ideas that solve user problems. They must also have a good understanding of product development, software engineering, and marketing.
Key UI/UX Design Tools
Different software and tools can be used throughout the UX design process. There is some overlap between the tools (especially UI design and prototyping software), though not all UX design tools are built to manage the entire lifecycle of a UX design process.
UX Design Tools
Here are suggestions to help you build out your UX toolbox:
- Respondent: Respondent is a user research platform that connects businesses with high-quality participants for surveys, interviews, and usability testing.
- Balsamiq: Create low-fidelity wireframes for websites and apps in a cloud-based platform.
- Axure: Create fully workable prototypes and advanced program interactions (with conditional logic or dynamic content) to make them realistic.
- Maze: Recruit participants at every stage and run tests for card and tree sorting, concept validation, wireframes and prototypes, usability, and more.
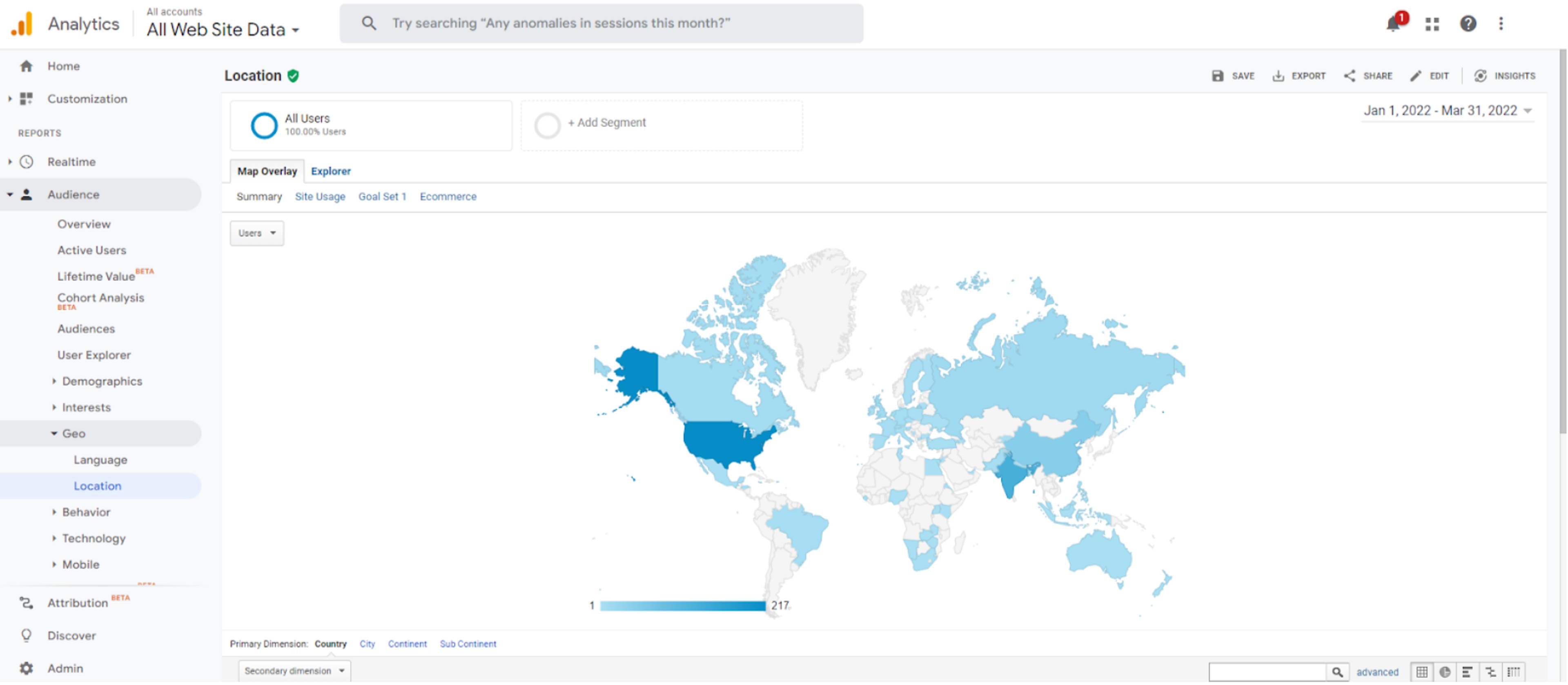
- Google Analytics: Post-launch, monitor and analyze user demographics, behaviors, and conversion rates in the website or app.
Here’s an example of some of the demographic data that researchers might pull from Google Analytics:
Source: Google Analytics
UI Design Tools
For designers with researchers and information architects to handle the earlier stages of a product, separate interface design tools can come in handy. Regardless, professional design software is a must-have for anyone creating digital interfaces.
There are plenty of UI design tools to choose from:
- Adobe Creative Cloud: Adobe’s Creativity & Design product suite enables designers to create custom designs and graphics of all types — photos, videos, illustrations, logos, digital interfaces, and more.
- Figma: A collaborative design platform enabling teams to brainstorm and turn their concepts into mockups and prototypes.
- Sketch: Create everything from mockups to prototypes and even manage design-to-developer handoffs, all within the same UI design tool.
- Storybook: Storybook is an open-source tool for building, testing, and documenting UI components in isolation.
Often, designers can save time upfront by tapping into the wealth of templates available or building them from scratch with their wireframes as the base. Like this example from Figma:
Source: Figma
Best UX Books to Read
UX books provide invaluable advice to aspiring UX designers and professionals alike. They provide theoretical instruction and practical tips, tricks, and real-life case studies about the user experience design process.
We collected some of the best UX books to read in 2026:
- Universal Principles of Design
- The Design of Everyday Things
- Sprint: How to Solve Big Problems and Test New Ideas in Just Five Days
- Smashing UX Design
- Lean UX
- Quantifying the User Experience
- Strategic Writing for UX
- The Elements of User Experience
Source: Thought Catalog on Unsplash

Wrapping Up
UX design is a complex process that involves understanding user needs, creating designs and interfaces with the right tools, prototyping and testing those designs, collaborating across teams to ensure customer satisfaction, and more.
With the right UX design tools and resources, such as books on UX Design or templates available online, you can make this journey much easier than it would be otherwise. Whatever your level of experience in UX design, these tips should help you start moving forward!
Read More
Frequently Asked Questions About UI/UX Design
What Are The Five Elements of UX Design?
The five elements of UX design refer to the five vital components that must be considered when designing a product or service. These elements are:
- Strategy
- Scope
- Structure
- Skeleton
- Surface
All these five elements must work together seamlessly to create an enjoyable user experience that meets user needs while also reaching business goals - something only experienced UX designers can achieve precisely!
What Are the Laws of UX?
The laws of UX design are principles design professionals use to create user-friendly, intuitive experiences. The laws are based on human-computer interaction and usability studies research and include elements such as design consistency, visibility, and feedback.
There are 20+ UX laws. Here are some of them:
- Miller’s Law
- Parkinson’s Law
- Jakob’s Law
- Hick’s Law
What Are the Common Myths About UX?
One of the common myths about UX is that it is just a boom and will soon be forgotten. This misconception could not be further from the truth, as UX design has existed since the early days of computing and is still relevant today.
While many people assume that UX is only about innovation, this is untrue, as UX design is about understanding user needs and creating intuitive experiences that meet those needs.
What Are the Latest UX Design Trends in 2026?
Inclusive design, AI-assisted UX, immersive onboarding, and data-driven personalization top the list of 2026 UX trends.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more