Product design in 2026 goes far beyond looks. It turns messy problems into solutions that ship, work, and last. Designers build digital and physical products, think about materials and prototypes, and align with market and business goals.
The job blends research, design, teamwork, and project management. The best work feels invisible because it anticipates needs and removes friction.
A product designer sits at the crossroads of user needs, business goals, brand, and engineering limits. Titles differ, but the core duty is the same: protect quality from discovery to launch and beyond. Hiring late often costs more - strong design prevents rework and speeds real progress.
Introduction to Product Designers
What Is a Product Design?
Imagine trying to build something - a new app, a piece of furniture, maybe even a smart kitchen appliance - that people don’t just use but truly enjoy. That’s product design at its core.
It might sound simple, but designing a product is rarely straightforward. It all starts with asking the right questions: What do people actually need? How do they interact with similar products? What problems haven’t been solved yet?
Research is the heartbeat of product design. Whether it’s digging into user behaviors, testing prototypes, or exploring materials and tech, the goal is always the same - to create something meaningful.
While product design has roots in industrial design - think physical items, manufacturing, and form-meets-function - today, the spotlight is often on digital products. Apps, websites, and software now dominate the conversation, pushing the field to evolve. But no matter the medium, the essence of product design remains: to imagine and build solutions that improve people’s lives.
Source: Kumpan Electric on Unsplash

What Is a Product Designer?
These professionals serve as creative problem solvers who ensure the world keeps getting useful things. Combining engineering concepts with design principles, a product designer creates things that stakeholders never knew they needed but now can’t live without.
The job requires understanding customer desires, technological capabilities, competitor strategies, and desired features within your designs. You’ll also need data analysis skills to utilize feedback from real customers and research sources.
Product specifications must also be created during this process so you have all those details down pat from the get-go.
With such an influx of digital tools like Adobe Photoshop and Sketch, you won’t have to worry about your ability to bring your ideas to life quickly and efficiently. Prototyping will become easier, allowing for more brainstorming time for visual designers.
Benefits of Prototyping by Clay
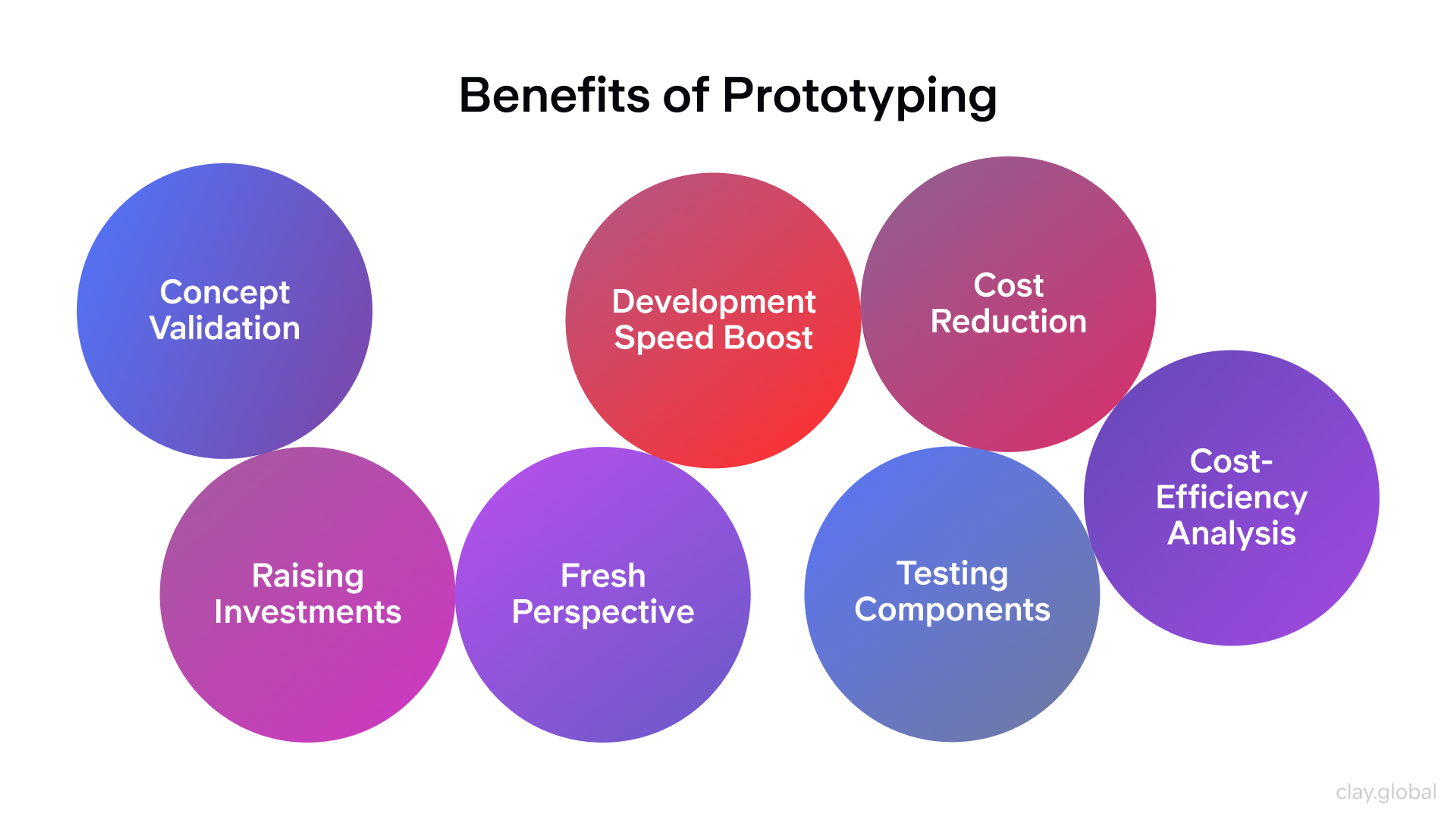
Your designs must also be user-friendly at their core. Incorporate UX principles into your everyday work so that everything is intuitive and simple for the end user to interact with.
Making products is all good, but you must ensure yours are better than others. Stay on top of industry trends, collaborate with other experts like engineers, marketers, and UX researchers, take part in user testing sessions to get real feedback from people currently engaging with your design, meet deadlines consistently, and deliver high-quality products in record times. It’s a lot of work, but it keeps companies ahead of the game - which is ultimately why they pay you the big bucks.
Product Designers vs. UX Designers
Product designers and UX designers are two different roles with much in common. Both focus on the same things but with differing qualities. Product designers do just what it sounds like: they design products!
They do planning, research, and development from start to finish. They learn about what the customer wants and needs and about technology and design principles to create unique products that sell. Though it may sound like a product manager, it's a very different job.
UX designers test how products work once they’re made. Using user testing sessions and data analysis, they can see what works well with customers and what needs improvement. With this information, they ensure customers get exactly what they expect when interacting with a brand or product.
UX Designer Responsibilities by Clay
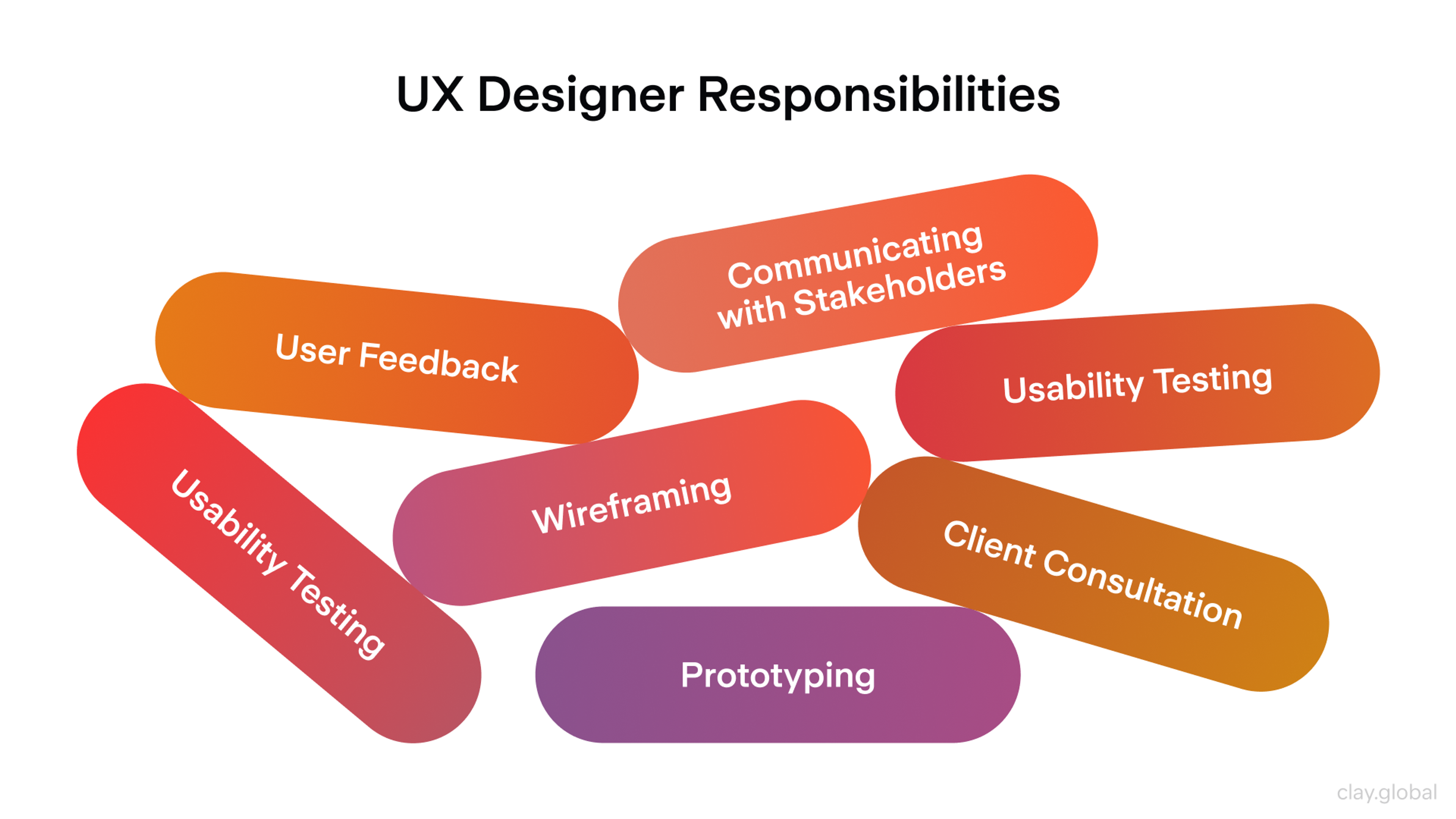
While these jobs require many skills for designers to be successful, teams must understand that one team may need a product designer more than a UX designer and vice versa. The roles are similar but different enough for them to take on entirely separate projects.
What Are The Most Common Product Design Roles?
There are many titles someone working in product design could hold, such as:
- Interaction Design: Improves functionality of an interface interaction.
- Experience Architect: Maps user stories through info architecture and UI.
- Information Architecture: Organizes information so navigation feels intuitive.
- Industrial Design: Physical refinement of physical designs such as furniture.
Types of Product Design
Product design isn’t just one thing - it’s a blend of many disciplines, each bringing its own flavor, tools, and focus to the creative table. Like a team of specialists working toward a shared goal, each type of product design tackles a different aspect of how we interact with the world - both digital and physical. Let’s take a look at the main branches that make up this diverse field.
1.
Digital Product Design: Every smooth tap, scroll, or swipe comes from a digital product designer. They shape the apps and sites we use every day. They craft clear interfaces and meaningful experiences. They do research, prototype, test, and iterate.2.
Industrial Product Design: Industrial designers create the objects we hold and use, like chairs, phones, headphones, and blenders. They balance function and form. They understand materials, manufacturing, and human movement. That comfy chair or easy-to-grip coffee maker is no accident. It’s careful design backed by technical skill and taste.3.
Consumer Product Design: Consumer designers build the goods we rely on at home. They make products useful, safe, affordable, and appealing. They watch trends but stay grounded in real needs. Ergonomic handles and sustainable packaging show how empathy and innovation meet. The aim is to make daily life easier and more enjoyable.4.
Service Design: Service designers map full journeys, not single touchpoints. Booking a hotel, returning an item, or getting support should feel smooth from start to finish. They connect screens, spaces, and people into one coherent experience. The result is a service that works well and feels right.5.
Experience Design: Experience designers ask, “How does this make people feel?” They use emotion and story to make moments stick. Unboxing a device, a graceful loading animation, or finishing a wellness task can all spark delight. Their secret is human connection woven into function.
No matter the discipline, all product designers share a common goal: to create things that improve lives, solve real problems, and make the world - whether digital or physical - a little better. Their tools and methods may differ, but their purpose is unified by one principle: design with empathy, build with purpose.
Qualifications for a Product Designer
Like any other job, a candidate for this position should possess certain qualifications. Critical thinking, problem-solving communication, and collaboration skills are all necessary attributes.
Knowing user experience (UX) principles and trending ideas within the industry is also important. Effectively using software tools, including Adobe Photoshop or Sketch, is crucial, too!
Source: Photo by Daria Nepriakhina 🇺🇦 on Unsplash

Lastly, the technical aspects of product design include knowledge of coding languages and web standards, which are needed for a successful career.
What Are Product Designer Skills?
It comes down to having a combination of technical and creative skills while still being able to problem-solve. Here are some examples.
Hard skills
- User research and testing
- Interaction and user interface (UI) design
- Visual design
- User experience (UX) design, including wireframing and prototyping
- Project management
Soft skills
- Creativity
- Leadership and teamwork
- Attention to detail
- Problem-solving
- Communication
- Empathy
- Decision-making and accountability
How to Become a Product Designer
A product designer is responsible for shaping the look, feel, and functionality of both physical and digital products. This role requires a combination of creativity, problem-solving skills, and technical knowledge. If you want to become a product designer, follow these steps to build a strong foundation and launch your career.
Step 1: Understand the Role of a Product Designer
Product designers do more than create visuals; they work on the entire user experience. Their responsibilities include:
- User Experience (UX): Ensuring products are intuitive and user-friendly.
- User Interface (UI): Designing attractive and functional digital interfaces.
- Prototyping & Testing: Creating wireframes, mockups, and interactive prototypes to validate ideas.
- Collaboration: Working with developers, marketers, and stakeholders.
- Problem-Solving: Identifying and addressing user pain points through design solutions.
Step 2: Product Designer Education Requirements
There are multiple ways to gain the necessary knowledge and skills:
- Formal Degree (Optional):
- Bachelor’s degree in Industrial Design, UX/UI Design, Graphic Design, Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), or a related field.
- Self-Learning:
- Many product designers teach themselves using online resources.
- Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, Interaction Design Foundation (IDF), and Google UX Design Certificate offer affordable courses.
- Bootcamps & Certifications:
- Short-term intensive programs like General Assembly, CareerFoundry, and Designlab provide structured training.
Step 3: Develop Essential Design Skills
Product designers need both technical and soft skills to succeed.
Technical Skills:
- UX/UI Design: Understanding user needs, wireframing, and usability testing.
- Visual Design: Mastering typography, color theory, and layout.
- Prototyping & Design Tools: Proficiency in Figma, Sketch, Adobe XD, and InVision.
- Front-End Knowledge (Optional): Basic understanding of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript can be useful.
Soft Skills:
- Problem-Solving: Finding creative solutions to design challenges.
- Collaboration & Communication: Working with cross-functional teams.
- Empathy: Understanding users’ perspectives to create human-centered designs.
Step 4: Build a Strong Portfolio
A well-crafted portfolio is crucial for showcasing your skills and experience.
What to Include in a Portfolio?
- Case Studies: Show the design process from research to final prototype.
- Problem-Solution Approach: Explain the challenges faced and how they were solved.
- User Research & Testing Insights: Demonstrate a data-driven approach to design.
- Before & After Screenshots: Highlight improvements made.
Tips for a Strong Portfolio:
- If you lack professional experience, redesign existing apps or websites.
- Participate in UI/UX challenges to practice and showcase your work.
Source: Unsplash+

Step 5: Gain Real-World Experience
Hands-on experience is key to building confidence and credibility. Consider the following:
- Freelancing: Work on small projects through platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, or Behance Jobs.
- Internships & Apprenticeships: Gain structured work experience in a design role.
- Open Source Contributions: Contribute to open-source projects on GitHub or Dribbble.
Step 6: Network and Learn from the Design Community
Networking helps you stay updated on industry trends and opportunities.
- Join Design Communities: Engage in groups like Design Buddies (Discord), UX Mastery, and Dribbble.
- Attend Workshops & Conferences: Participate in events like Adobe MAX, Figma Config, and AIGA Design Conference.
- Follow Influential Designers: Learn from experts on LinkedIn, Twitter, and Medium.
Step 7: Apply for Jobs and Keep Learning
Once you have a solid portfolio, start applying for product design roles.
Common Job Titles for Product Designers:
- Product Designer: Focuses on UX/UI, problem-solving, and strategy.
- UX Designer: Specializes in user experience and usability testing.
- UI Designer: Works on interface design and visuals.
- Interaction Designer: Focuses on animations and micro-interactions.
Job Search Tips:
- Tailor your resume and portfolio for each application.
- Apply to entry-level roles or internships to gain experience.
- Keep improving your skills, as product design trends change frequently.
Collaboration and Communication in Product Design
Effective collaboration and clear communication drive successful product design. They help cross-functional teams work smoothly so ideas become real products without friction.
1.
Design handoffs matter. Share complete files and specs with developers. Precise handoffs prevent confusion and keep the build aligned with the design vision.2.
Design systems create a shared language. Reusable components and rules speed up work, keep visuals consistent, and make it easier to scale across products and platforms.3.
Feedback loops keep teams honest. Regular input from stakeholders and users ties decisions to real needs and business goals. Usability tests and research guide smart iterations.4.
Communication tools keep everyone synced. Use chat and task trackers to share updates, manage work, and track progress in one place.5.
Design critiques raise the bar. Frequent, constructive reviews help teams spot gaps, refine solutions, and improve continuously.
Prioritize collaboration and communication from start to finish. You will ship designs that implement cleanly, satisfy users and stakeholders, and strengthen the entire design process.
Product Designer Salary
Product designers can also look forward to bonuses and advancements each year they spend in the industry. After only a few years, you can expect salaries of around $60k, but if you’re a senior designer, you could make up to $125k or more. Some employers may even offer up to 25% of an individual's base salary as a bonus.
Where these designers work will also impact their income. Those in San Francisco or New York, cities home to many tech companies, who work for major tech companies will be paid more than those in other cities or industries.
Mobile designers are generally paid more than web designers, especially when they have worked on groundbreaking products many people use.
This makes product design one of the best-paying design jobs out there. Those with problem-solving and critical thinking skills and knowledge about user experience principles and software development tools stand to gain a lot financially and professionally from working in this field.
What Do Product Designers Typically Do?
No set profession exists for any kind of designer because every company will require something different from them. However, there are still some things that all product designers should know how to do by heart. These tasks include:
1.
Creating surveys and usability tests to check user feedback and determine what users want from your product.2.
Working with other team members to make sure the product satisfies all requirements.3.
Taking customer input into account when making improvements.4.
Constructing prototypes for testing purposes.5.
Researching new technologies and trends related to your industry so that you can create innovative products.6.
Managing projects within time limits and budgets.7.
Monitoring the success of finished products and making changes if they need to.
The Future Of Product Designers
Product designers earn good pay today, and salaries will likely rise. Faster tech means constant demand for new products, so strong design skills will matter even more.
AI will cut busywork. It can analyze data and test ideas, so designers spend more time creating user-friendly products and catching issues early.
Teams will get more diverse. UX researchers, visual designers, marketers, and engineers will work together more. Designers must sharpen communication and collaborate across roles.
Sustainability and ethics will shape the future. Designers will use greener materials and push for responsible manufacturing.
To succeed, you need creativity, solid technical skills, and a deep feel for customer needs. With those, product designers will thrive in a fast-changing industry.
FAQ
What Does A Product Designer Do In 2026 Beyond Making Things Look Good?
They turn messy problems into usable solutions that ship. They run research, prototype, test, align with engineering and stakeholders, and protect quality from discovery through launch.
Product Designer Vs UX Designer What Is The Simplest Difference?
Product designers usually own the end to end design outcome across the lifecycle. UX designers often go deeper on usability, research, and interaction quality, but titles overlap by company.
What Skills Matter Most For A Modern Product Designer?
User research, interaction and UI design, prototyping and testing, design systems, and strong collaboration. Clear communication and decision making matter as much as visual skill.
What Should A Strong Portfolio Include In 2026?
Case studies that show the problem, constraints, research insights, iterations, key decisions, and results. Employers want to see how you think and how your work links to user and business outcomes.
How Is AI Changing Product Design Work?
AI speeds up drafts, variations, and research summaries. Designers stay responsible for defining the problem, choosing tradeoffs, handling edge cases, and making the experience feel coherent and trustworthy.
Read More
Conclusion
To create products that customers love, we need innovative minds. Product designers have exactly that – and so much more! With technology advancing daily, designers must stay current on trends and learn automated technologies such as AI. Strong communication skills are also necessary because working within diverse teams is crucial to meeting customer needs.
Remember: creativity paired with technical knowledge makes a great designer - so start today if you have what it takes!


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more



