What Is UX Research?
User experience research helps you understand how real people use your product. Jakob Nielsen, a leading UX expert, defines it as "the systematic study of target users to collect and analyze data that will help inform the design process."
UX research gathers facts about user behavior. It shows you what works and what doesn't. This data helps teams make better design choices instead of guessing what users want.
Good UX research combines different methods. You might watch users navigate your website, ask them questions in interviews, or test two different designs. Each method reveals something different about the user experience.
Importance of UX Research
Conducting UX research is a vital part of the product design and development process. It gives you valuable insights into how users actually interact with your product — what works, what doesn’t, and where improvements can be made. Teams that apply design research methodologies are better able to translate this data into practical design solutions.
This research helps shape the entire user experience, guiding decisions that make the product more useful, enjoyable, and engaging. It reveals opportunities to refine features, streamline interactions, and create something people genuinely want to use.
UX Research Methods by Clay
Ever used an app or website that felt so smooth that you didn’t have to think twice? Everything just worked, and you barely noticed how seamless the experience was? That’s not by accident - it’s the result of great UX research.
UX research is all about understanding real people - how they think, what they need, and what frustrates them. It’s what separates a product people tolerate from one they love.
Why does UX research matter?
- It makes products easier to use. If something feels confusing or clunky, people won’t stick around. Research helps remove friction so users enjoy the experience.
- It helps businesses focus on what really matters. Instead of guessing, companies can rely on real feedback to make the right improvements. This is how great teams utilize user research methods to enhance strategy.
- It keeps companies ahead of the competition. Trends change fast. Studying what users want (and what competitors are doing) helps businesses stay relevant.
- It gives users a voice. Interviews, surveys, and testing let companies hear directly from the people who matter most - actual users. This practice extends user research methods into continuous engagement.
- It leads to smarter decisions. Tools like Hotjar and Google Analytics show how people interact with a product, revealing where tweaks can make the biggest impact.
At its core, UX research isn’t just about making a product look good - it’s about making it feel right. The best products aren’t just functional. They connect with users on a deeper level. And when companies listen, adapt, and improve based on real user feedback, everyone wins.
Want to build something people actually enjoy using? Start with UX research.
UX Research Flow by Clay
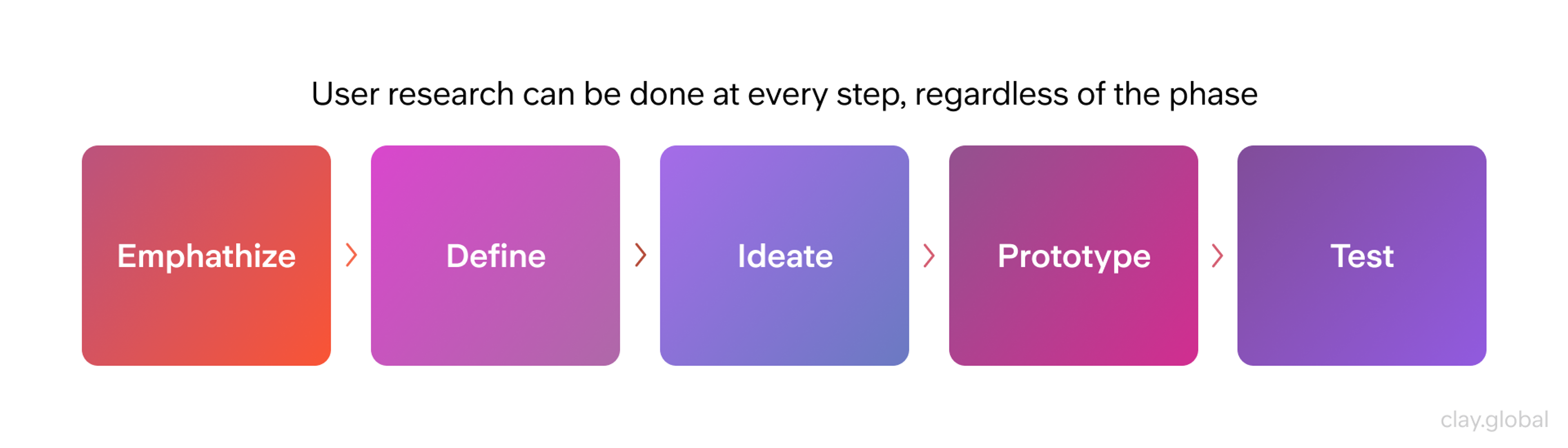
UX Research’s Role In Helping Businesses
The improvements driven by UX research offer real, measurable benefits for businesses. When a product becomes easier and more enjoyable to use, it naturally attracts more attention — leading to higher sign-up rates, more conversions, and increased sales.
Customer satisfaction also gets a major boost. Happy users are more likely to leave positive reviews, recommend your product to others, and drive up your Net Promoter Score (NPS). Satisfied customers often turn into loyal ones, returning again and again — which means more predictable revenue over time.
NPS Example by Clay
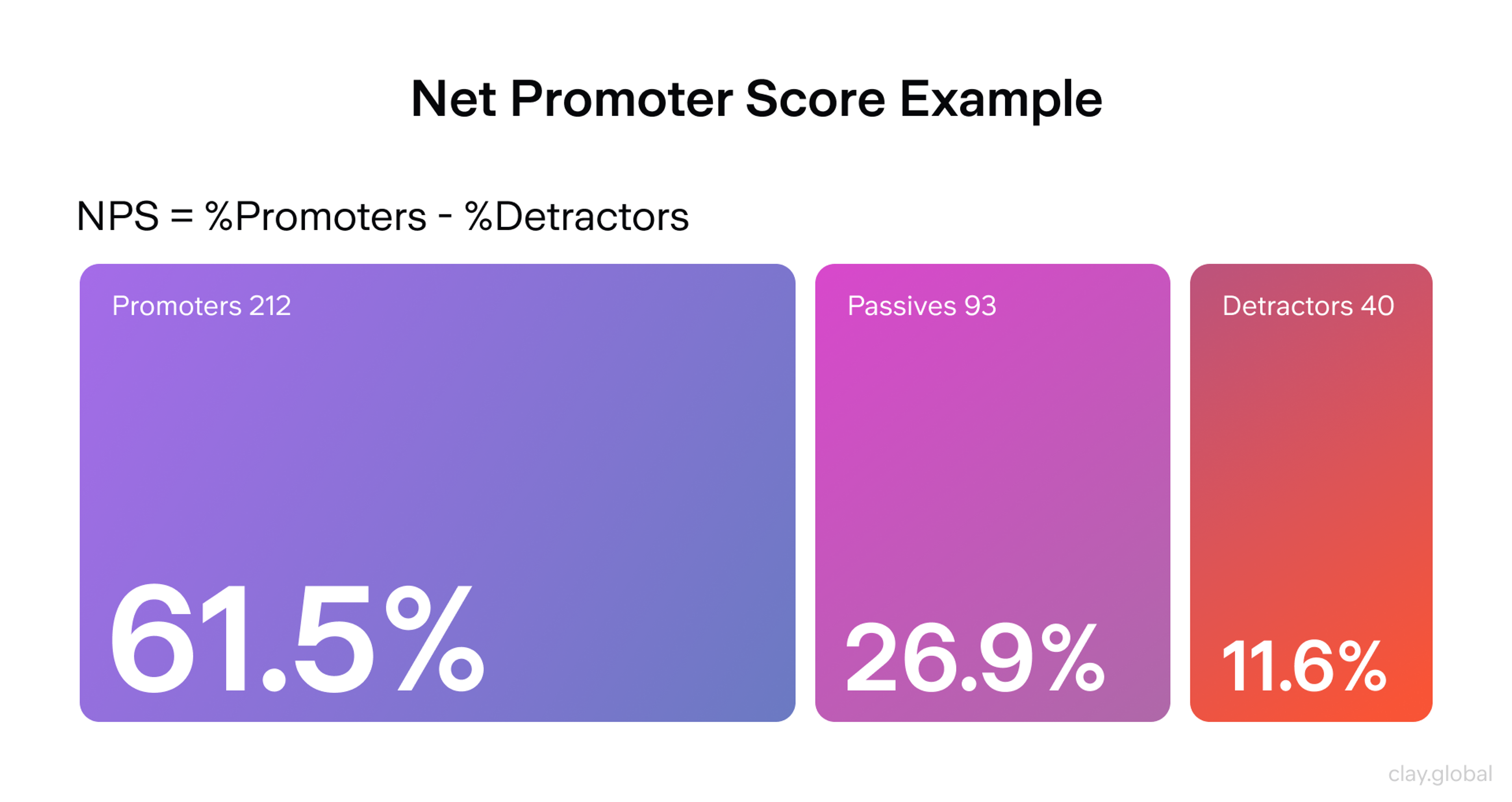
On the cost side, better usability means fewer people running into problems. That translates to fewer support requests and a lighter load on your customer service team, reducing operational costs.
In short, UX research enhances the experience and makes smart business sense. When integrated into the design and development process, it helps companies save time and money while also building a deeper understanding of their users. It uncovers what people are trying to achieve, how they think, and where they’re getting stuck — insights that are essential for creating products people truly love.
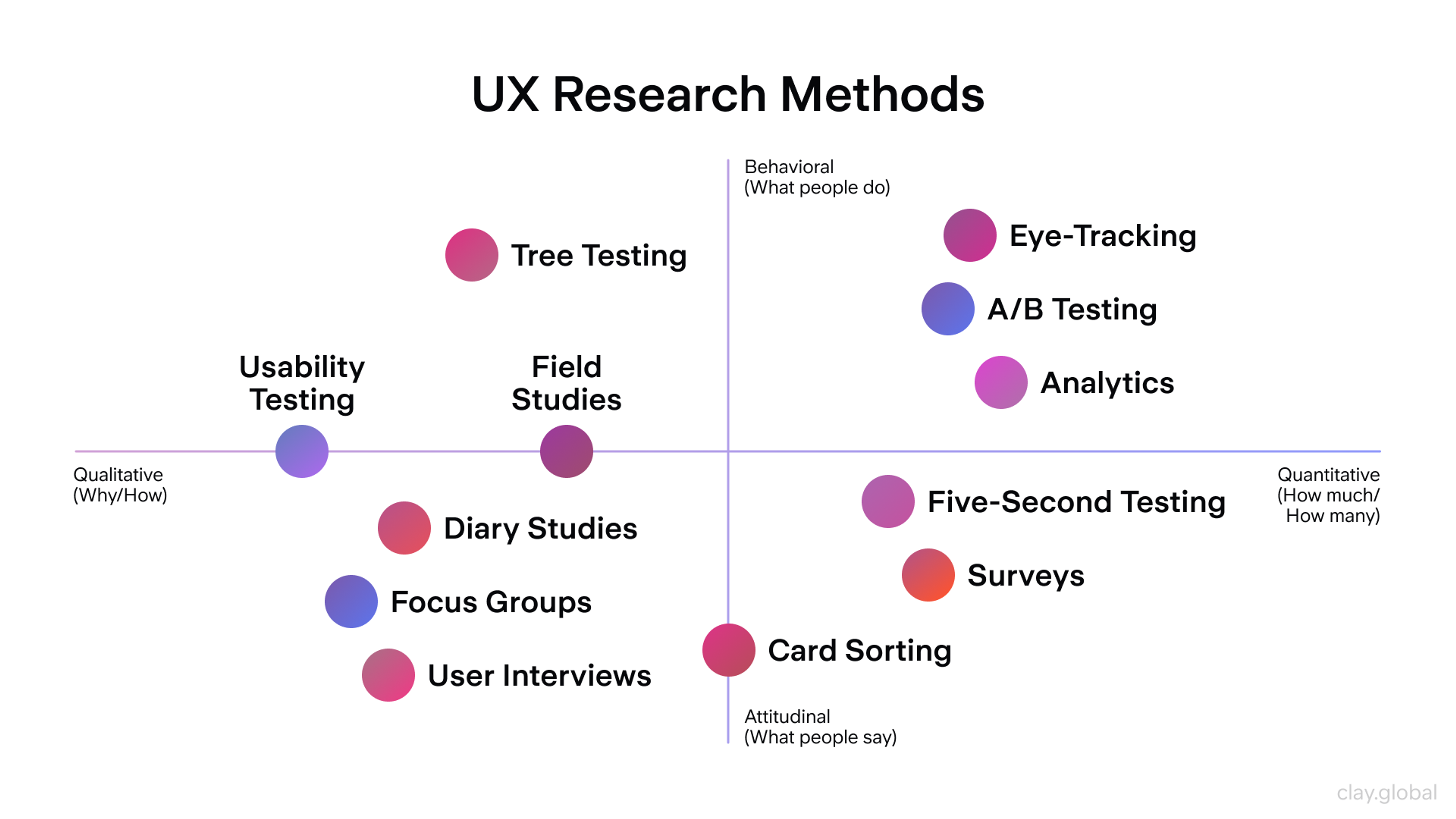
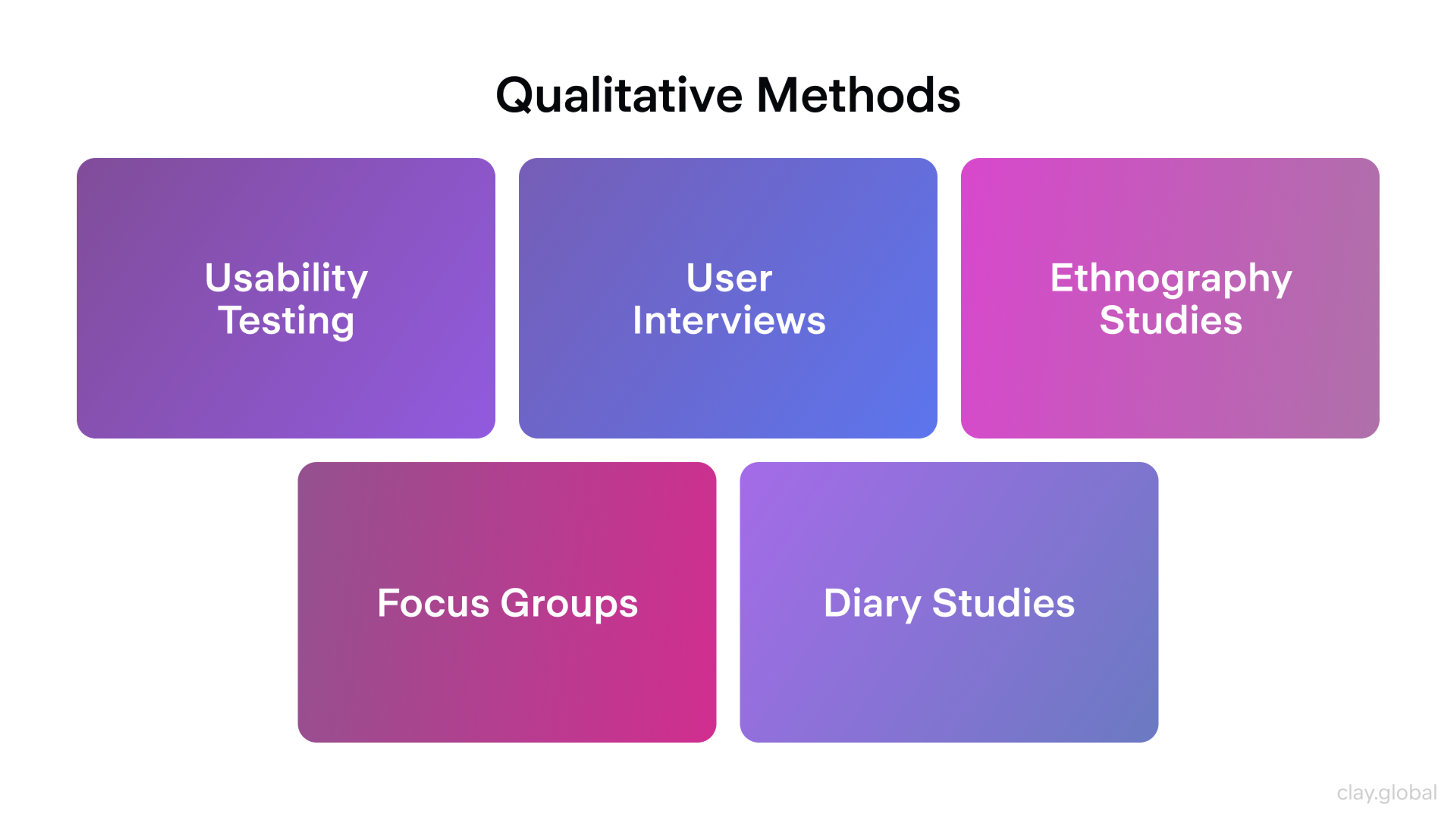
Types of UX Research Methods
Research methods fall into two main categories. Qualitative methods help you understand why users behave in certain ways. Quantitative methods show you what happens and how often.
Qualitative Research digs into user motivations and feelings. Methods include interviews, diary studies, and ethnography. These approaches reveal the story behind user behavior.
Quantitative Research provides measurable data. Surveys, A/B testing, and analytics show patterns across many users. Numbers help you prioritize which problems to solve first.
Smart teams use both types together. Qualitative research explains user problems, and quantitative data proves how widespread those problems are.
UX Research Methods by Clay
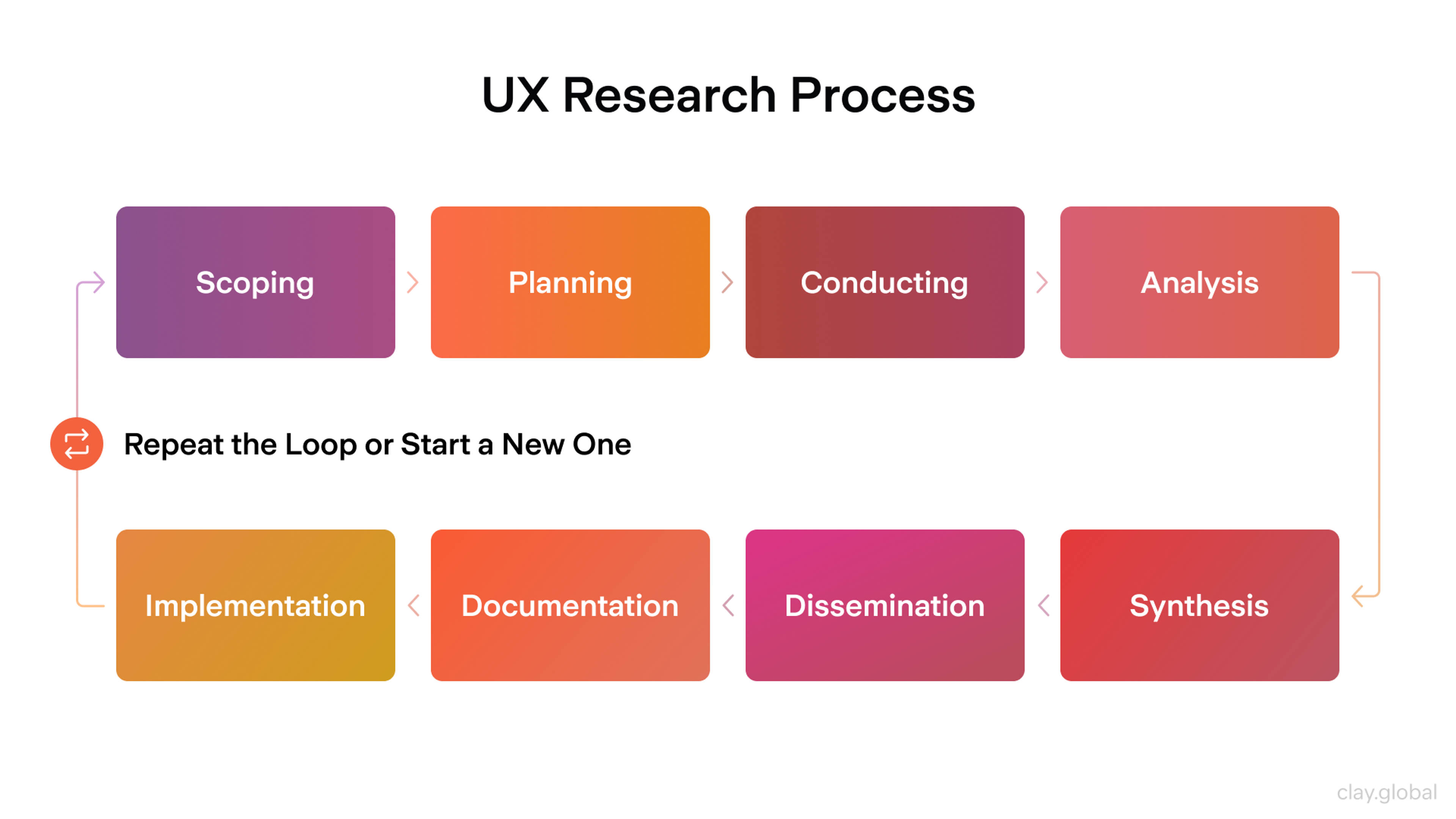
Qualitative UX Research Methods
Understanding opinions, motivations, and experiences — or in other terms, why users behave in particular ways — is at the heart of qualitative UX research methodology.
When a company better understands user behaviors, it can develop more finely tuned solutions for issues the users are not fully satisfied with. Such user research methods include conducting user interviews, studying diaries, exploring ethnography, and utilizing focus groups.
Qualitative UX Research Methods by Clay
User Interviews
When it comes to understanding user attitudes, experiences, and behaviors, there’s no better source than the users themselves. That’s why user interviews are one of the most powerful tools in qualitative UX research.
User interviews give you direct access to users' thoughts and feelings. This method works best when you want to understand users' motivations.
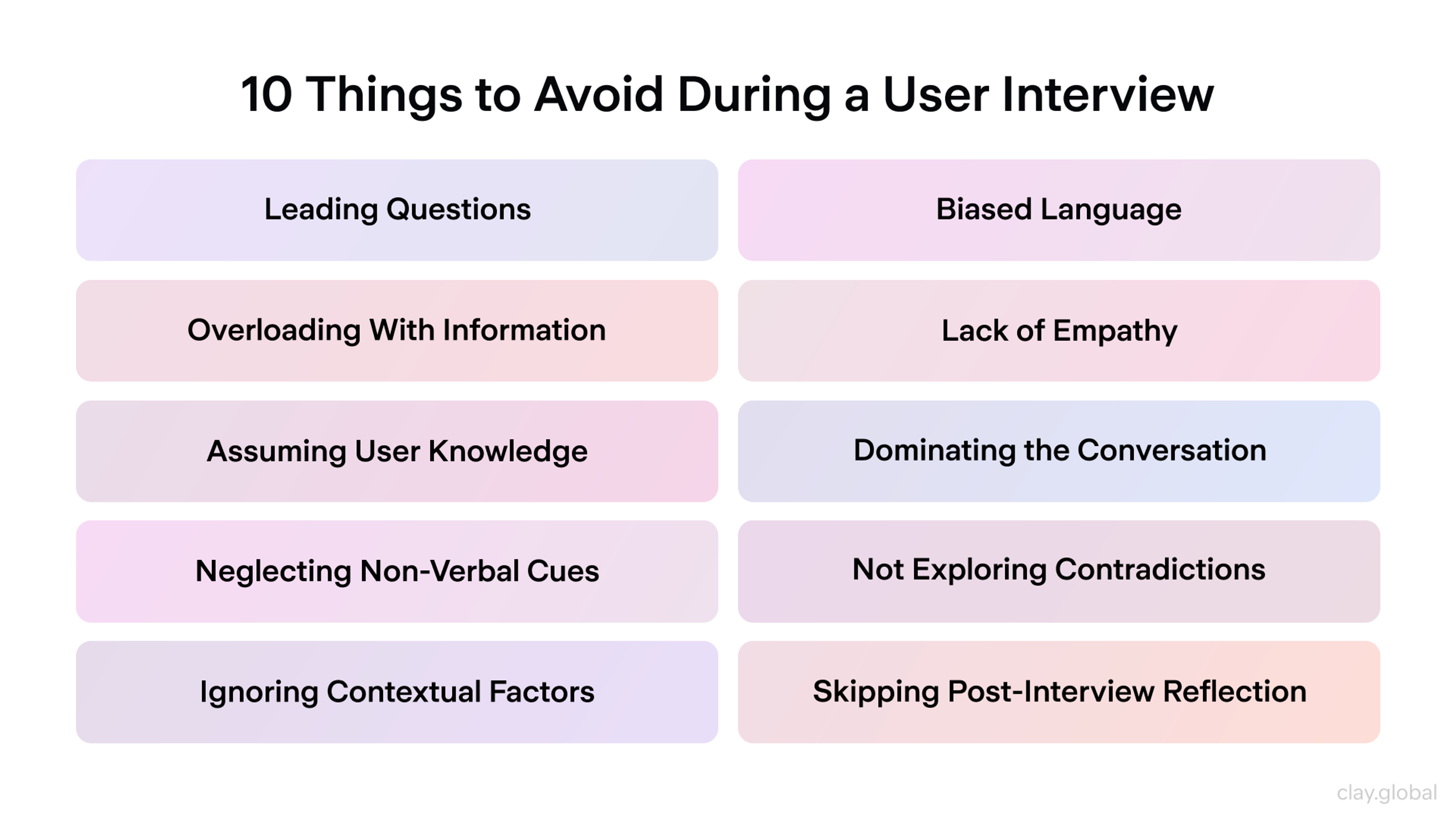
How to conduct effective interviews:
- Ask open-ended questions like "Tell me about the last time you..."
- Listen more than you talk
- Ask follow-up questions when users mention pain points
- Focus on specific examples rather than general opinions
Erika Hall, author of "Just Enough Research," emphasizes asking about actual behavior instead of hypothetical situations. Users often can't predict what they would do, but they can describe what they actually did.
For most research questions, plan 5-8 interviews. This usually reveals the main patterns without overwhelming your schedule.
What to Avoid During a User Interview by Clay
Diary Studies
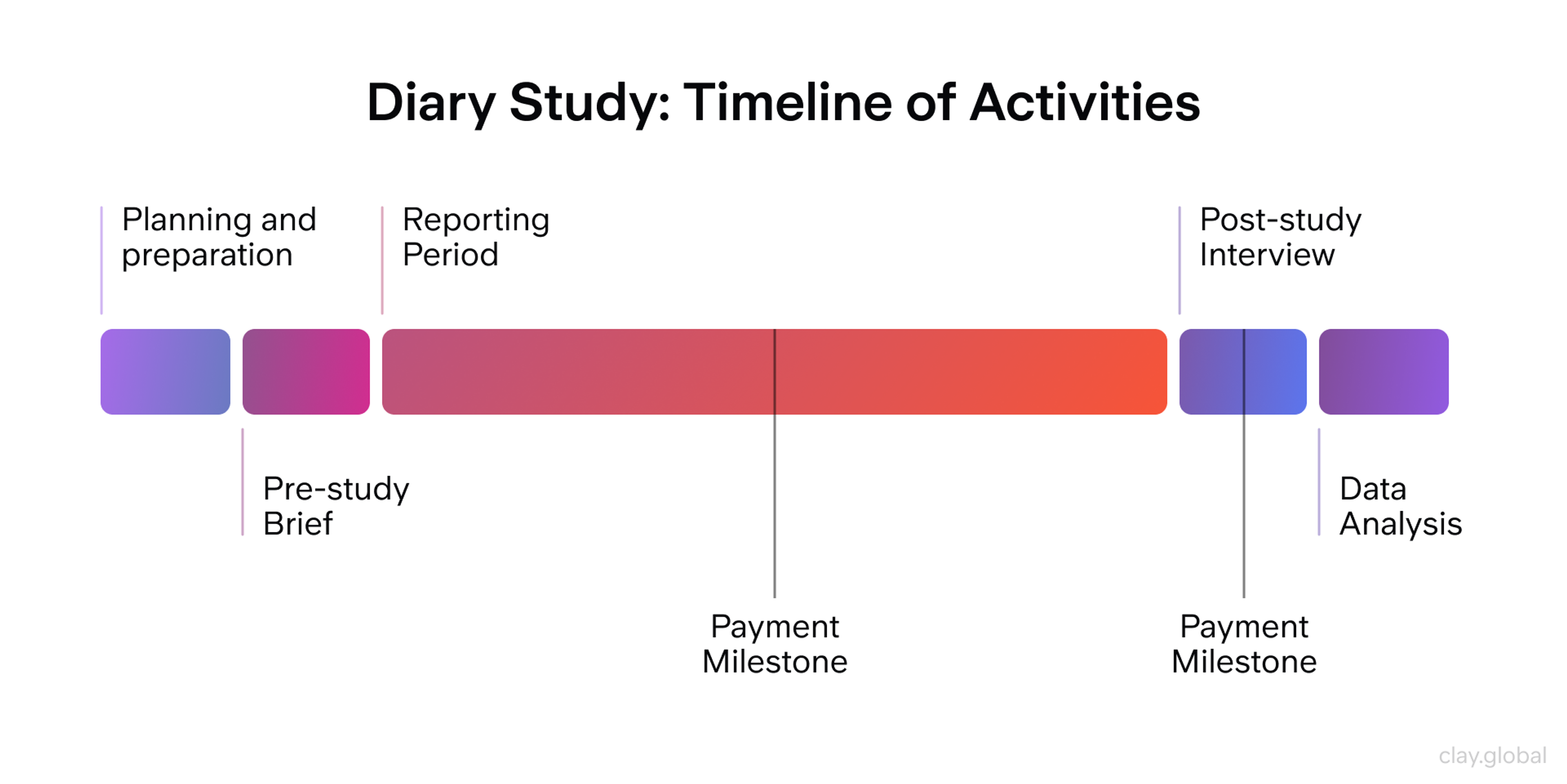
Diary studies track user behavior over time. Participants record their experiences with your product for days or weeks. This method reveals long-term usage patterns that single sessions miss.
When diary studies work best:
- Understanding how usage changes over time
- Studying products used irregularly
- Capturing real-world context and interruptions
The Experience Sampling Method (ESM) can combine diary entries with quick surveys. Users get prompts to record their current experience, creating a detailed picture of product interaction.
Diary Study Timeline by Clay
In our collaboration with Slack, we conducted comprehensive UX research, including ethnographic studies, to deeply understand user behaviors and needs. Through UX research, we brought together three very different audiences.
By observing how users interact with Slack in their real environments, we gathered valuable insights into unmet needs and existing challenges. This information was crucial in refining Slack's design, ensuring it effectively addressed user pain points. The research emphasized understanding user motivations, which informed decisions throughout the design process, resulting in a more user-centered product.
Slack Demo by Clay
Ethnographic Research
Ethnography means observing users in their natural environment. You watch how they actually use products during normal activities.
Key benefits:
- Reveals workarounds users create
- Shows environmental factors affecting product use
- Uncovers needs users might not articulate in interviews
Modern ethnographic studies use digital tools alongside traditional observation. Mobile apps and wearables can track behavior automatically, providing more accurate data than user self-reports.
Where Ethrographic Research Stands by Clay
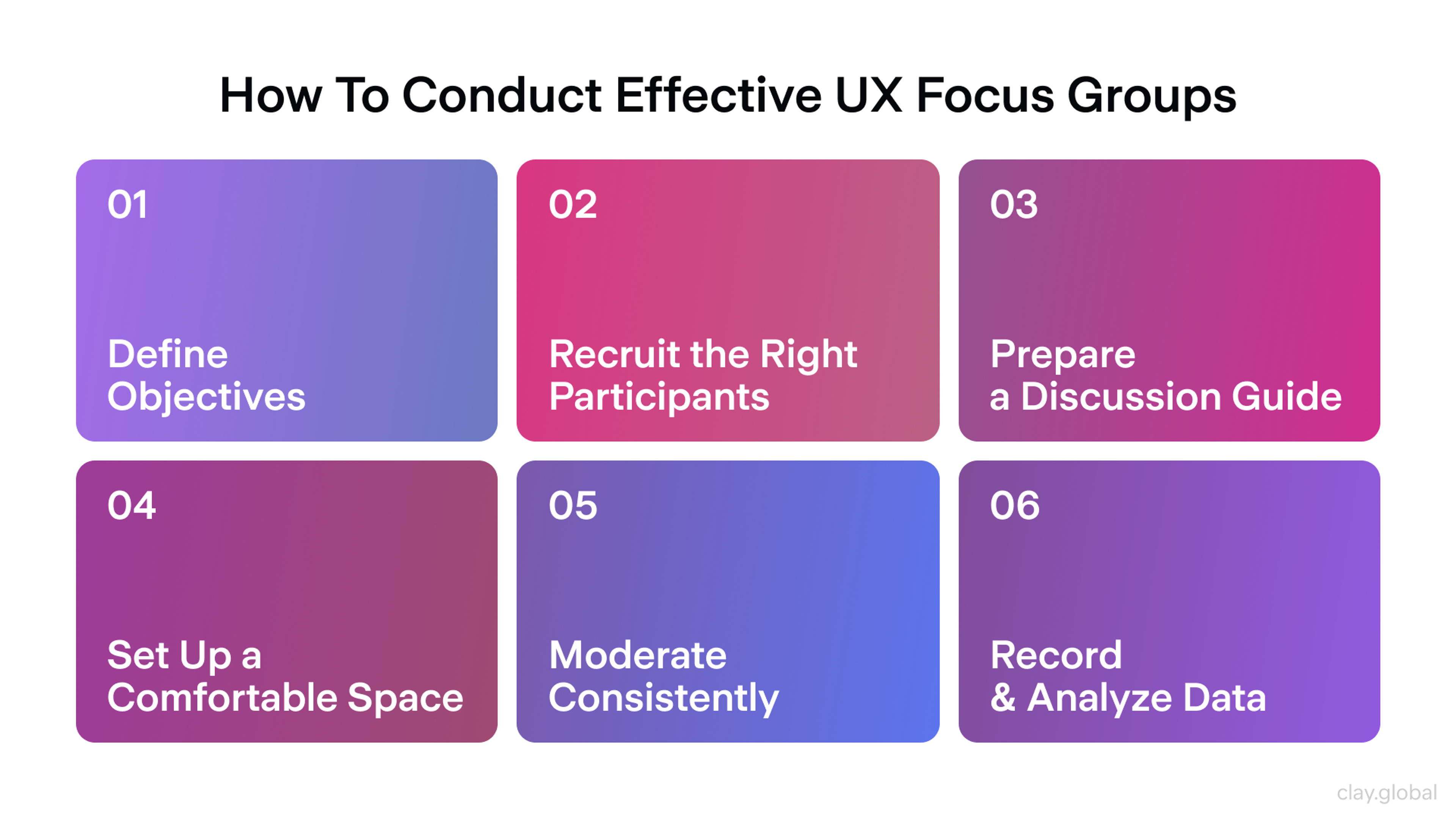
Focus Groups
Focus groups bring 6-8 users together to discuss your product. A skilled moderator guides the conversation while observing group dynamics.
Focus groups excel at:
- Understanding different user perspectives on the same issue
- Generating ideas for new features or improvements
- Revealing how users influence each other's opinions
The key is finding an experienced moderator who keeps discussions focused while encouraging all participants to share their views.
How to Conduct an Effective UX Focus Group by Clay
Quantitative UX Research Methods
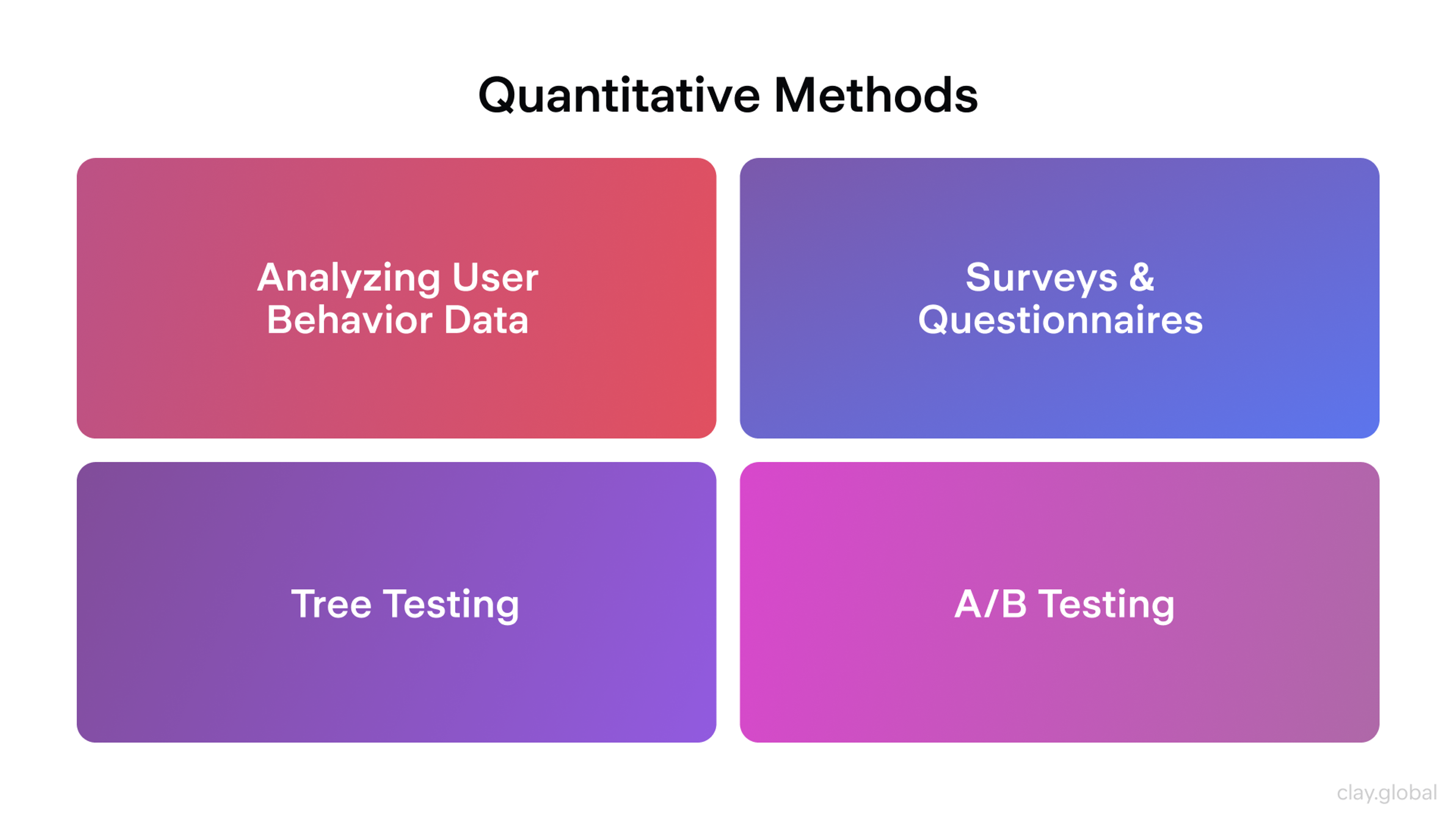
While qualitative data offers a lot of intangibles, quantitative user research methods are necessary to put hard numbers on various research points, allowing for a more thorough analysis of user preferences and behavior trends.
Quantitative research entails the collection of data sourced from usage logs, surveys, questionnaires, usability tests, and various other means over a lengthy period. This data is then sorted and analyzed to yield ways to optimize product design.
Quantitative UX Research Methods by Clay
Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys collect structured feedback from many users quickly. They work best for understanding user preferences and measuring satisfaction across your user base.
Survey best practices:
- Keep surveys under 10 minutes to maintain engagement
- Use clear, simple language
- Test questions with a small group before launching
- Mix question types (multiple choice, rating scales, open-ended)
Web-based surveys cost less than paper versions and make data analysis easier. Tools like Typeform and UserVoice create engaging survey experiences.
How to Conduct a UX Survey by Clay

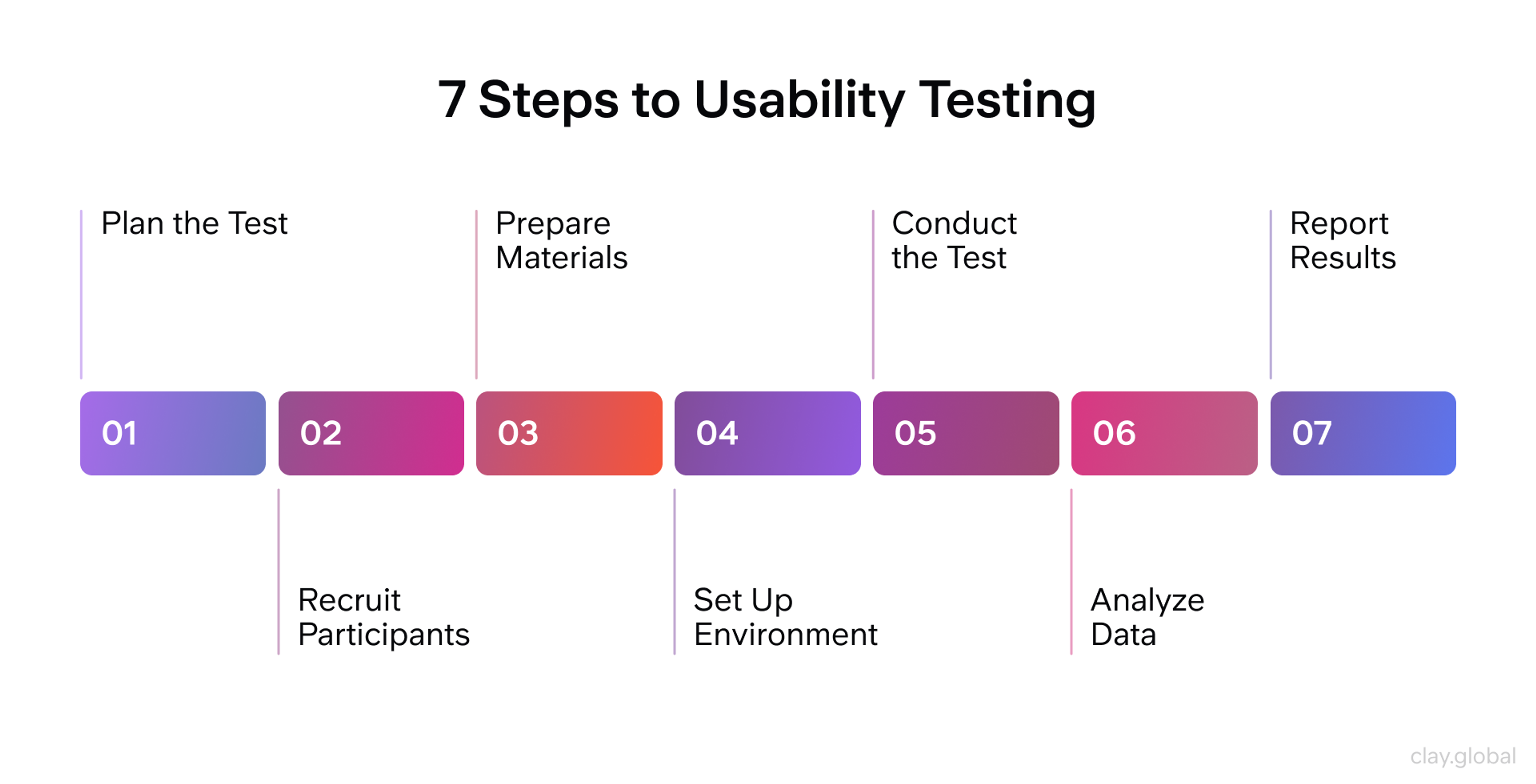
Usability Testing
Usability testing reveals how easy your product is to use. You watch users complete real tasks while noting where they struggle.
Common usability testing discoveries:
- Confusing navigation structures
- Unclear button labels
- Missing feedback when users complete actions
- Performance issues that frustrate users
Nielsen's research shows that five users find about 85% of usability problems. Testing with more users helps you prioritize which issues affect the most people.
Tools like UserTesting.com and Lookback make remote usability testing simple. Users record their screens while thinking aloud as they complete tasks.
Core Steps of Usability Testing by Clay
A/B Testing Method
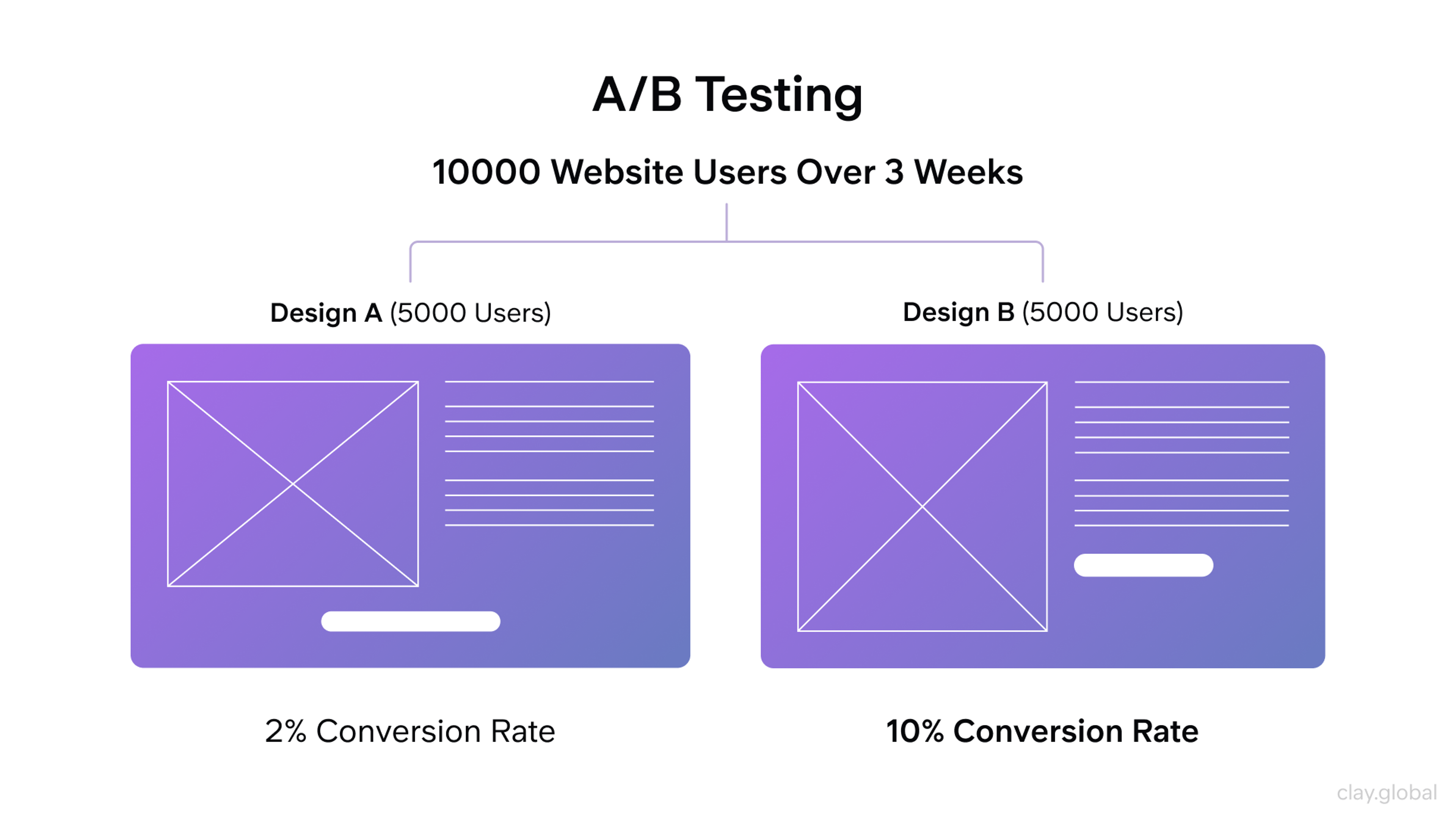
A/B testing compares two versions of your product with real users. Half your users see version A, half see version B. You measure which version performs better.
A/B testing works well for:
- Testing design changes like button colors or layouts
- Comparing different feature implementations
- Measuring the impact of copy changes
Set clear success metrics before starting any A/B test. Common metrics include conversion rates, task completion time, and error rates.
A/B Testing Example by Clay
Evaluative Research Methods
Evaluative research methods are essential for assessing the usability and effectiveness of existing designs or prototypes. These methods help designers and researchers identify areas for improvement and validate design decisions, ensuring that the final product meets user needs and expectations.
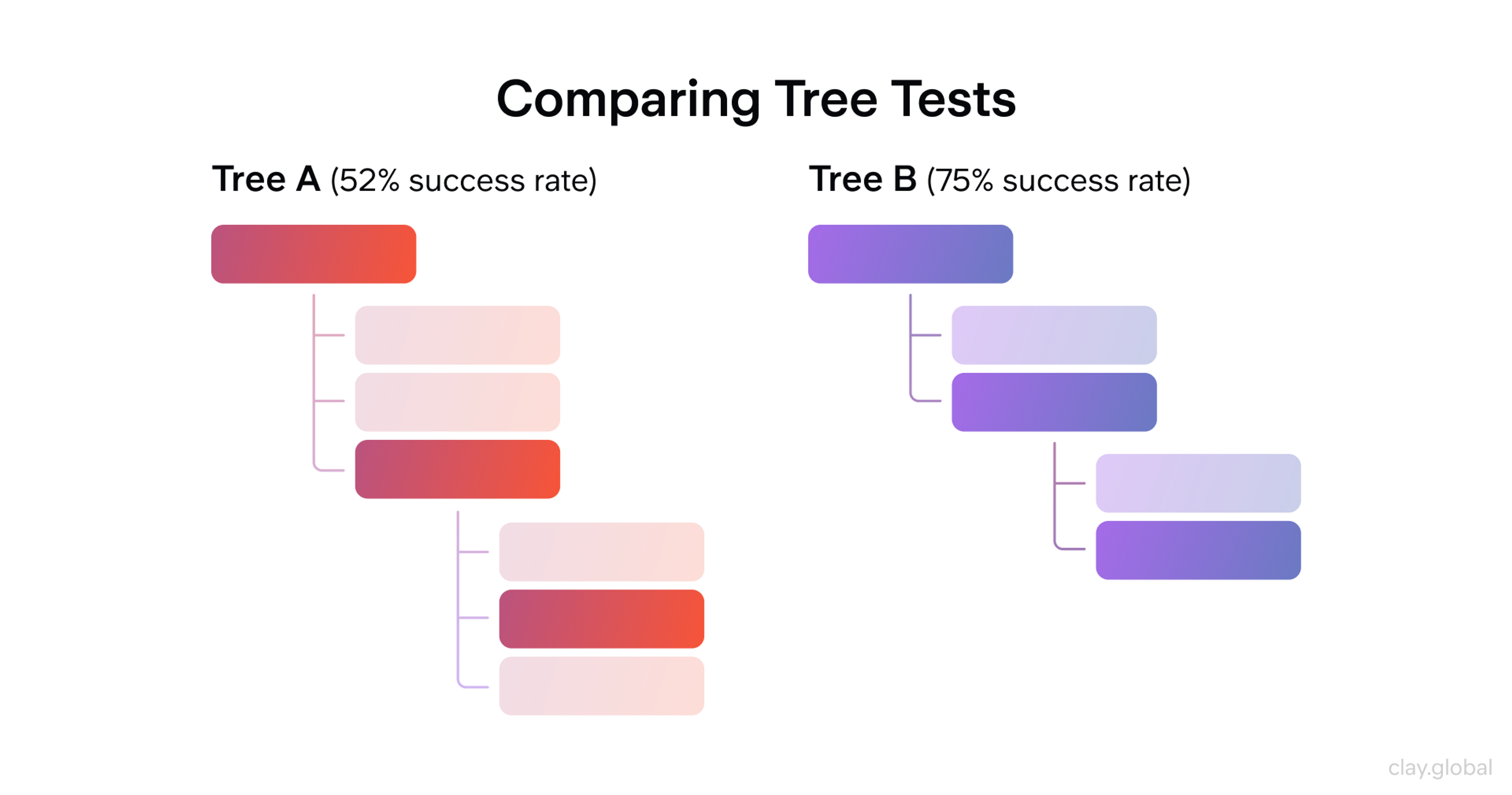
Tree Testing
Tree testing evaluates your information architecture. Users navigate a simplified site structure to find specific items. This method reveals navigation problems before you build the full interface.
Tree testing benefits:
- Tests navigation without visual design distractions
- Identifies confusing category names
- Shows where users expect to find different types of content
Tree Testing Example by Clay
Prototype Testing
Prototype testing gathers feedback on early designs. You can test anything from paper sketches to interactive prototypes.
Prototype testing stages:
- Low-fidelity wireframes test basic concepts and flow
- High-fidelity prototypes test detailed interactions
- Working prototypes test performance and real data
Testing prototypes saves time and money compared to changing finished products.
What Is Prototype Testing? by Clay
Choosing the Right UX Research Method
Choosing the right UX research method is critical to gathering valuable insights that inform design decisions. The selection process depends on the research goals, objectives, and available resources. Here are some key factors to consider when selecting a UX research method:
User Experience Research Methodology
Research methodology refers to the systematic approach used to collect and analyze data. There are two main types of UX methodologies: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative research methods involve collecting and analyzing non-numerical data, such as text, images, and videos, to understand user behaviors and motivations. Quantitative research methods, on the other hand, involve collecting and analyzing numerical data, such as statistics and metrics, to identify patterns and trends.
When choosing a UX research method, consider the following factors:
- Research goals and objectives: Clearly define what you want to learn from the research. Are you looking to understand user behavior, evaluate a user interface, or test a prototype?
- Resources: Assess the available resources, including time, budget, and personnel. Some research methods may require more extensive resources than others.
- User behavior: Determine which aspects of user behavior you want to study. Are you interested in understanding how users interact with a product or their attitudes toward it?
- User interface: Identify which aspects of the user interface you want to evaluate. Are you focusing on navigation, layout, or specific features?
- Natural environment: Decide whether you want to study users in their natural environment or in a controlled setting. Observing users in their natural environment can provide more authentic insights.
- Focus groups: Consider whether you want to gather feedback from a group of users or individual users. Focus groups can provide diverse perspectives, while individual interviews can offer more in-depth insights.
- Behavioral data: Determine if you want to collect data on user behavior or attitudes. Behavioral data can reveal how users interact with a product, while attitudinal data can provide insights into their perceptions and feelings.
- User testing: Decide if you want to test a prototype or a working model of a product or service. User testing can help identify usability issues and validate design decisions.
- Remote usability testing: Consider whether you want to conduct usability testing remotely or in-person. Remote usability testing can be more convenient and cost-effective, while in-person testing can provide more detailed observations.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the right UX research method for your project, ensuring that you gather valuable insights to inform your design decisions and create user-centered products and services.
Behavior Data Analysis
The most effective aspect of UX research is its ability to dive into the user experience and collect important insights about it through the data collected. It allows researchers to better understand users’ needs, behaviors, motivations, and preferences with products and services.
Once the user-product interaction data is analyzed, patterns and trends emerge, allowing researchers to understand which features are easier to understand, which navigation can be refined, how much time a user spends on a particular aspect of utilizing the product, and other actionable insights that drive a more optimized design and development process for the product.
However, data collection alone is of little use unless it can be visualized in a meaningful way and queried for particularly interesting aspects. For digital products, this can be done through analytics tools like Google Analytics or via A/B testing. After the data is collected and visually rendered, it needs to be used to detect trends of behavior patterns.
Let’s consider the example of a website with a page or feature with low engagement. Through UX research, it might be noted that this page will be reached when users navigate to it after a particular action, but the navigational paths to reach it are not easily available or are seldom used.
A deeper dive into the usage trends collected through an extended usage period can illuminate how a product or service is used in the daily lives of those interacting with it. UX researchers are able to collect valuable insights into user behaviors, which will then increase their knowledge about which parts of the process need improvements.
Traditional methods of observation do not yield the types of results that researchers need to dive deeply enough into the product, but they are certainly not without merit. The ultimate goal of UX research is to detect problematic features or aspects and then optimize them, increasing the satisfaction of user experiences.
UX Research Best Practices
Here are some best practices for conducting effective UX research:
1.
Define clear research objectives: before starting any research, clearly define your goals and what you hope to learn. This will guide your research methods and ensure that you gather relevant insights.2.
Use a mix of qualitative and quantitative methods: combine methods such as user interviews, surveys, usability testing, and analytics to gather both in-depth insights and broad trends.3.
Recruit representative participants: ensure that your research participants are representative of your target audience in terms of demographics, behaviors, and needs. This will help you gather accurate and relevant insights.4.
Conduct research in context: whenever possible, observe and interview users in their natural environment to understand how they interact with your product or service in real-world situations.5.
Ask open-ended questions: when interviewing users, ask open-ended questions that encourage them to share their thoughts and experiences in their own words. Avoid leading questions that may bias their responses.6.
Analyze data systematically: use a structured approach to analyze research data, such as affinity mapping or thematic analysis, to identify patterns and insights across multiple participants.7.
Collaborate with cross-functional teams: involve stakeholders from different departments, such as design, product management, and engineering, in the research process to ensure that insights are shared and acted upon.8.
Iterate and test: use research insights to inform design decisions and create prototypes or mockups. Then, test these solutions with users to validate assumptions and refine the design.9.
Communicate findings effectively: share research findings with stakeholders in a clear and compelling way, using visuals and storytelling techniques to highlight key insights and recommendations.10.
Continuously monitor and adapt: UX research is an ongoing process. Continuously gather user feedback and monitor product usage to identify areas for improvement and adapt your research approach as needed.
By following these best practices, companies can conduct effective UX research that leads to the creation of user-centered products and services that drive business success.
Common UX Research Challenges
Common User Research Challenges by Clay
Finding the right participants can be difficult. Use recruiting services or customer databases to reach your target audience.
Time and budget constraints limit research scope. Start with quick, low-cost methods like surveys or guerrilla testing.
Getting stakeholder buy-in requires showing business value. Share concrete examples of how research findings improved key metrics.
Analyzing large amounts of data overwhelms small teams. Focus on the most important research questions and use collaboration tools to share the workload.
Real-World User Research Examples in Action
User research is at the heart of great digital experiences. It helps us understand what users truly need, where they struggle, and how we can make products that feel effortless to use. Here are some real-world examples of how we’ve used UX research to create better digital products:
1. Joe & The Juice: Making Ordering & Rewards Seamless
Joe & The Juice, a global chain of juice bars and coffee shops, wanted to improve their digital experience. Through deep user research, we found that customers craved a smoother ordering process and a more engaging loyalty program.
So, we designed an app that made it easy to order on the go while rewarding loyal customers with personalized perks — creating a digital experience as refreshing as their juices.
2. JOKR: Bringing Instant Grocery Delivery to Life
JOKR, an on-demand grocery delivery startup, needed a frictionless mobile app. After speaking with users, we uncovered a clear priority: speed and convenience.
People didn’t just want groceries fast — they wanted a seamless, intuitive way to order. We designed an app that allowed users to find what they needed in seconds, checkout effortlessly, and get their groceries delivered almost instantly.
JOKR Design by Clay
3. Lulo Bank: Reinventing Digital Banking in Colombia
As Colombia’s first digital-only bank, Lulo Bank needed to build trust with users who were new to online banking. Our research revealed that security concerns and accessibility were major barriers.
So, we crafted a mobile experience that felt secure yet simple, making digital banking approachable for everyone. The result? A banking app that users could trust — and actually enjoy using.
4. Nuant: Simplifying Crypto Asset Management
Managing crypto investments can be overwhelming, with complex dashboards and unclear data. When working with Nuant, a crypto asset intelligence platform, we dug deep into how users interacted with their portfolios.
Through UX research, we discovered that they needed clearer visualizations and a more intuitive interface. By simplifying the design, we helped users track and manage their assets with confidence.
Nuant Design by Clay
5. Corsair: Creating a Unified Experience for Gamers
Corsair, a leader in gaming gear, faced a challenge: its digital presence felt inconsistent across different platforms. Our user research revealed that gamers wanted a more seamless and cohesive experience when interacting with Corsair’s products online.
So, we built a unified design system that made navigation easier and reinforced the brand’s identity in a way that resonated with the gaming community.
Measuring UX Research Success
Track these metrics to show research impact:
- Conversion rate improvements from design changes
- Task completion time reductions
- Error rate decreases
- Customer satisfaction increases through Net Promoter Score surveys
- Support ticket volume reductions
Companies using Customer Journey Mapping and Service Design see these metrics improve over time as they better understand user needs.
The Future of UX Research
Jobs-to-be-Done framework and AI-powered research tools are changing how teams understand users. Remote research capabilities expanded during recent years, making user feedback more accessible.
The most successful teams combine traditional research methods with new technologies, always keeping user needs at the center of their decisions.
FAQ
What Are Heuristics in UX?
Heuristics are broad usability guidelines used to evaluate a product’s design. They help identify potential user experience issues by comparing an interface against recognized best practices, such as clarity, consistency, and feedback.
What Is a Primary UX Research Method?
A primary UX research method is a way of gathering first-hand information from users. Examples include interviews, usability testing, surveys, and observation sessions.
How to Decide Which UX Research Method to Use?
Choose a method based on your project goals, the type of data you need (qualitative or quantitative), your timeline, and available resources. Early-stage projects often use exploratory methods like interviews, while later stages may rely on usability testing or analytics.
What Are the 4 Stages of UX Research?
The four stages are:
1.
Discovery – Define the problem and understand the user.2.
Exploration – Generate ideas and concepts.3.
Testing – Validate solutions with user feedback.4.
Implementation – Apply insights to the final product.
Read More
Final Thoughts
UX research transforms guesswork into knowledge. It shows you what users actually need rather than what you think they need.
The best research combines multiple methods and involves your entire team. When everyone understands user needs, products naturally become more user-friendly.
Remember: good UX research isn't just about collecting data. It's about creating better experiences that users love and businesses benefit from.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more


