Testing gives designers honest feedback from the people who matter most. Developing user personas helps teams understand their intended audience, guiding both product design and user testing strategies. It catches issues early when they're cheap to fix.
Conducting user testing in the early stages and during the discovery process can generate valuable insights before substantial investment is made.
This guide covers everything you need to know about user testing. You'll learn what it is, why it matters, and how to do it right.
What Is User Testing?
User testing means watching real people use your product. Pick testers who match your target audience. Give them tasks, observe how they work, and note where they struggle.
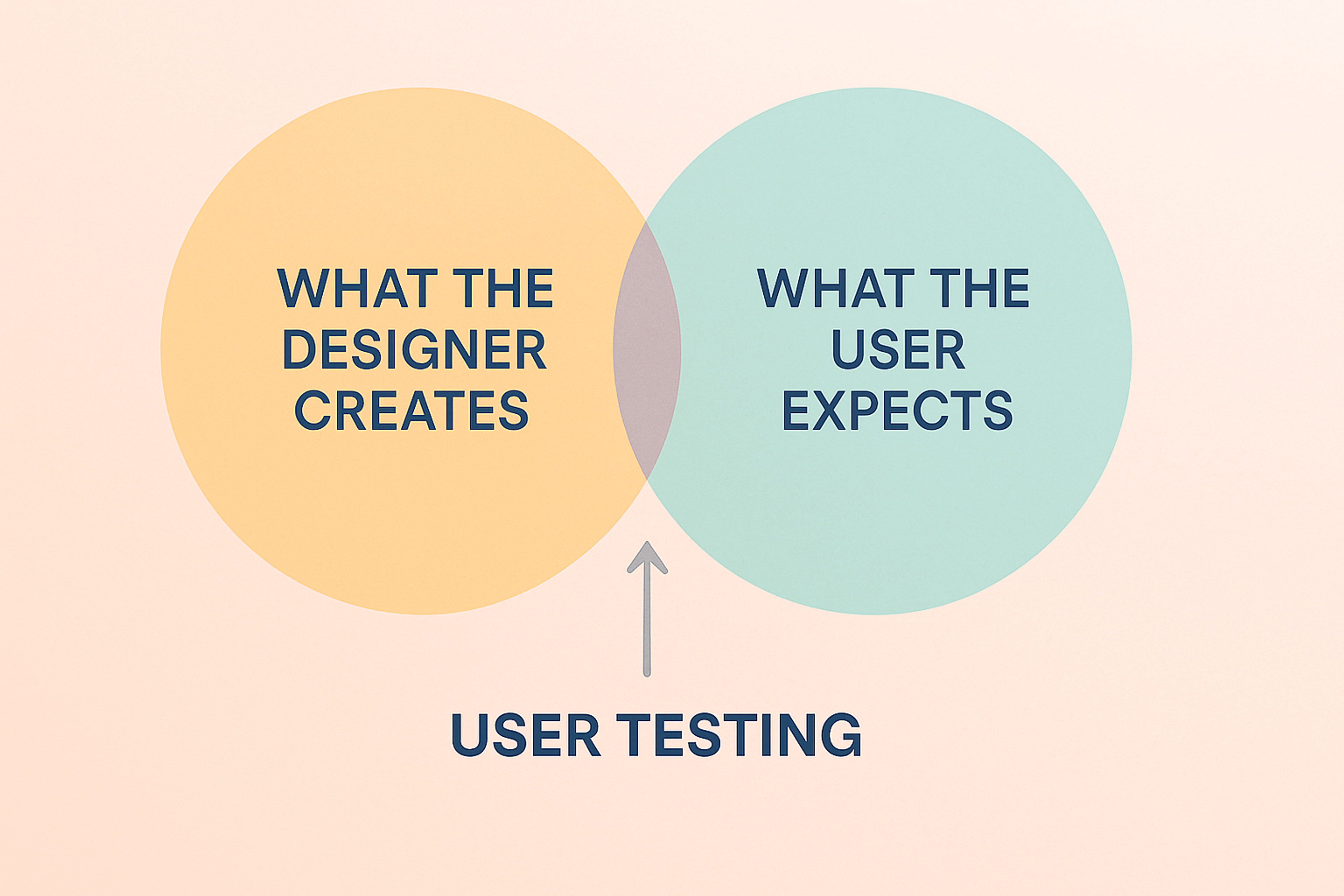
Testing surfaces issues teams miss from the inside. Designers see products differently than users, and tests close that gap. You can test at any stage, even before a full prototype exists.
Use both qualitative and quantitative methods. Qualitative testing explains why people act a certain way. It captures thoughts, feelings, and frustrations. Quantitative testing measures what they do, like completion rates, errors, and time on task. Set up realistic conditions so your data is accurate.
User Testing
Run several rounds. Early tests catch big problems. Later tests refine details. Ask users to complete clear tasks and watch from their point of view.
Why Is User Testing Valuable?
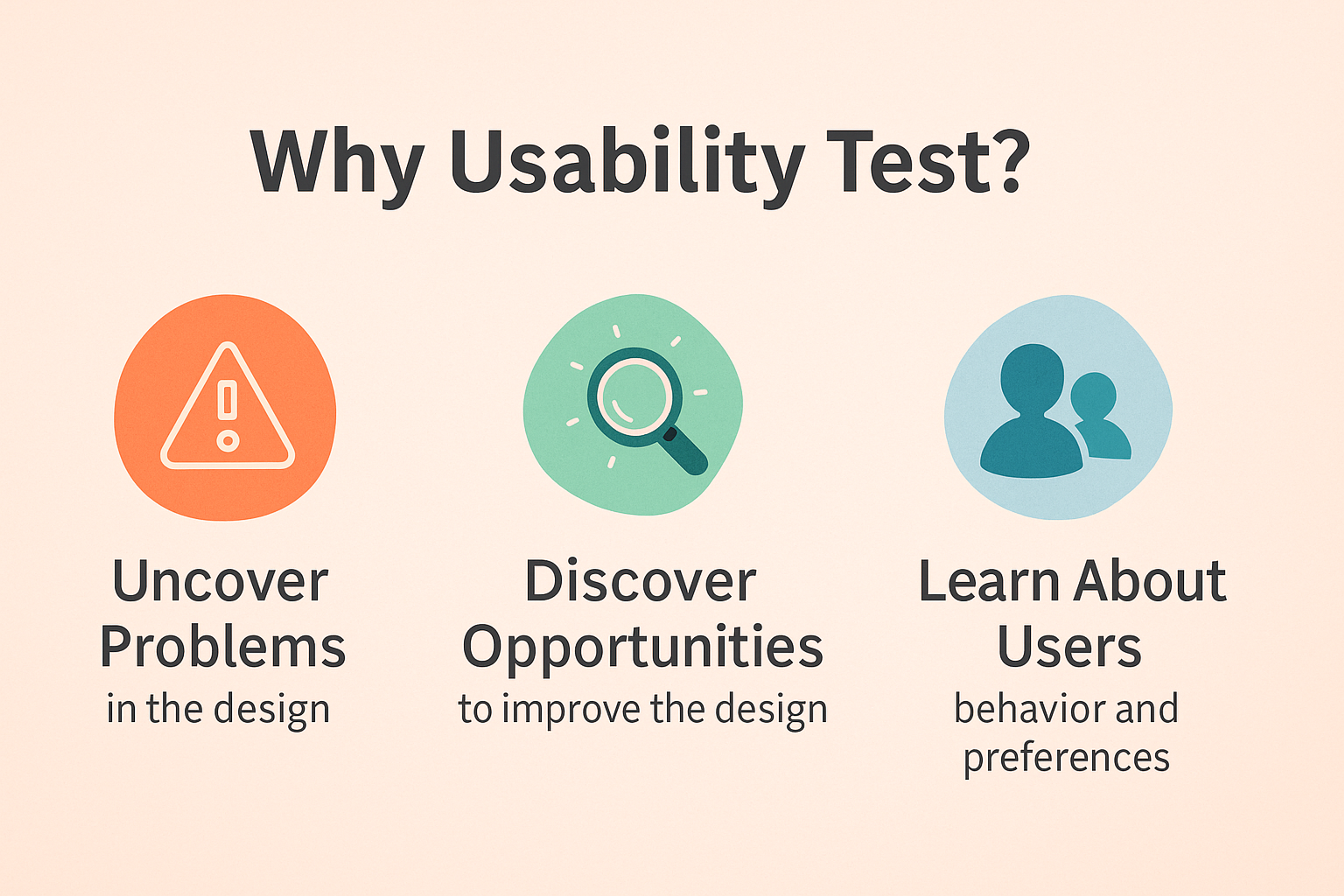
User testing keeps your product grounded in real needs, not guesses. It shows exactly where people struggle and what delights them.
It exposes gaps between user expectations and what your product delivers. You see which features confuse users and which they love. Those insights drive smarter design choices.
Testing improves results you can measure. Easier flows keep people engaged longer. Clear paths raise conversion rates and reduce friction. Happy users return and recommend you to others.
Remote tools like UserTesting let you reach people in many places and backgrounds. This diversity reveals different perspectives and sparks new ideas.
Usability Test
Testing also saves money. Fixing a broken checkout in testing takes hours. Fixing it after launch costs sales and trust.
Teams that prioritize testing gain an edge. They ship better products, see higher ROI, and win more often.
4 Types of User Testing
Usability Testing: Examines user interactions to identify navigation issues, pain points, and areas for improvement, ensuring a smooth experience. Usability testing includes moderated, unmoderated, remote, in-person, exploratory, and comparative methods. Selecting the right type based on goals and audience is crucial for valuable insights.
A/B Testing: Compares two versions of a design or feature by measuring user engagement, conversion rates, and performance metrics to determine which version is more effective.
Desirability Testing: Focuses on users’ emotional responses to a product’s design, branding, and visual elements. It helps assess whether the design evokes the intended feelings and aligns with brand perception.
Beta Testing: Involves releasing a product to a limited group of users before launch to identify bugs, usability issues, and overall user satisfaction, allowing for refinements before the full release. Unmoderated testing can be a cost-effective approach here, as it allows participants to complete tests in their own environments with less supervision.
Each type of user testing provides valuable insights, helping designers and developers create products that are functional, engaging, and user-friendly.
UX Testing Methods
Effective UX testing helps ensure that a product is intuitive, user-friendly, and meets user needs. Here are some key UX testing methods used to gather insights and improve usability:
- Heatmaps & Click Tracking: Visual tools that analyze user behavior by showing where users click, scroll, or hover, helping designers optimize layouts and interaction points.
- Surveys & Questionnaires: Collects qualitative and quantitative feedback from users about their experience, preferences, and challenges.
- Eye Tracking: Uses specialized technology to analyze where users look first, how they scan a page, and what elements grab the most attention.
- Card Sorting: Helps improve navigation and information architecture by having users group and label content in a way that makes sense to them.
- First-Click Testing: Evaluates whether users can quickly and accurately find the right button, link, or path when completing a task. A quick usability test can also be an effective way to gather immediate feedback in public locations.
Using a combination of these UX testing methods ensures that products are well-optimized for user needs, leading to higher engagement, better usability, and improved overall experience.
How to Create an Effective User Testing Plan
Create a clear plan so testing gives real insights. Set specific goals. Choose a few success metrics. Know exactly what you want to learn.
Pick methods that match your goals. If you need to hear how people think, use moderated tests with think-aloud. If you need speed and scale, use unmoderated tests.
Recruit the right people. Testers should match your real users. Bad recruiting wastes time and money. Build screeners from your personas so only suitable participants get in.
Use multiple sourcing options. In-house panels work fast. Third-party panels let you target niche groups. Customer lists bring engaged users. Web or app intercepts recruit people already using your product.
Set up the environment carefully. Remove distractions. Check all tech ahead of time. For remote tests, send simple, clear instructions.
Write tasks that expose pain points like navigation or usability issues. Run a pilot first to catch flaws in your plan. Adjust tasks and questions based on what you learn.
Document everything. Record sessions when possible. Take detailed notes on behavior and quotes. Good records make analysis faster and more accurate.
User Testing Plan

Elements of Usability Testing
Usability testing is a vital aspect of the user experience (UX) design process, focusing on evaluating a product by testing it with real users. This practice aims to identify usability problems, assess user satisfaction, and understand how easily users interact with a product.
Unmoderated usability testing is particularly efficient in gathering data from larger sample sizes quickly, as it allows users to complete tasks independently, often in their own environments, without real-time interaction with a researcher.
Remote usability testing offers significant advantages by enabling researchers to collect valuable insights into user behavior and experiences during product interactions without the need for real-time interaction.
Facilitator
A facilitator is a vital person present in usability tests who oversees that participants complete all activities during testing while ensuring the application of neutrality in the process.
Presentation

Environment
The location and surroundings of the participants during the tasks play an important role in efficiency and comfort. The environment should be devoid of irrelevant elements and replicate the real-world scenarios in which the product will be used.
Think about the location, such as in what circle lights, headphones, or telephones are helpful for interaction with others and will foster the experience rather than using fake circumstances.
Documentation
Comprehensive documentation during usability testing is essential for tracking observations, participant feedback, and any issues encountered.
This documentation is a reference point for analysis and fosters a clearer understanding of user interactions and experiences over time.
Thus, teams will be able to improve the usability performance of usability tests, making it possible to create products that their users will enjoy.
Feedback Mechanism
The process of gaining feedback can be accompanied by some aspects that allow the participants to offer their opinions about the testing process.
This may be in the form of their impression about the outcomes of usability testing and what was being asked, including any other information that might help the researchers improve the usability test, such as whether the process was easy or difficult.
Feedback

How Does User Testing Work?
Testing follows a clear process. First, decide what you want to learn. Then create tasks that mirror real life.
Recruit people who match your user personas. They should reflect real customers and their expectations. The right participants give useful, unbiased feedback.
Select participants carefully. Brief them on the process without revealing your goals. You want natural reactions, not coached answers.
Ask users to complete tasks while you observe. Encourage them to think aloud. This exposes their expectations and reasoning and helps you spot usability issues and emotional reactions.
Take notes on what they do and what they say. Watch for hesitation, confusion, and moments of delight. These signals show where the design works and where it fails.
How User Testing Works

After sessions, look for patterns. Find common struggles and shared wins. Use these insights to guide improvements.
User testing often happens early to shape direction. Usability testing often happens later to polish details. Both matter. Catching problems early saves time and money by reducing rework.
How to Do User Testing?
Practical user tests are essential to gather meaningful insights that drive product improvement. Here are the key points to focus on:
- Creating Realistic Scenarios: It is vital to design test scenarios that closely mimic real-world usage. This helps users feel comfortable and reduces the likelihood of atypical behavior during the test, leading to more authentic feedback.
- Selecting Appropriate Tasks: Choose tasks that reflect the product’s most critical functionalities. These tasks should be relevant to the user goals and represent typical interactions, enabling testers to evaluate the product effectively. An unmoderated test allows participants to complete these tasks independently, often in their own environments, which can lead to cost savings.
- Recruiting the Right Participants: Selecting participants resembling the target user demographic is crucial for obtaining relevant insights. Engaging user testing services can help recruit suitable test subjects for large-scale projects, streamlining the process and ensuring a diverse group of testers captures a wide range of user experiences and perspectives.
- Moderating Sessions Effectively: A skilled moderator can elicit valuable feedback by encouraging users to express their thoughts and feelings while navigating the product. The moderator should balance guidance and observation, allowing users to explore naturally while ensuring the test remains focused.
Defining clear goals for a user test is essential, whether focusing on usability, learnability, or user satisfaction.
By emphasizing these core aspects, designers can facilitate practical user tests that yield valuable insights for enhancing usability and overall user experience.
Analyzing and Interpreting Results
The analysis and evaluation of the results of a usability test represent the last step, the most important one since it evaluates data collected to provide helpful information. Key aspects include the following:
Quantitative testing focuses on measurable performance metrics and larger sample sizes, making it particularly advantageous for evaluating usability and task performance through data that quantitatively expresses user interactions.
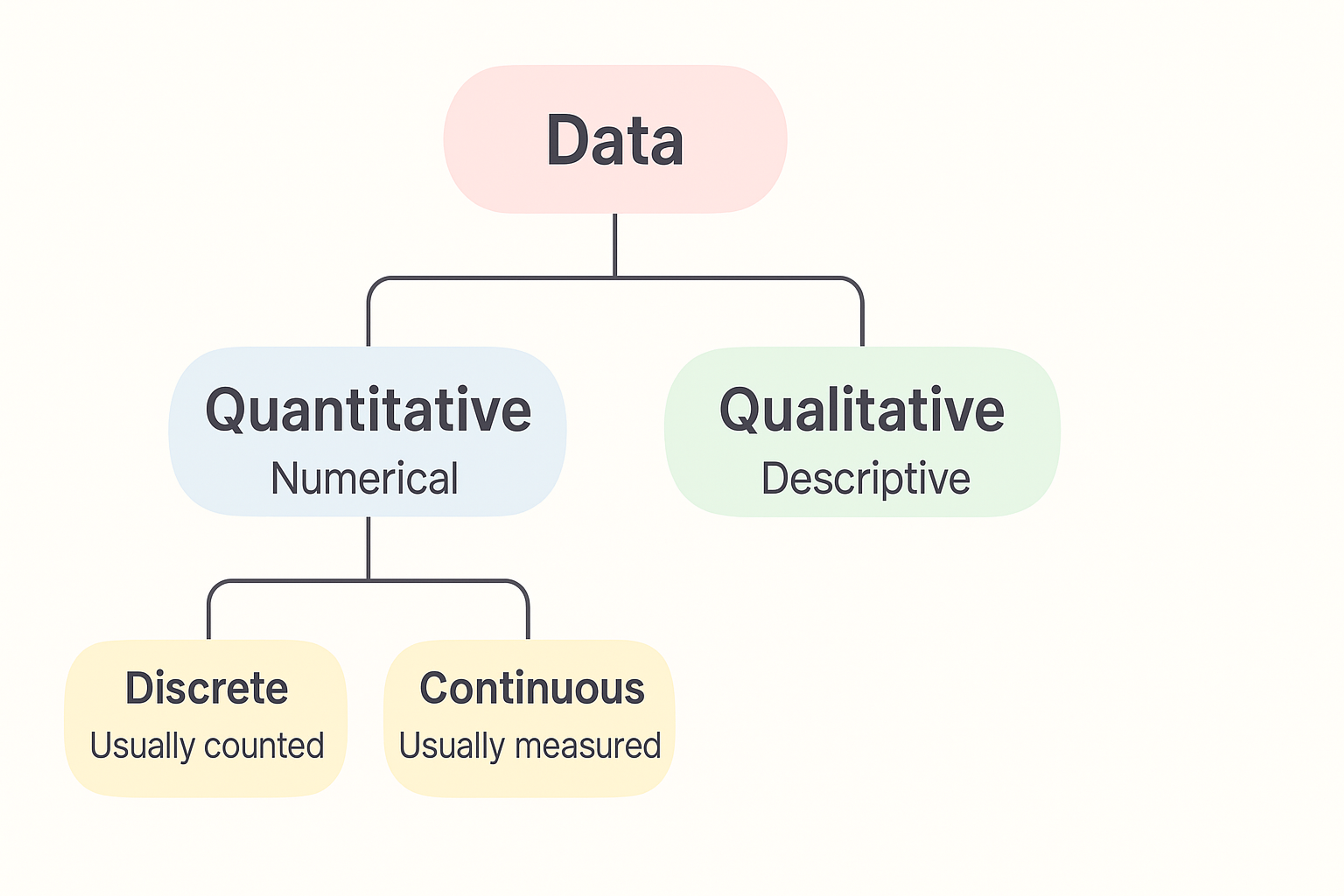
Qualitative Data vs. Quantitative Data
In this case, clearly distinguishing between qualitative and quantitative data is essential.
Qualitative data, mainly user comments and observations, gives an in-depth understanding of the controllers' actions and driving forces.
On the other hand, metrics and statistical analysis form part of quantitative data and help illustrate the problems of usability and user satisfaction.
Qualitative Data vs. Quantitative Data
Identifying Patterns and Trends
After collecting data, the next step involves diagnosing some of them as logical and recurrent themes or patterns.
This requires that qualitative comments be coded and quantitative questionnaire data be used to identify problem areas, likes, and successful elements.
These trends may offer more in-depth reasoning as to why users do certain things and assist in building structure.
Read more:
Conclusion
User testing reveals how real people interact with and experience your product. It transforms assumptions into knowledge and guesses into data.
Testing works best when integrated throughout your design process. Test early concepts to validate direction. Test working prototypes to refine details. Test finished products to ensure quality.
The methods covered here provide you with practical tools for improved design. Start small if you're new to testing. Even informal testing with a few users is better than no testing at all.
Remember that user testing serves your users and your business. Products that work well for users succeed in the market. Testing helps you build that success systematically.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more


