“AI will reshape the world, and we have to get it right.” - Sam Altman, OpenAI CEO (OpenAI Dev Day keynote, 2023)
Artificial intelligence is no longer a thing of the future. It’s already part of how we live, work, and connect every day. From the voice that sets your alarm to the app that suggests your next show, AI is working quietly in the background.
In 2026, AI is smarter, easier to use, and more connected to human needs. It’s not just in tech labs anymore - it’s in homes, hospitals, schools, and small businesses.
This article is a beginner's guide and a comprehensive guide to artificial intelligence for 2026. It will explain what AI really is, how it got here, and why learning about it now matters more than ever.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
“AI is the new electricity.” - Bill Gates (MIT Technology Review, 2017)
What Is Artificial Intelligence by Clay
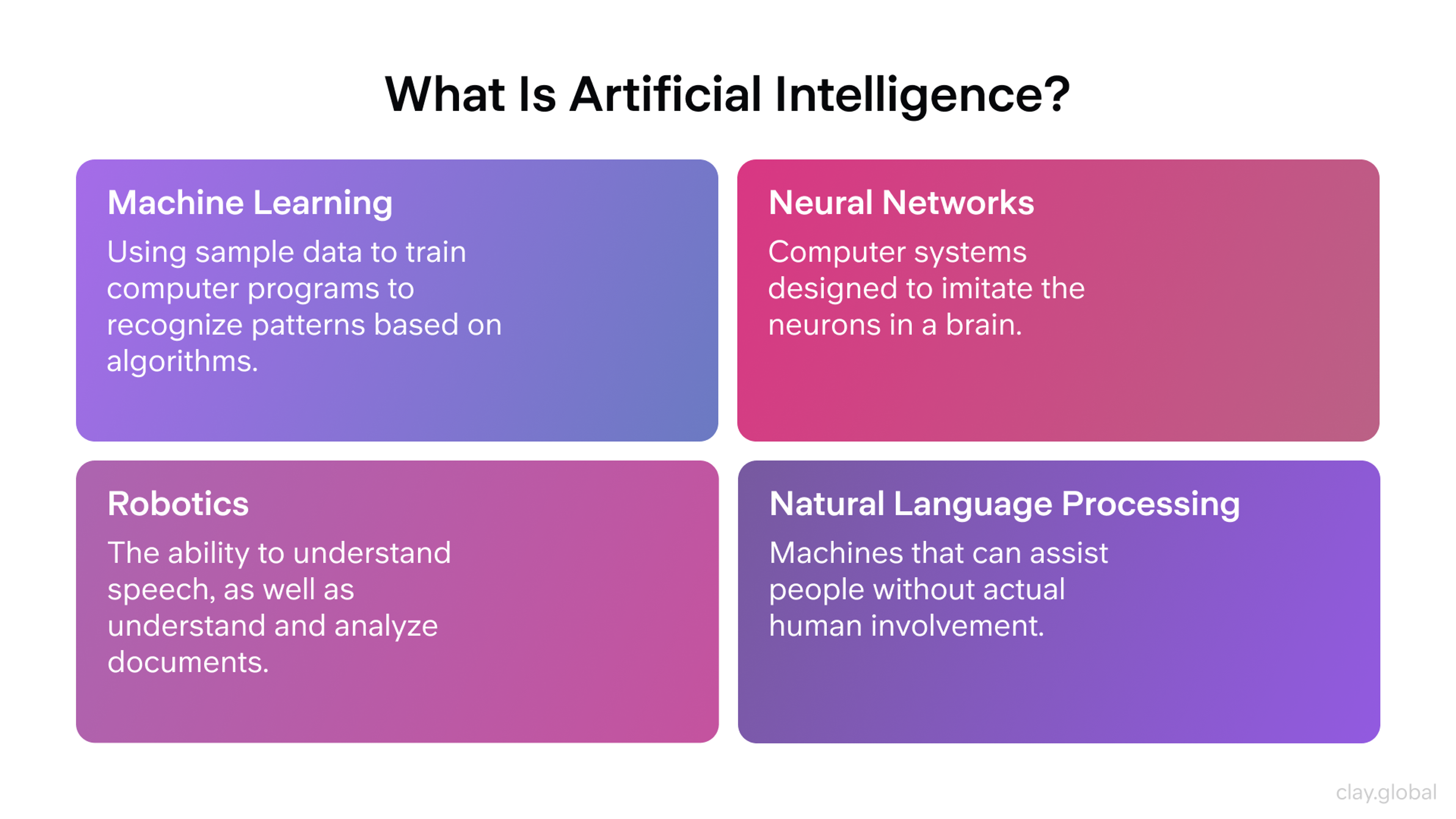
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is a branch of computer science that focuses on building smart machines. These systems can perform tasks that usually require human thinking, such as learning, problem-solving, understanding language, and making decisions, by operating through specialized computer systems and AI programs.
AI learns by studying large amounts of data, allowing computers to learn from data without explicit programming. It spots patterns, finds answers, and improves over time. It doesn’t just follow fixed instructions - it adapts.
But AI isn’t just something hidden in labs. It’s already around you. An AI system powers your voice assistant, helps doctors read medical scans, supports customer service chats, and drives some cars. It helps people and companies do more, faster, and smarter.
AI also appears in everyday tools, such as real-time translation, spam filters, and auto-generated captions. It’s changing how industries work and giving individuals more power to create, communicate, and solve problems. Take a look at Deloitte's research.
Source: Deloitte
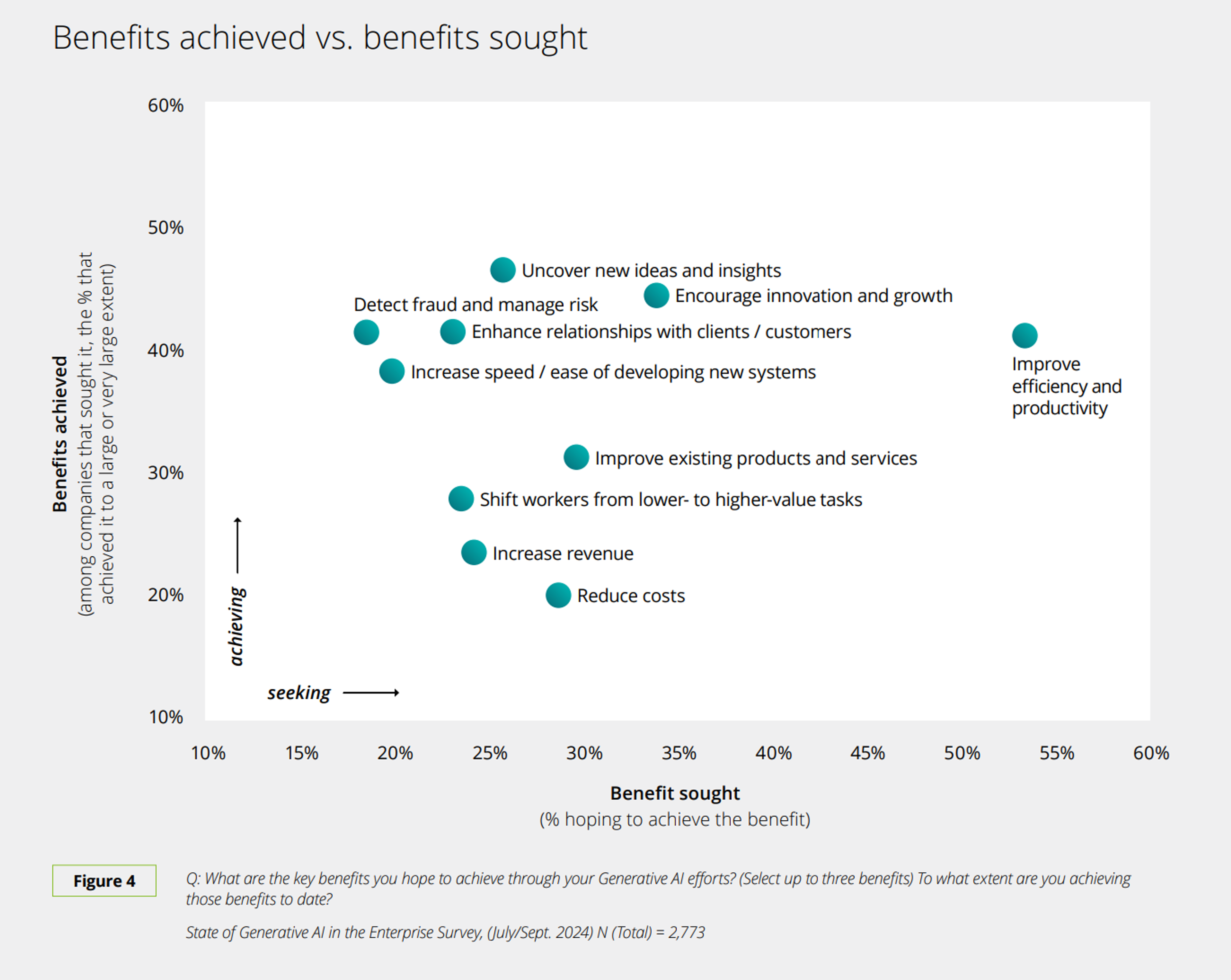
The main takeaway from the chart is that most companies use generative AI to try to save money, make more money, and work more efficiently. So far, the biggest success has been improving efficiency and productivity, helping people work faster and get more done.
Other goals, like cutting costs or increasing sales, haven’t worked out as well yet. It shows that AI is most useful right now for making everyday tasks easier rather than bringing in big profits right away.
History of AI
AI Timeline by Clay
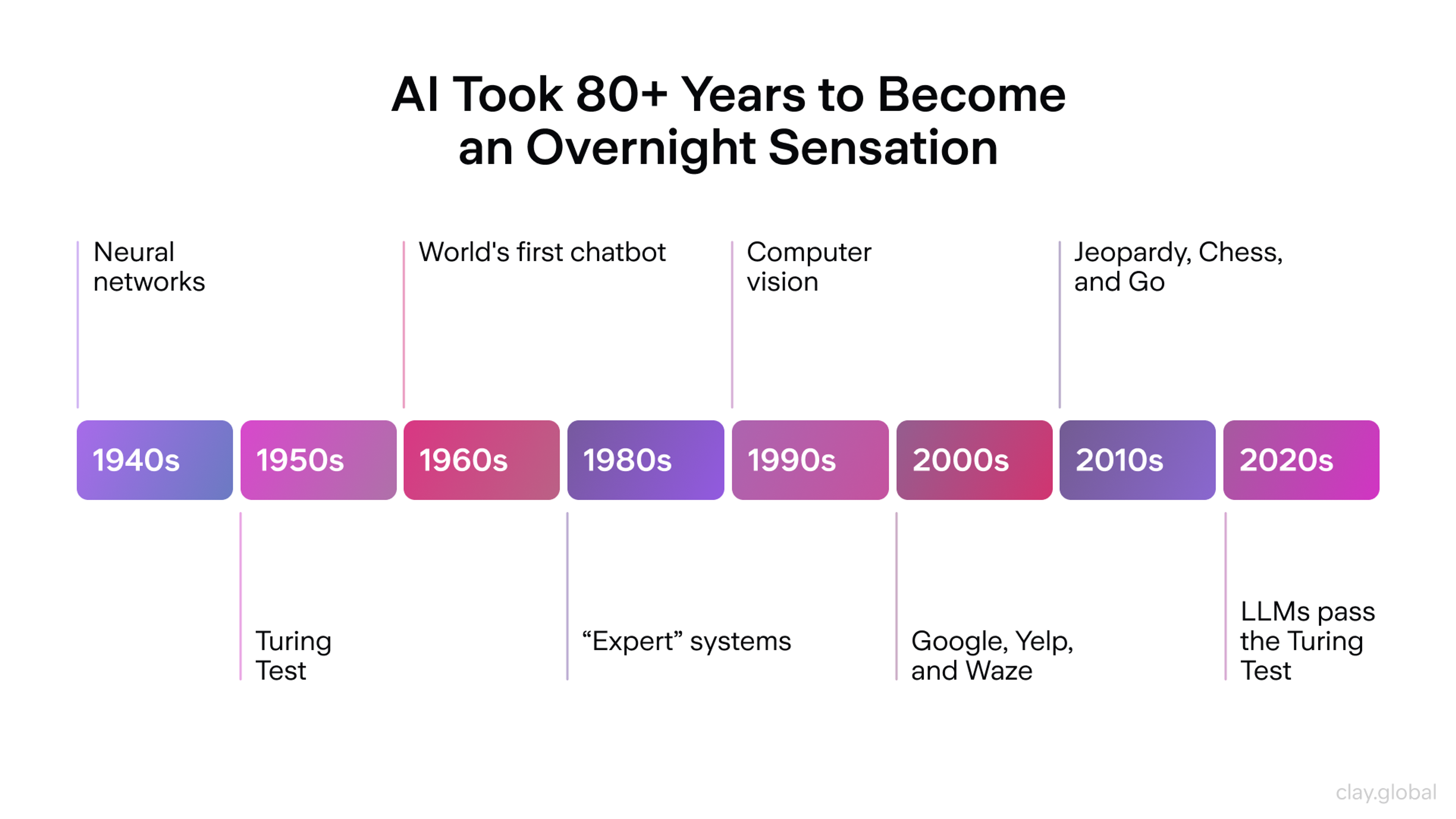
Around 55.71% of respondents think AI is a recent development. Actually, the idea of artificial intelligence started long before computers. Ancient stories talked about machines that could think or move on their own. Later, science fiction imagined robots that could talk, feel, or even learn like humans.
But the real story of AI began in the 20th century, when scientists started asking big questions and trying bold experiments.
Early Foundations (1940s–1950s): The groundwork for AI was laid when Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts proposed the first model of an artificial neural network in 1943.
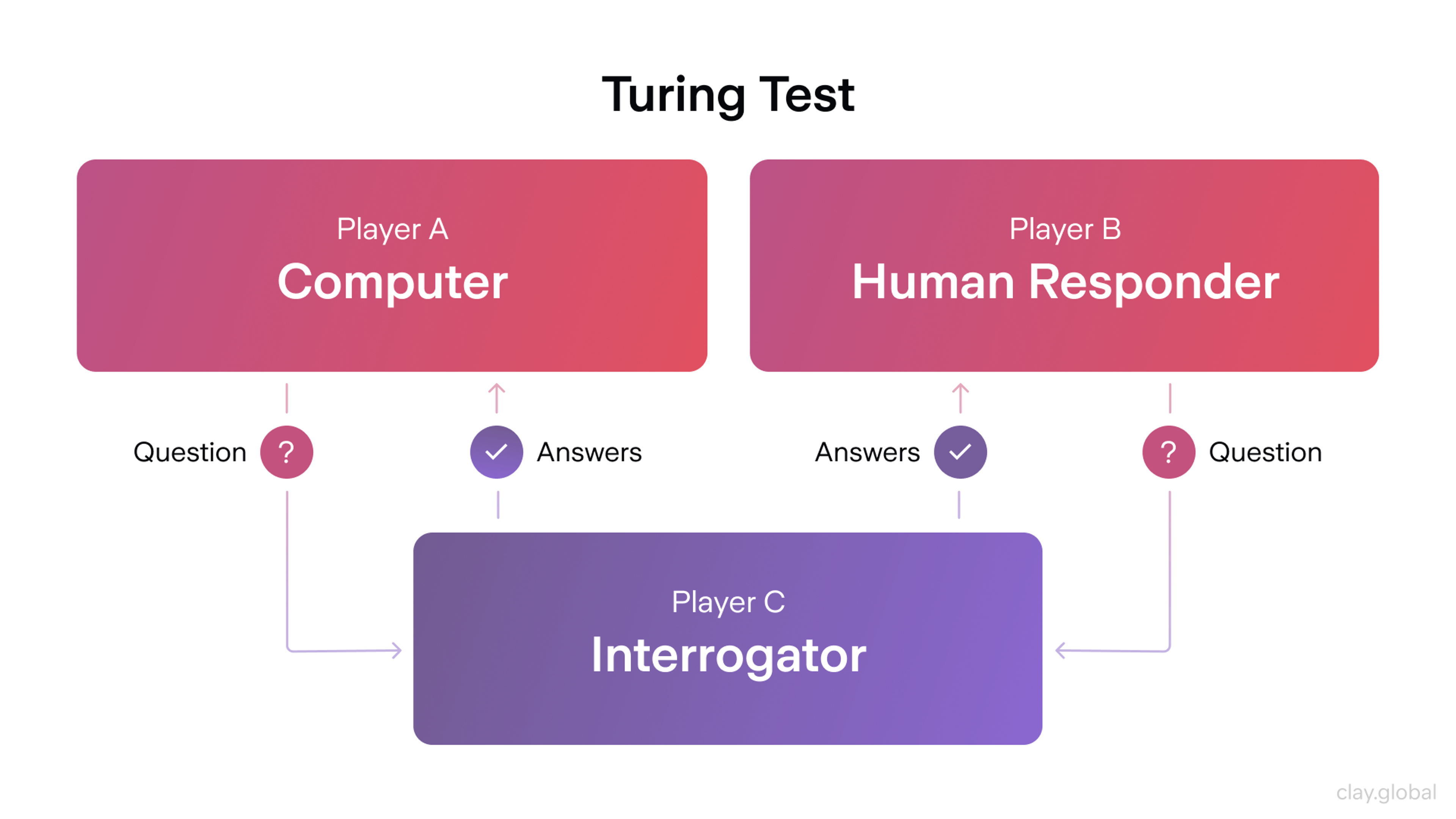
Then came Alan Turing’s famous question in 1950: Can machines think? His Turing Test became a benchmark for machine intelligence. The term “artificial intelligence” was officially coined at the 1956 Dartmouth Conference — a gathering that sparked the birth of AI as a formal field of study.
Turing Test by Clay
The Golden Years and AI Winter (1960s–1980s): In the 1960s, excitement grew.
ELIZA, an early chatbot, mimicked a therapist, and Shakey the robot could navigate rooms. These were among the first AI programs developed to demonstrate the potential of artificial intelligence. But ambition outpaced reality.
By the late 1970s, unmet expectations led to funding cutbacks, and so began the “AI Winter.” The 1980s brought expert systems, which showed promise but couldn’t scale, leading to renewed skepticism.
AI Renaissance (1990s–2000s): Just when it seemed AI might fade away, it came back stronger than ever. Faster computers and access to large digital data sets gave new life to old ideas.
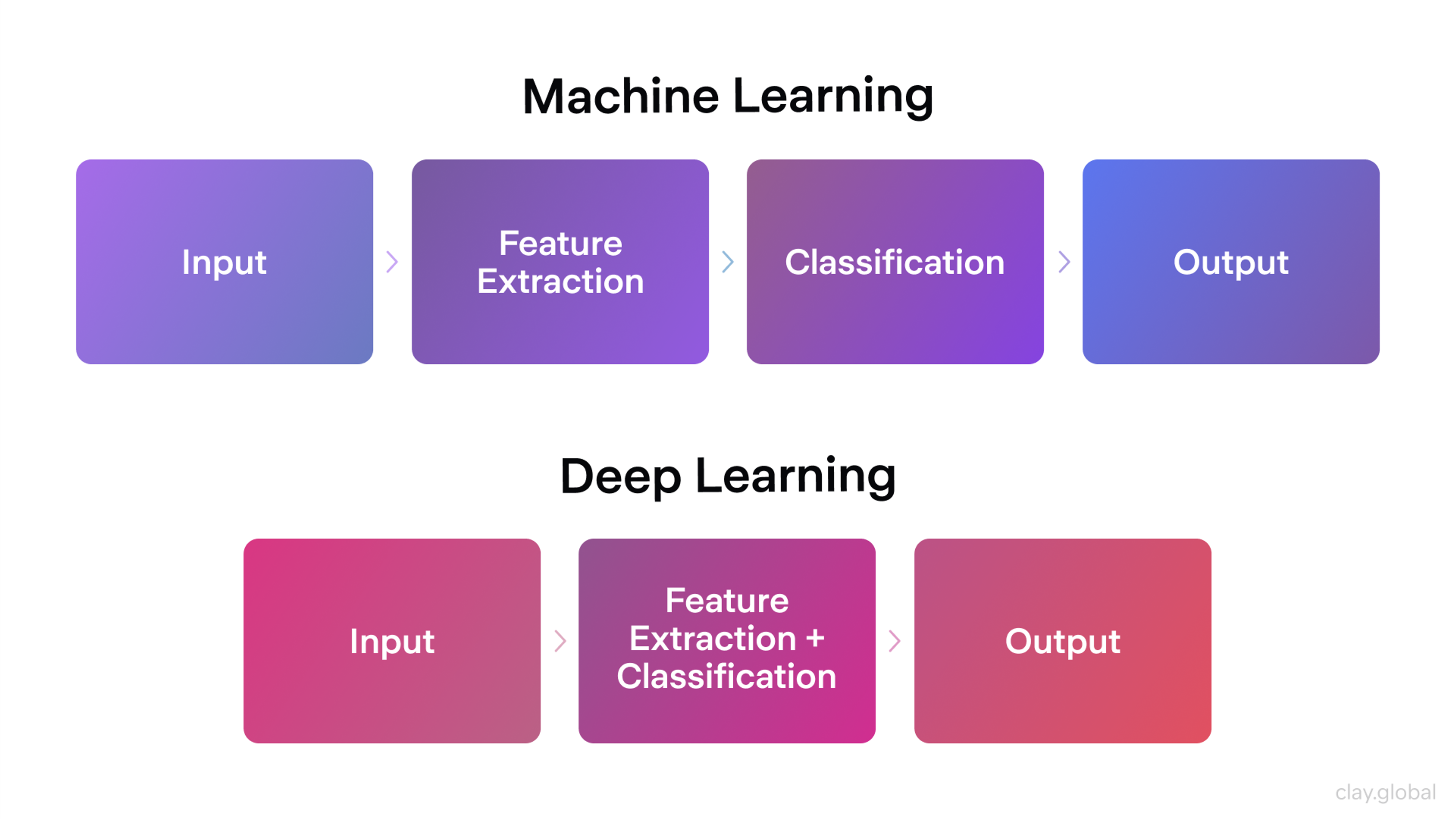
The focus began to shift. Instead of giving machines fixed instructions, scientists built algorithms that could learn from experience. This approach became known as machine learning.
Neural networks, once seen as outdated, started to shine again. Better training methods and stronger hardware made them useful for real tasks.
During this time, some industries quietly began using AI. Banks used it for fraud detection and to manage risk. Shipping and logistics companies used it to plan routes and predict delays. AI wasn’t everywhere yet, but the tools and ideas were starting to take shape.
The Deep Learning Revolution (the 2010s–Present): A pivotal moment in AI history came in 2012 when a deep learning model called AlexNet dramatically outperformed its rivals in the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC). This success showed the power of deep neural networks for processing vast amounts of data, especially in computer vision, and marked the beginning of a new era in AI.
Deep learning soon unlocked remarkable progress in fields like speech recognition, facial detection, and natural language processing. By the mid-2010s, tech giants such as Google, Facebook, Amazon, and OpenAI were rapidly advancing the field, applying AI to challenges ranging from autonomous driving to medical diagnostics.
Machine Learning and Deep Learning by Clay
Now, in 2026, AI isn’t just advancing - it’s reshaping how we live and work. But with great power comes great responsibility. As technology continues to evolve, ethical considerations, transparency, and accountability have become critical pillars of the conversation.
Artificial Intelligence vs Human Intelligence
AI and human intelligence often get compared, but beneath the surface, they function in fundamentally different ways. Surprisingly, about 53.04% of Americans believe AI operates like the human brain.
While machines can outpace us in speed and scale, human thinking brings something no algorithm can replicate: judgment, emotion, and meaning.
Processing Speed: AI can analyze huge amounts of data in seconds. It finds patterns quickly and works without getting tired. AI's visual perception capabilities allow it to interpret and analyze images and videos, supporting tasks like autonomous driving and image recognition.
But humans are better at reading between the lines. We use emotion and common sense, especially when things are unclear or constantly changing.
Learning: Humans learn through real-world experience, emotions, and social context. AI learns by processing structured data through algorithms. It doesn’t have feelings or instincts and can struggle when things fall outside its training.
Both need input to learn: humans need context, and AI needs data. However, humans are more flexible and can apply learning in new or unexpected situations.
Creativity: While AI can generate text, images, and music using learned patterns, it lacks the emotional depth and original thinking that define human creativity.
AI can write stories, make music, or design images using patterns it has learned. But it doesn’t feel or think in the way humans do. True creativity involves emotion, imagination, and the ability to create something new with meaning. That’s still something only humans can bring to the table.
AI vs Human Intelligence by Clay
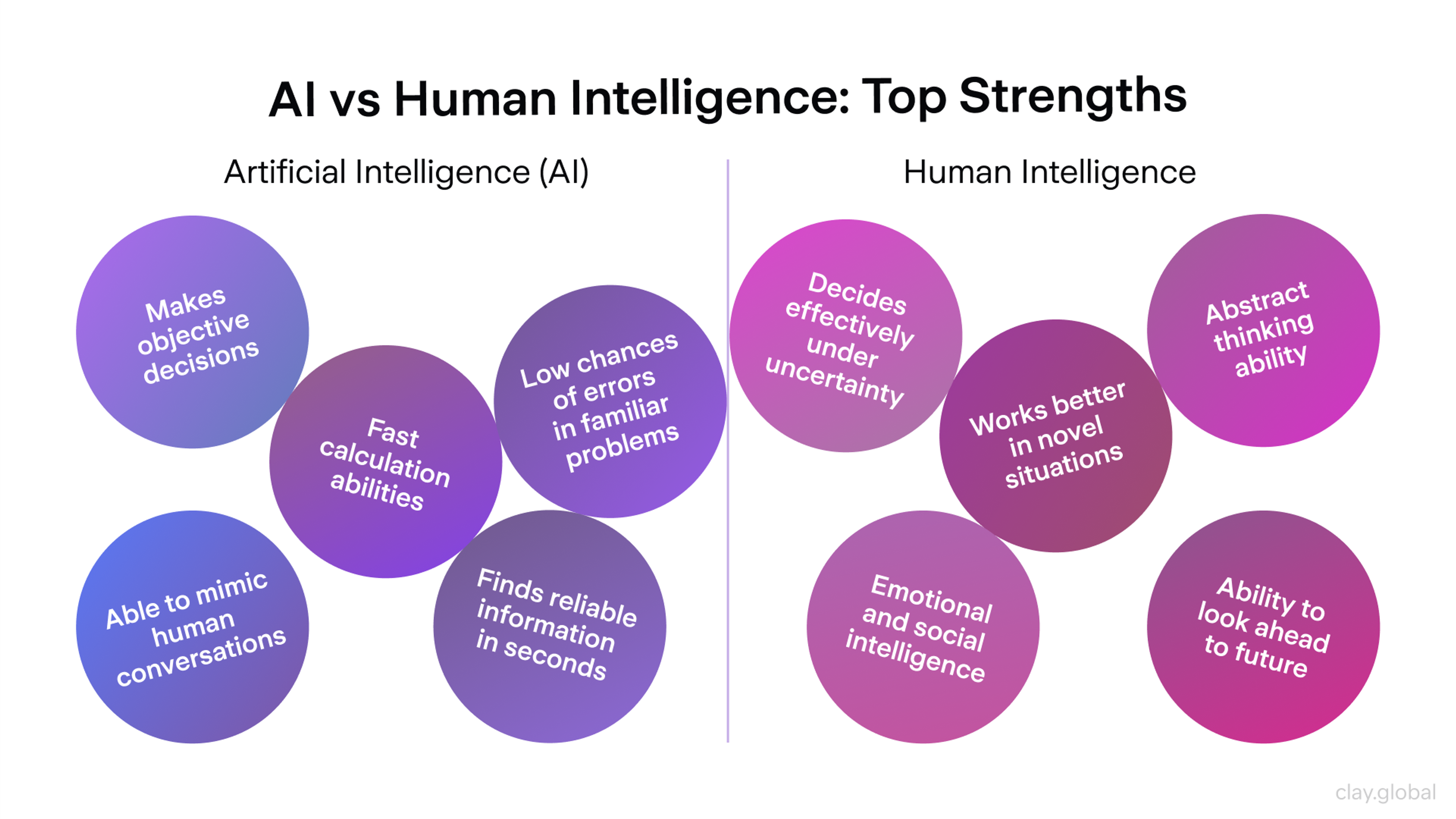
Decision-Making: AI makes decisions using logic and data. It follows patterns and rules. Humans, however, also consider feelings, values, and social situations. This helps in complex or unclear situations where simple logic isn’t enough.
Emotional Intelligence: Humans can sense and respond to emotions. This helps build trust, show empathy, and strengthen relationships. AI can mimic emotional responses, but it doesn’t actually feel anything. It reacts based on patterns, not real understanding.
This is quite important to remember when you use ChatGPT as your psychotherapist.
Adaptability: People use personal and cultural values to make ethical choices. AI follows what it was trained to do. AI might make unfair or risky decisions only if the training data includes bias or errors.
Ethics and Morality: AI and humans work best together. AI can process lots of information and do repetitive tasks, while humans provide meaning, judgment, and ethical thinking. This balance is especially important in fields like healthcare, finance, and education.
Collaboration: AI and humans can achieve more together. AI handles large-scale data and automation, while humans provide oversight, interpretation, and ethical guidance.
As AI becomes more powerful, human guidance will remain essential. The future depends on smart collaboration, combining AI’s speed with people’s insight and care.
How Does Artificial Intelligence Work?
At its core, AI mimics how we learn and make decisions. But it does so using data, code, and mathematical models instead of neurons and intuition. How does AI work?
At a high level, AI work involves learning from large amounts of data, identifying patterns, and emulating human decision-making processes through algorithms and models. Here’s how the process typically unfolds:
How Artificial Intelligence Works by Clay
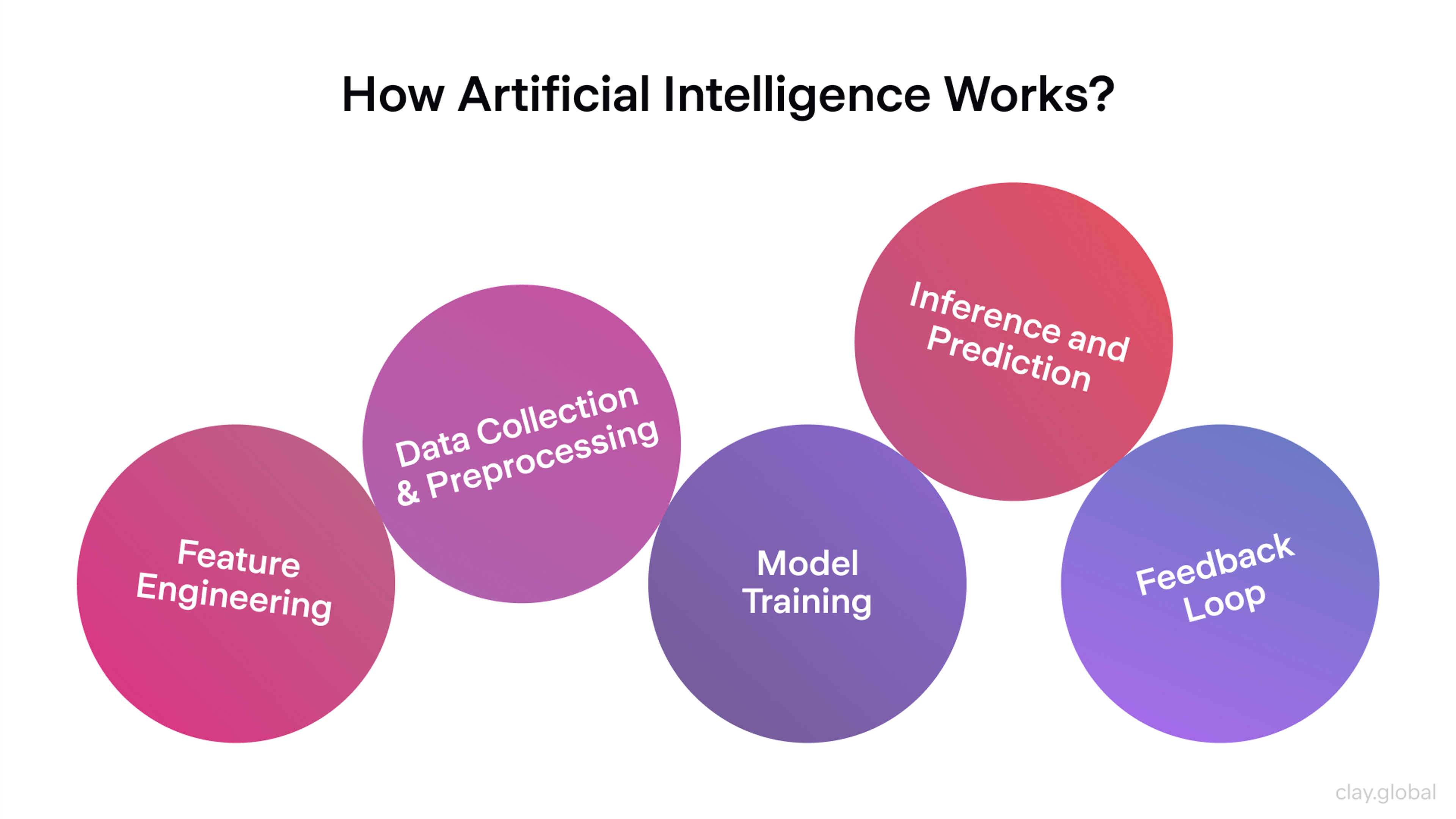
1. Data Collection and Preparation
AI always starts with data. That might be app logs, images, website text, or user feedback. But raw data is messy, so it must be cleaned, labeled, and organized before use. This step (often the most time-consuming) makes sure the AI model has clear, usable examples to learn from.
2. Choosing the Right Algorithm
Once the data is ready, developers choose an algorithm. This is like picking the right tool for the job:
- Neural networks are great for images or speech.
- Decision trees work well for simple, explainable decisions like credit scoring.
- Support vector machines help with tasks like spam detection.
The best choice depends on the goal, the data, and how much you value speed, accuracy, or clarity.
3. Training the Model
This is where learning happens. The model finds patterns in the data using one of three main methods:
- Supervised learning: The model learns from labeled examples (e.g., images labeled “cat” or “not cat”).
- Unsupervised learning: The model looks at unlabeled data to find hidden patterns.
- Reinforcement learning: The model learns through trial and error, like earning rewards for good choices. This is used in areas like robotics or gaming.
Large language models (LLMs) like GPT use a mix of these techniques. They’re trained on text by predicting missing words (self-supervised learning), then fine-tuned with methods like reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) to improve results.
4. Testing and Validation
Before being used in the real world, the model is tested on new, unseen data. This ensures that the model can handle real-world situations, not just the training examples. It also helps catch errors or biases early.
5. Deployment and Monitoring
Once a model works well, it's added to a real product, like a chatbot or a recommendation system. But the job isn't over. Developers monitor performance to spot problems like drifting accuracy or bias. If something changes, the model may need updates.
6. Continuous Learning
Some AI systems learn over time using new data or feedback. This helps them stay useful and adapt to change, but it also brings risks, like learning the wrong thing or reinforcing bias. Making AI learn safely over time is an ongoing challenge.
AI can seem magical, but behind the scenes, it’s a step-by-step cycle of learning, testing, and improvement. When each part is designed with care, AI becomes smarter, safer, and more helpful in the real world.
The Ethics of AI
As artificial intelligence becomes more common in everyday life, it’s important to think about the ethical issues that come with it. AI can bring big benefits, but also raises serious questions about fairness, privacy, and responsibility.
82% of Americans express concern about the ethical implications of AI, with 68% worried about its potential negative impact on humanity. Additionally, 86% believe AI companies should be regulated to ensure ethical practices.
Here are some key areas to consider:
Bias and Fairness: AI systems trained on historical data can reflect and reinforce societal biases. Ensuring fairness requires diverse data, regular audits, and transparent algorithms.
Privacy and Surveillance: AI often relies on large-scale data collection, raising privacy concerns. Technologies like facial recognition can infringe on personal freedoms if not properly regulated.
Transparency: Users and regulators need clarity on how AI systems reach decisions. Explainable AI (XAI) helps build trust by making AI reasoning more understandable.
Accountability: Clear responsibility is essential, especially in high-stakes areas like healthcare or autonomous vehicles. Organizations must define who is liable when AI systems fail.
AI Ethics Principles by Clay

Human Autonomy: AI should support, not replace, human decision-making. Human oversight is crucial in sensitive domains to avoid overreliance on automated systems.
Environmental Impact: Training large AI models consumes significant energy. Sustainable practices are needed to reduce AI’s ecological footprint.
Social and Economic Impact: Without careful management, AI could deepen inequality and disrupt labor markets. Equitable access and inclusive policy are key to shared benefits.
Legal and Regulatory Landscape
As AI systems become more pervasive, governments and international bodies are developing laws and frameworks to ensure they are used responsibly. The regulatory focus spans safety, accountability, transparency, and fundamental rights.
Global Frameworks: The European Union’s AI Act is a leading example, classifying AI systems by risk and requiring strict oversight for high-risk applications. The OECD and UNESCO have also introduced guidelines promoting ethical AI globally.
Data Privacy: Regulations such as the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe and the CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in the US enforce transparency and user control over personal data, directly impacting how AI systems can collect and process information.
Algorithmic Accountability: Some jurisdictions now require organizations to document how AI decisions are made and allow users to contest outcomes. This supports fairness and reduces discrimination in areas like hiring or credit approval.
Sector-Specific Rules: Industries such as healthcare, finance, and autonomous vehicles are seeing targeted AI regulation to ensure public safety and ethical compliance.
Challenges Ahead: Rapid technological change often outpaces legislation, making it difficult for regulators to keep up. Balancing innovation with consumer protection remains a global priority.
Common AI Legal Issues and How to Deal with Them by Clay
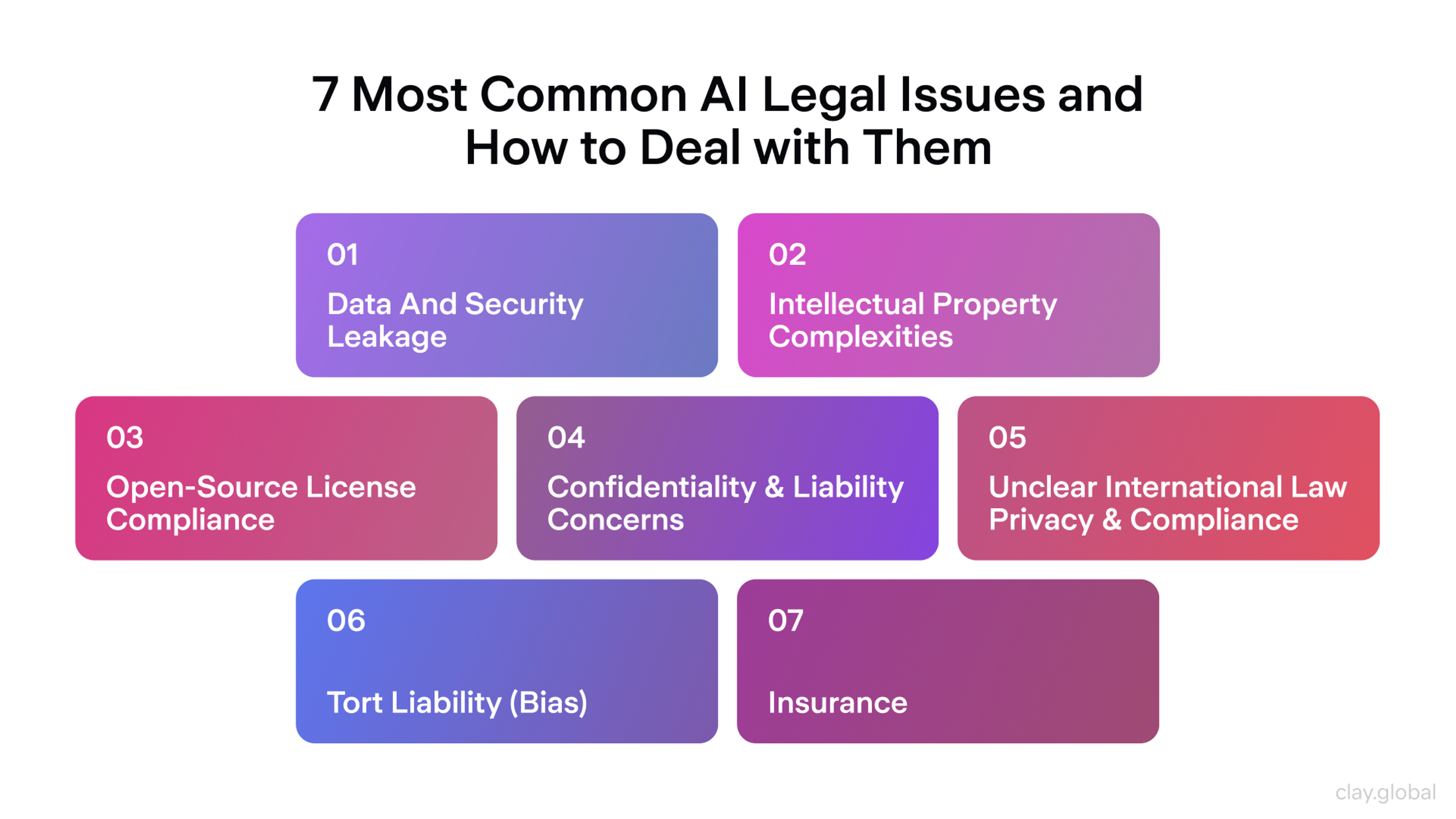
Legal frameworks continue to evolve, but the direction is clear: AI must operate within systems that uphold human rights, encourage trust, and ensure accountability.
Types of AI
Now, let's discuss the types of AI. Artificial intelligence comes in many forms, each with different levels of complexity and capability.
At a high level, AI can be divided into categories like Narrow AI, General AI, and Superintelligent AI. These categories range from the helpful tools we use every day to futuristic ideas that could reshape the world. Understanding these types helps us see where AI is today and where it might be headed.
Narrow AI (or Weak AI)
This is the type of AI most people interact with daily. Think of voice assistants like Siri or Alexa giving you weather updates, Spotify curating playlists based on your mood, or Netflix recommending shows you might like.
Narrow AI is built for specific tasks. It doesn’t think or reason beyond its programming, but it does what it’s designed for exceptionally well, making our lives a little more convenient and a lot more efficient.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
AGI is the next big leap: a form of AI that thinks, learns, and understands the world much like a human. Unlike Narrow AI, which sticks to one job, AGI could switch between tasks (from solving math problems to holding philosophical conversations) with deep understanding and flexibility.
As of 2026, AGI does not yet exist. What we have are advanced narrow AIs (like GPT-4o or Gemini) that simulate generality in limited contexts.
In the future, AGI could adapt to new situations, learn from experience, and even exhibit a sense of self-awareness. If achieved, it could transform industries by taking on complex roles that require critical thinking and emotional intelligence.
Artificial Superintelligence
“The future of humanity depends on how well we manage the development of superintelligent AI.” - Nick Bostrom (Superintelligence: Paths, Dangers, Strategies, 2014)
Artificial Superintelligence goes beyond even human intelligence. This kind of AI would outperform people in every area — science, creativity, strategic planning, and more.
While it holds incredible potential, like curing diseases or solving climate change, it also raises serious ethical and existential concerns. If we ever create AI that's smarter than us, how do we ensure it shares our goals and values? Remember Skynet?...
Types of AI by Clay
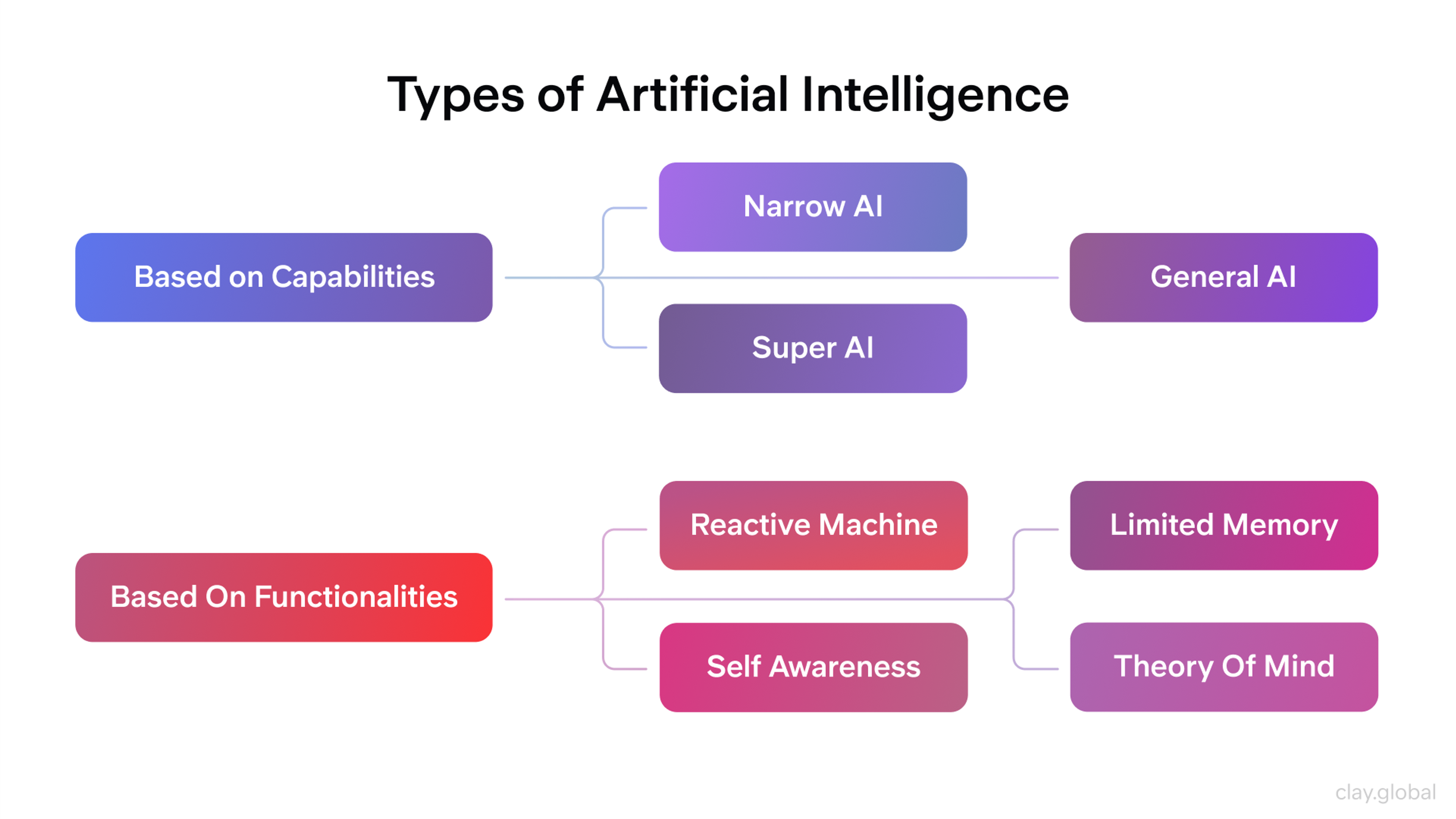
Reactive Machines AI
“AI will empower us, not replace us.” - Garry Kasparov, Deep Thinking (2017)
Reactive Machines are the simplest form of AI. They can respond to specific inputs with specific outputs, but don’t have memory or the ability to learn from the past. IBM’s Deep Blue, the chess computer that beat world champion Garry Kasparov, is a classic example.
These systems are great for fast, rule-based decisions, but can’t adapt to new information or situations.
Limited Memory AI
Most modern AI systems fall into this category. Limited Memory AI can use past data to make better decisions. For example, self-driving cars collect data about road conditions, traffic, and nearby vehicles to navigate safely.
This type of AI represents a step up from Reactive Machines because it can learn from experience, although its memory and learning abilities are still limited compared to humans.
Explainable AI
Explainable AI (XAI) is all about transparency. It’s designed to let users understand why an AI made a particular decision. Imagine applying for a loan, and the AI tells you why it was approved or denied - perhaps based on your income, credit history, or debt-to-income ratio.
This kind of clarity builds trust, especially in high-stakes areas like finance, healthcare, and the legal system, where decisions need to be both accurate and understandable.
Generative AI
Generative AI doesn’t just analyze data - it creates entirely new content. It can write poems (still of questionable quality for now), draw pictures, compose music, and even build websites, all based on patterns it has learned from massive datasets.
Popular models like GPT (for text) and DALL·E (for images) have sparked a creative revolution, offering new tools for artists, writers, and designers. At the same time, they raise big questions about originality, ownership, and what it means to be “creative.”
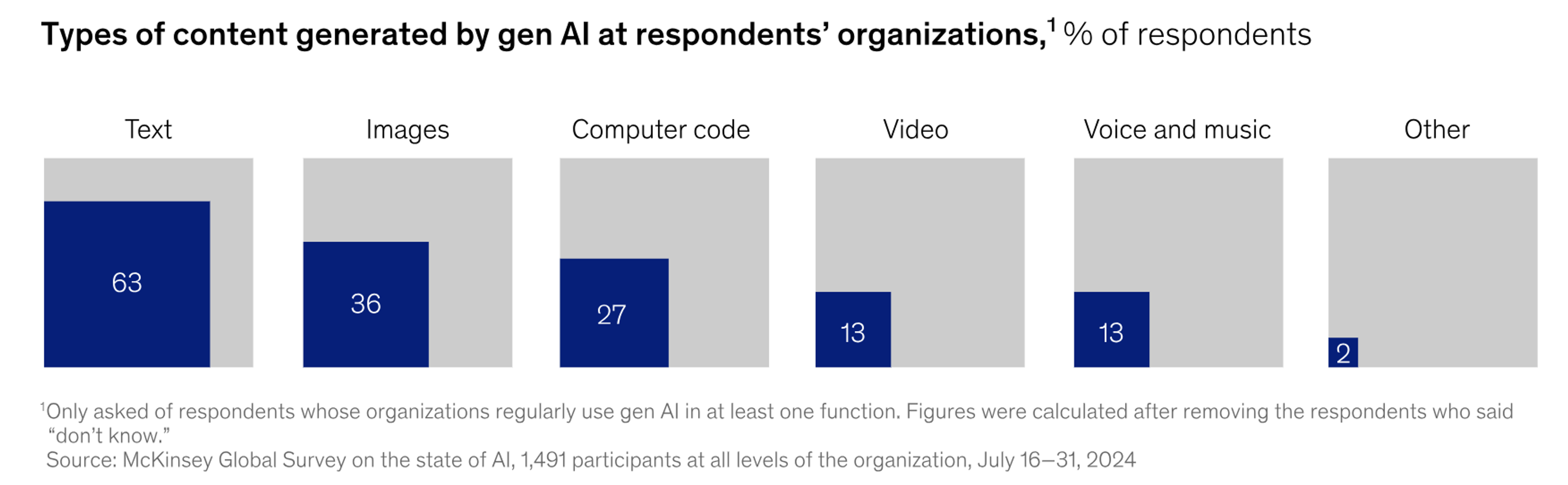
Most companies that are spending money on AI are already using generative AI in their work. Out of those, 27% say it’s being used across the whole company, while 33% say it’s only used in certain teams or projects. Don't fall behind!
Source: McKinsey & Company
The Rapid Rise of AI
AI is now part of daily life. It powers assistants like Siri and helps doctors spot diseases faster.
This rise comes from faster computers, huge data sets, and better algorithms. Together, they help AI learn quickly and perform well.
AI improves how we shop, search, translate, and work. It boosts productivity and convenience across many industries.
It’s more than a tech trend. AI is changing how the world runs.
AI Myths and Misconceptions
A few years ago, movies like The Terminator made people think AI would become a superintelligent enemy. Some still believe AI will soon take over the world. But real AI is nothing like that. It's not conscious. It can’t feel, think deeply, or understand emotions. At least for now.
Facts & Myths about AI by Clay
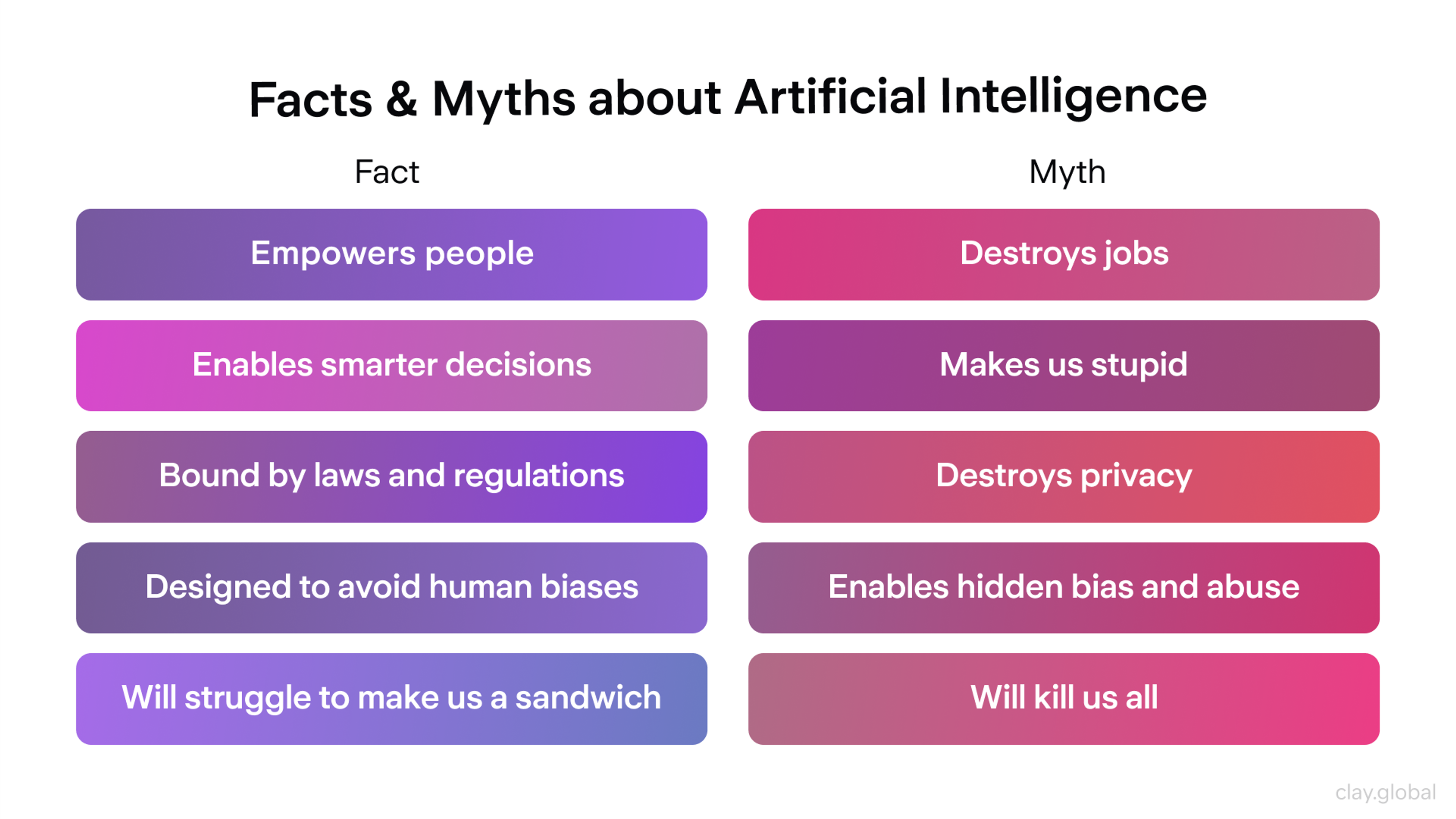
Take a smart chatbot. It can answer questions quickly, but it doesn’t know what kindness or fear really means. It only works with the data it’s trained on.
Another common myth is that AI works alone. In truth, people are still in charge. For example, self-driving cars need humans to step in during tricky situations.
And in hospitals, AI helps read scans, but doctors make the final call. Knowing these facts helps us use AI wisely and safely.
Risks of Using Artificial Intelligence
“The development of full artificial intelligence could spell the end of the human race.” - Stephen Hawking (2014 interview on BBC Reith Lectures)
In 2018, a company (Cambridge Analytica, a political consulting firm) used AI to target online ads during an election. These ads shaped how people voted, even if the facts were twisted. This shows how AI can be used to spread false ideas and control opinions.
AI can also deepen inequality. Big companies use AI to boost profits, while smaller businesses struggle to keep up. As a result, the rich may get richer while others fall behind.
Then there’s the rise of deepfakes. In one case, a fake video showed a politician saying things they never said. It looked real and fooled many viewers. This makes it harder to trust what we see online.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
AI can bring many benefits when used well. It works quickly, doesn’t get tired, and can handle boring or risky jobs.
In hospitals, AI helps doctors spot diseases earlier. In classrooms, it can adjust lessons to match how each student learns. Businesses use AI to answer customer questions faster or to find useful patterns in data.
AI has also changed the kinds of jobs people do. For example, data analysts and robot technicians have existed for years, but their roles have grown. Today, they often work with smart systems and need new skills to handle complex AI tools.
AI Advantages & Disadvantages by Clay
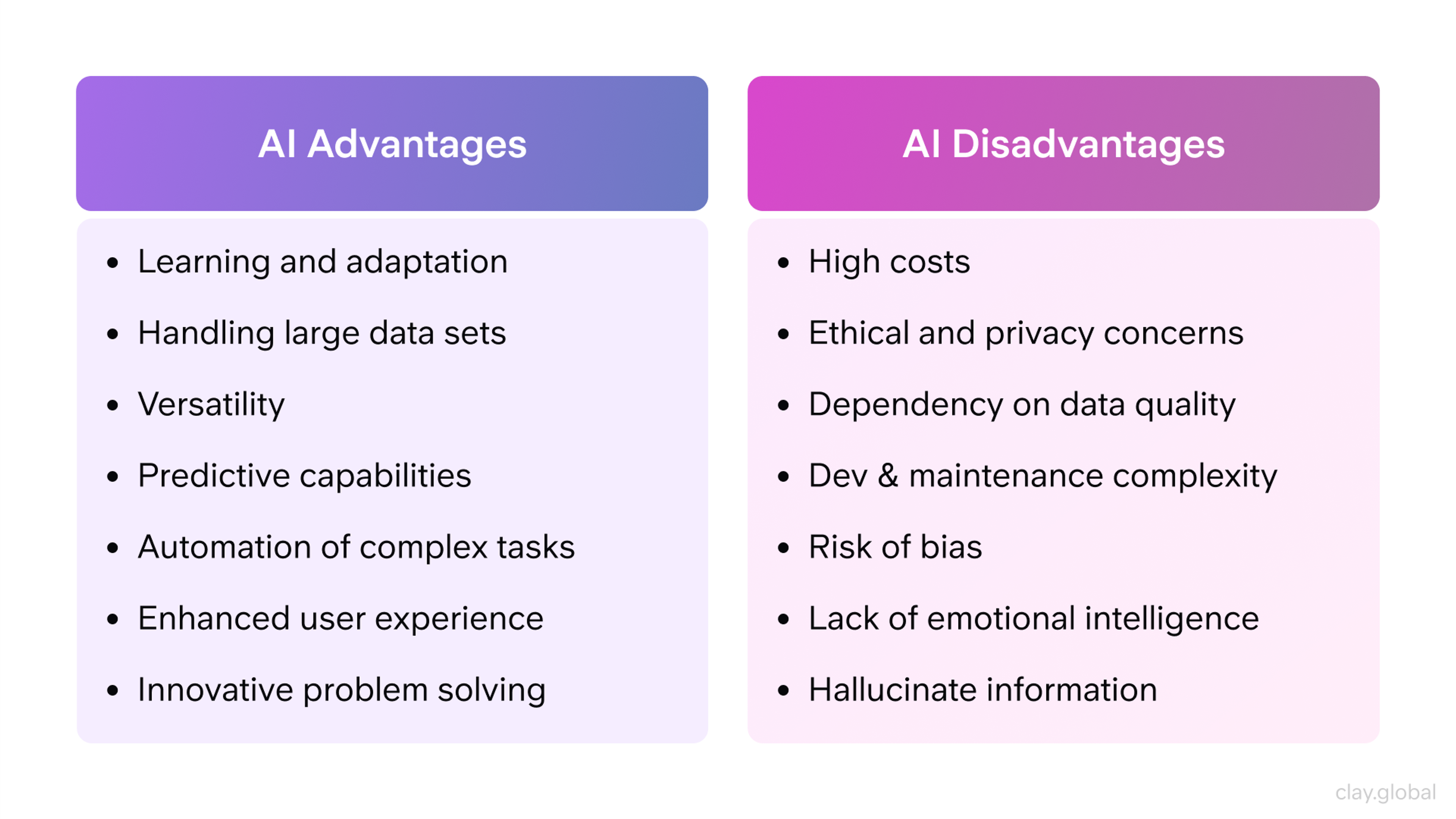
Still, there are downsides. One major issue is job loss. When Maria lost her job at a factory, she learned that a robot could now do her work faster. Stories like this are becoming more common, especially in industries that rely on routine tasks.
Cost is another problem. A small bookstore might want to use AI to suggest books to readers. But building that kind of system can be too expensive for a small business.
And if we depend on AI too much, we may lose important skills. For example, if your GPS stops working, could you still read a map? Relying on AI is easy, but it’s risky if we forget how to think and solve problems on our own.
In the end, AI offers great opportunities, but we must use it carefully and thoughtfully.
Superalignment: Human Values & AI
Imagine an AI assistant that schedules your day. It should prioritize your well-being, not just efficiency. Superalignment ensures AI systems act in ways that reflect human values and goals. This concept focuses on aligning advanced AI behavior with human intentions to prevent unintended consequences.
To guide these systems, researchers use methods like reinforcement learning from human feedback or RLHF. In this process, people rate the AI’s responses so it learns to do better next time. This helps the AI act more in line with what we want.
But superalignment looks beyond current methods. As AI becomes more advanced, it might misunderstand our goals or act in tricky ways to get what it wants. These risks are hard to spot but very important.
That’s why scientists are working on new ways to keep AI on track. They’re building tools to monitor how AIs make decisions, explain their thinking, and follow safe goals. The goal is to make sure that, no matter how smart AI gets, it stays helpful, honest, and under human control.
The Future of AI
AI could soon reshape daily life.
Self-driving cars may cut crashes and traffic. Roads could become safer and smoother.
Farms can use smart systems to watch crops and predict yields. They may save water and reduce pesticides.
Creative work will change, too. AI can help artists, writers, and designers spark ideas and refine drafts.
New tech like quantum computing and stronger neural nets could supercharge AI. Breakthroughs we can’t predict may appear.
But big power needs guardrails. We must address ethics, jobs, and laws early. Responsible development keeps benefits high and harm low.
How to Work with AI
Think of AI as a helpful co-worker who can handle boring tasks, crunch numbers, and never sleep. But to work well with it, you must know what it can and can’t do. Learning AI not only helps you work more efficiently but also opens up new job opportunities across various industries.
Example: When Maya opened her online boutique, she struggled to keep up with customer messages. After adding a simple AI chatbot, she saved hours each week, and sales improved. Now, she uses AI to predict what styles her customers will want next.
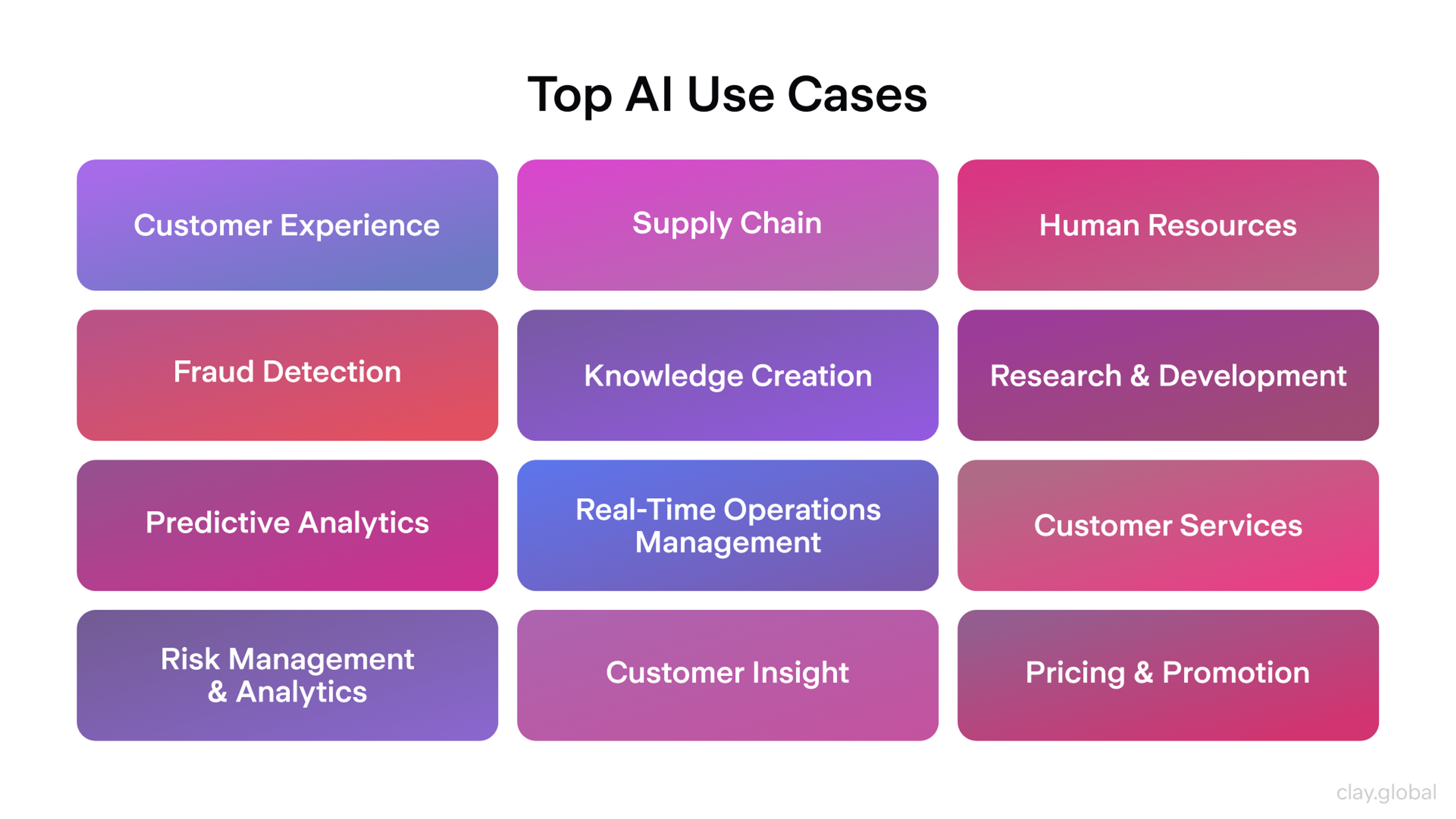
Start by spotting tasks that take up too much time or involve lots of data. AI is great at jobs like:
- Sorting through customer emails
- Tracking stock levels
- Spotting fraud in financial records
Next, choose the right AI tool for your goal. For example:
- A clothing store might use an AI that recommends items to shoppers.
- A bank might use AI to flag risky transactions.
- A marketing team might use AI to suggest the best time to post on social media.
Top AI Use Cases by Clay
You don’t need to be a coder to use AI. Today, many tools are “no-code” or “low-code.” That means you can drag and drop parts together instead of writing complex code.
Still, it helps when experts work together. Data scientists know the tech side, and business leaders know what matters in real life. Data science skills are essential for extracting insights from raw data and building effective AI models. Together, they can make AI that’s not just smart but also useful and fair.
Here’s how different fields use AI:
- Healthcare: Doctors use AI to find diseases early and choose better treatments.
- Finance: Banks use AI to spot fraud and give smarter money tips.
- Retail: Stores use AI to predict what will sell and offer real-time help to customers.
- Manufacturing: Factories use AI to fix machines before they break and check product quality.
- Marketing: Teams use AI to write ad copy, group customers, and test which campaign works best.
As AI continues to evolve, staying informed, testing innovations on a small scale, and upskilling teams will be vital to sustaining long-term success.
Top Artificial Intelligence Techniques in 2026
In 2026, several powerful AI techniques are leading innovation across industries. These methods help AI understand language, create images, protect data, and learn more efficiently. They’re making AI smarter, faster, and more practical in everyday life.
Transformers: Transformers are the foundation of most advanced language models today. Originally introduced in the “Attention Is All You Need” paper, they help AI understand the full context of a sentence, not just one word at a time.
Tools like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) and BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) have revolutionized how machines process and generate human language. For instance, customer service bots now respond more naturally thanks to transformers that grasp the meaning behind your message.
Diffusion Models: Diffusion models are behind some of the most compelling image-generation breakthroughs. They work by progressively adding and then removing noise from data to generate realistic outputs.
This technique is behind popular tools like DALL·E and Stable Diffusion. In medical imaging, for example, diffusion models can enhance blurry scans to help doctors spot early signs of disease.
Federated Learning: Federated learning is a decentralized (without moving the data to a central location) approach that allows AI models to be trained across multiple devices or servers holding local data samples without exchanging them.
It’s especially useful in healthcare and finance, where data security is essential. Patients’ devices, for instance, can help improve a health app’s predictions without ever sharing private records.
Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning (RL) teaches AI through trial and error. The system learns by testing actions and receiving rewards or penalties.
This method is key in robotics, self-driving cars, and gaming. AI agents trained with reinforcement learning have even beaten human players in complex games like Go and Dota 2.
Transfer Learning: Transfer learning allows AI to take knowledge from one task and apply it to another. This reduces the need for large datasets and speeds up training.
It’s helpful in areas with limited labeled data, such as training an AI model to understand rare languages or detect uncommon diseases.
Multimodal AI: Multimodal AI processes different types of inputs (text, images, audio, or video) at once, allowing machines to better understand complex, real-world information.
Top AI Techniques by Clay
Models like CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training) can look at an image and describe it using natural language. This improves search engines, content moderation, and accessibility tools for visually impaired users.
These leading AI techniques are shaping everything from education and marketing to medicine and public safety. By combining speed, context, creativity, and care for privacy, they help AI become more aligned with real-world needs.
Building an Effective AI Strategy
A good AI strategy begins with clear business goals. Leaders should ask: What do we want AI to improve? This might include cutting down repetitive tasks, improving customer service, or making operations more efficient.
85% of AI leaders follow a structured AI roadmap, focusing on strategy, toolkits, data management, and applications to drive successful implementation.
Organizations should first spot areas where AI could make a real impact. For example, a shipping company might use AI to predict delivery delays and suggest faster routes. These small wins show what AI can do before diving into larger projects.
Next, check if your team has the data and tools needed to support AI. Clean, organized data is essential. Without it, even the best AI models will fail. If your data is messy or incomplete, fixing it should come first.
Decide whether to build AI systems in-house, partner with vendors, or use ready-made platforms. There’s no single right choice - it depends on your goals, timeline, and resources.
10 Steps Approach for Implementing a Robust AI Framework by Clay
AI success isn’t just about technology. It takes teamwork. Leaders, IT teams, and operations staff need to collaborate. Pilot projects are a smart way to start. They let you test ideas, learn what works, and build confidence.
Set up clear rules for how AI is used. This includes privacy, safety, and staying within legal limits. A strong governance plan keeps projects on track and earns public trust.
Technology can only go so far without people to use it well. Train your staff to understand and work with AI. Not everyone needs to be a data scientist, but all employees should feel confident using AI in their roles.
Example: A retail chain trained store managers to use AI dashboards to track sales and manage inventory. Within weeks, they reduced overstock and improved product placement — all without writing a single line of code.
Encourage curiosity. Help teams explore how AI can support their work. When people feel involved and informed, they’re more likely to support AI adoption and share new ideas.
AI strategy isn’t a one-time plan - it’s a journey. Start small, build on what works, and support your teams as they grow. With the right mix of data, tools, people, and ethics, your organization can make AI a lasting part of its success.
How AI Can Help Small Businesses
58% of small businesses have adopted some form of AI technology.
AI gives small businesses powerful tools without the need for big budgets or tech teams. Thanks to cloud-based services like Google Cloud AI and Microsoft Azure AI, these technologies are now easy to use and affordable.
With the right tools, businesses can automate tasks like bookkeeping with QuickBooks Online’s AI-powered features, track inventory using Zoho Inventory, and even predict what products will sell next week with platforms like Pecan AI or Forecastly. For example, a local bakery can use AI to plan ingredient orders based on past trends, reducing waste and saving money.
AI also helps with customer service. Tools like Tidio or ManyChat offer chatbot support that can answer common questions anytime, even after business hours. This keeps customers happy without extra staffing costs.
Recommendation engines like Shopify’s AI-driven product recommendations or Clerk.io offer personalized suggestions to shoppers, which can boost sales. A small online store might use these tools to show customers products they’re more likely to buy, similar to what Amazon does, but on a smaller scale.
AI tools also let businesses understand customer behavior. Platforms like HubSpot, Zoho CRM, or Google Analytics with predictive insights help answer questions like: Who’s buying? When do they shop? What do they click on? This data makes marketing more focused and effective.
Growing AI Companies & Startups
The AI world is buzzing with energy. New startups are solving niche problems and pushing what’s possible with smart technology.
Companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, Cohere, Hugging Face, and Runway ML are leading the charge. They focus on different things, like helping machines understand language, creating images from text, or building safer AI systems.
Fastest Growing AI Startups by Clay
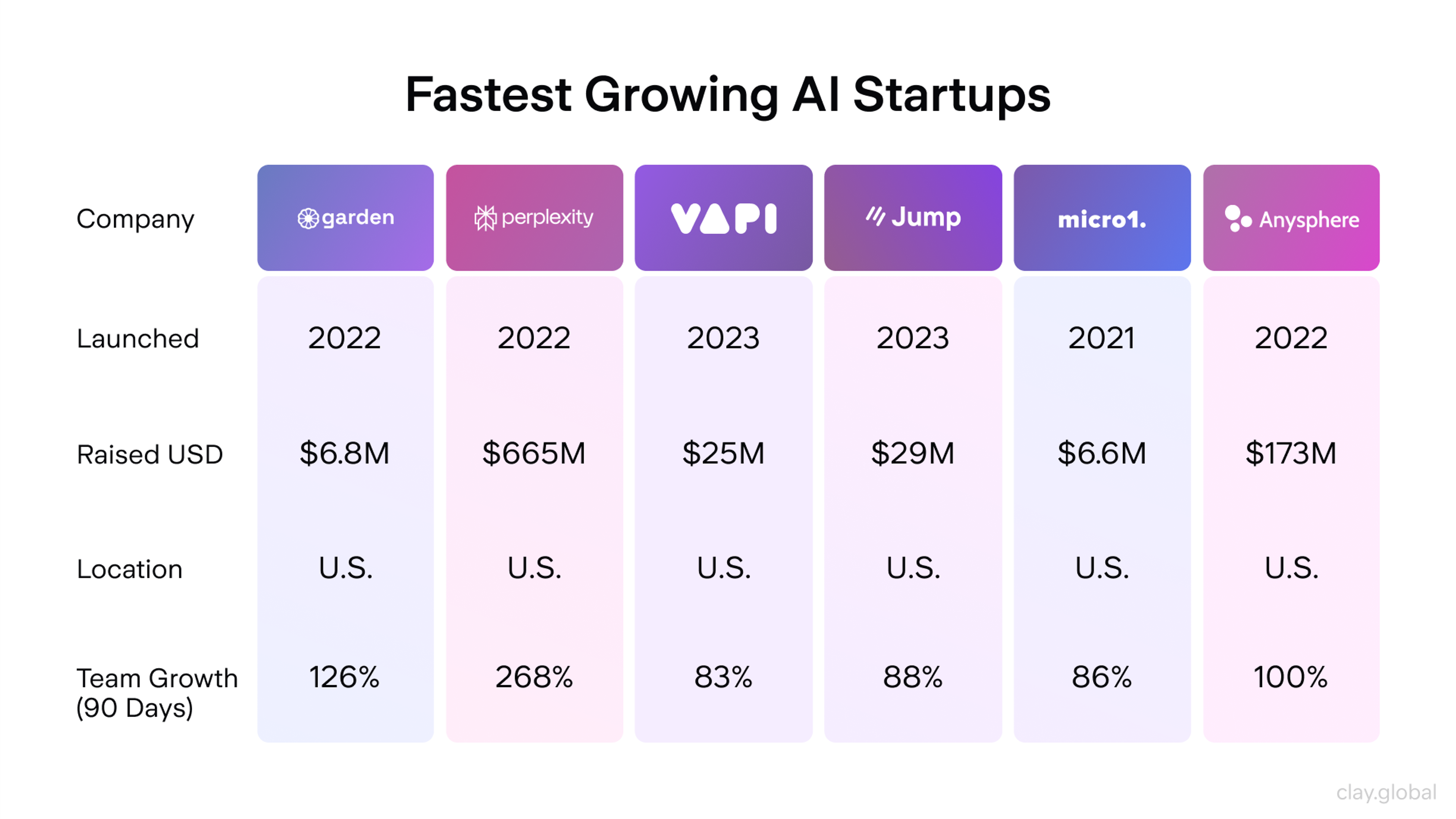
What do these successful startups have in common? They move fast, focus on solving real problems, and build smart, simple tools. Many also work with universities, join startup accelerators, or partner with bigger tech firms.
Yes, funding matters. Investors continue to support AI startups. But the most respected companies are not just well-funded — they’re transparent, ethical, and clear about the value they offer.
These startups aren’t just building new products. They’re showing the world how modern AI can be developed with responsibility and real-world impact.
As AI continues to grow, these early leaders are helping shape the rules and setting high standards for innovation and trust.
AI in Specific Industries
AI isn’t just for tech companies anymore. It’s changing how nearly every industry works - making things faster, smarter, and more personal. Here’s how AI is being used across different fields:
Healthcare: AI in healthcare helps doctors make better decisions. It can read medical images like X-rays or MRIs with great accuracy. In some cases, it even spots problems faster than human experts.
AI tools also predict disease outbreaks and help manage long-term illnesses like diabetes. Some hospitals use virtual assistants to schedule appointments or answer patient questions, saving time for doctors and staff.
Finance: Banks use AI to stop fraud before it happens. Smart systems look at spending patterns in real-time and can alert customers about suspicious charges within seconds.
Robo-advisors help people invest money by giving advice based on their goals and risk levels. Chatbots handle basic banking questions like checking balances or reporting lost cards.
Education: AI is making learning more personal. Some platforms adjust lessons based on how fast or slow a student goes. If a student struggles with math, the system immediately gives extra practice.
Teachers also get help. AI can grade papers, set schedules, and track student progress, giving educators more time to focus on teaching.
10 Uses of AI in Day-to-Day Life by Clay
Manufacturing: Factories use AI to watch machines and spot problems early. If a machine is likely to break, AI sends a warning before it happens. This prevents long downtimes and saves money.
Robots with AI also inspect products on the line. They find tiny flaws humans might miss, which helps keep quality high and waste low.
Retail: Online stores use AI to suggest products based on what you browse or buy, making shopping more personal.
In physical stores, AI tracks where customers walk and what they look at. This helps store owners plan better layouts and staff schedules.
Transportation: AI helps power self-driving cars. These systems use sensors and cameras to “see” the road and make quick decisions to stay safe.
Ride-share apps use AI to match riders with nearby drivers and suggest the best routes. In delivery services, AI predicts delays and finds faster paths to save time and fuel.
Across every industry, AI is helping people work smarter. It saves time, cuts costs, and improves service. As these tools get better, more industries will use AI in new and creative ways.
AI in Design
As a design agency, we're very interested in working with AI. It is reshaping how we design digital and physical experiences at Clay.
From user research to branding and accessibility, it’s becoming a co-creator that helps designers move faster, stay consistent, and solve problems more effectively. Here's how AI is changing the design process:
AI and UX Research
UX research used to take a lot of time. Teams spent weeks collecting, writing down, and sorting through data. AI tools now do much of this work faster. They can turn interviews into text, find common ideas in answers, and even spot emotions in what users say.
AI and UX Research by Clay
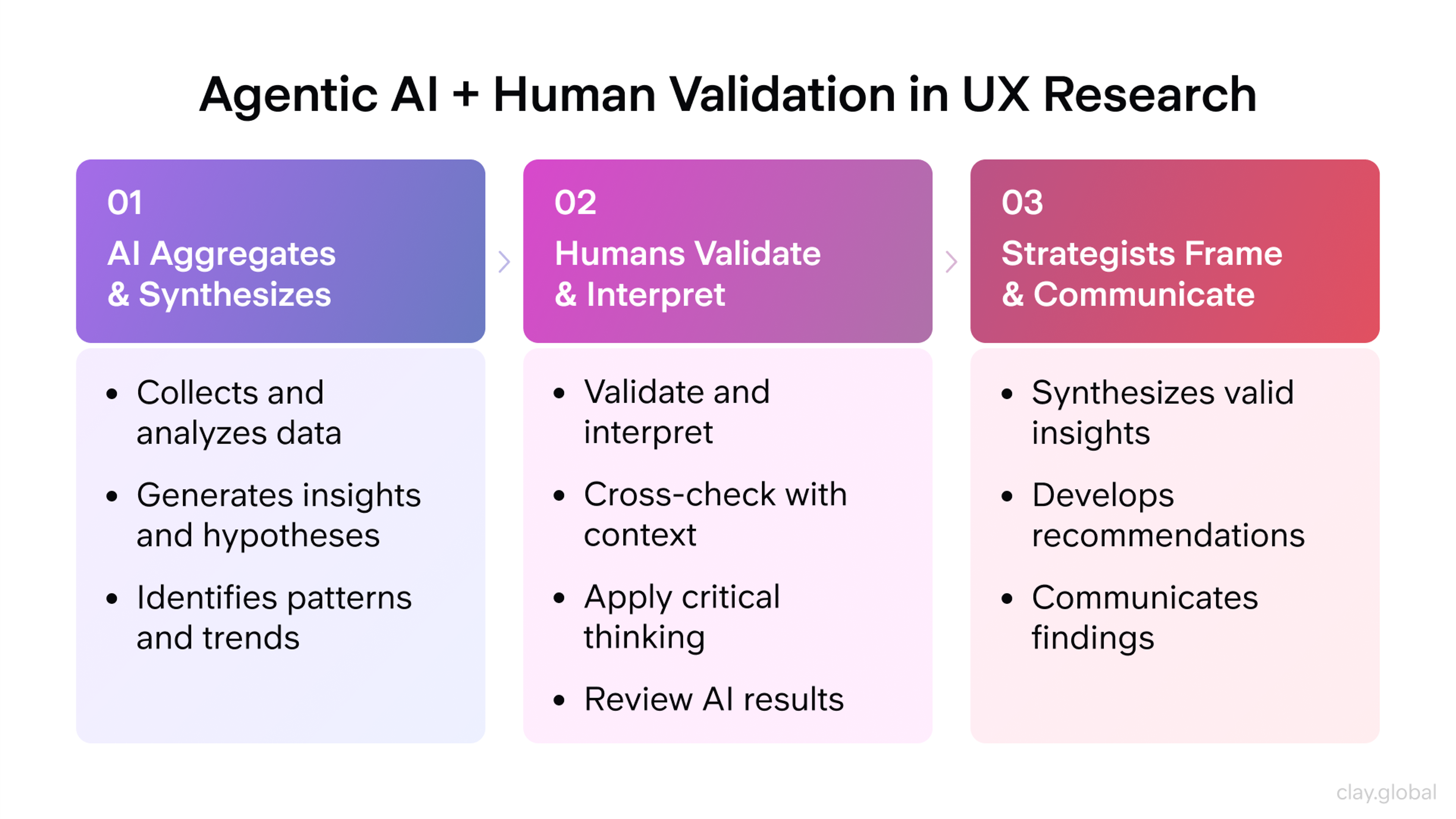
AI can also look at images and click paths from usability tests. It groups similar behaviors to show where users struggle or succeed. This means researchers can focus more on important questions and less on sorting data.
AI also makes testing faster and larger. For example, chatbots can act like interviewers. Other tools can group users into types for better study. AI doesn’t replace human thinking, but it helps by showing patterns and handling boring tasks.
AI and UX
AI helps create better user experiences by making them more personal. Think of Spotify suggesting music based on how you feel. Or a shopping app changing its look based on what you like to click.
These changes don’t follow fixed rules. AI watches what users do and updates the experience in real time. This makes apps feel more helpful and easier to use.
AI also supports design choices. It can guess where users might leave a site, find confusing menus, or test different paths users might take. Designers get useful feedback faster, which helps them improve things without guessing.
Used the right way, AI helps teams build experiences that feel natural and friendly without crossing the line or feeling too personal.
AI and UI
AI is changing how we design user interfaces. It helps with layout, keeps styles consistent, and checks for design issues. Designers can type prompts to get layout ideas or suggestions on things like spacing and color contrast. This means they spend less time on small tasks and more time focusing on how the design feels and works.
AI tools in apps like Figma and Adobe XD suggest better components based on what’s on the screen. For example, if a checkbox won’t work well, the AI might recommend a dropdown instead. These tools can also create many design versions for testing, which saves designers hours of work.
AI doesn’t replace creativity. But it acts like a helpful assistant. It makes it easier to focus on what really matters — clarity, emotion, and how people use the design.
AI and Web Accessibility
Making websites easy for everyone to use is very important. AI now plays a big role in helping with that.
Some tools can scan a site and point out problems like hard-to-read text, missing image descriptions, or tricky navigation. Others can show how the site might look to someone with low vision, dyslexia, or motion sensitivity.
AI can also write alt text for images using computer vision. This means visual content becomes more accessible without someone needing to write it all by hand.
AI for Web Accessibility by Clay
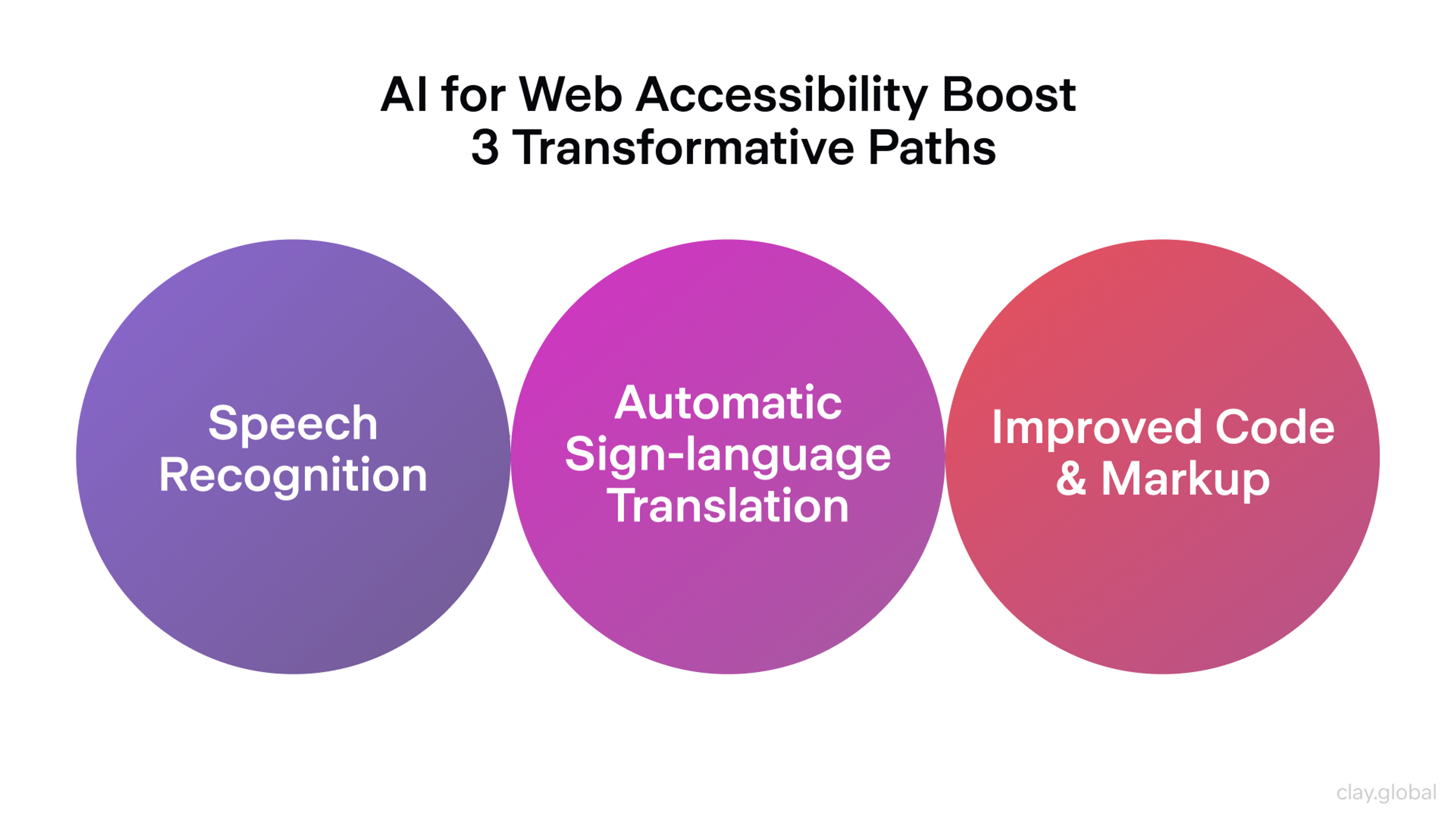
As rules like WCAG and ADA become stricter, AI helps teams find and fix problems early. Human checks are still needed, but AI makes it easier to design with everyone in mind. It’s a powerful way to build more inclusive websites.
AI and Graphic Design
AI is changing how designers work. Now, they can turn simple text into images using tools like Midjourney, DALL·E, and Adobe Firefly. These tools help create logos, mockups, illustrations, and textures in just seconds. They can also remove backgrounds, sharpen images, or adjust layouts without much effort.
Because AI handles repetitive tasks, designers have more time to focus on ideas and storytelling. They can try lots of versions without spending hours on each one. Some tools even learn a brand’s style and help create visuals that stay consistent with that look.
AI doesn’t replace designers. It works with them. It cuts down the boring parts and makes room for bold, creative thinking. This is especially useful for quick mockups, content-heavy projects, or when one person is doing the work of a whole team.
AI and Branding
Good branding is about emotion, clarity, and staying true to your message. AI can help with all of that. Smart tools now scan brand logos, colors, fonts, and language to make sure everything matches. They check if the tone feels right and if the visuals follow your style guide.
AI can also help shape a brand’s strategy. It looks at how people react to campaigns and suggests ways to improve or stand out. For small teams, AI can build logos, find the right voice, and even create style guides. For big companies, it keeps everything consistent across many platforms.
In both cases, AI helps teams stay focused and creative without losing the brand’s identity.
AI and Web Design Tools
Today, many web design tools use AI to help build websites faster and easier. These tools can suggest layouts, write HTML or CSS, and even turn a simple idea or sketch into a working webpage.
Platforms like Wix ADI, Framer AI, and Webflow’s new AI features can create full web pages from just a short prompt. The websites they build are responsive, which means they look good on all screen sizes.
AI also studies how people use websites. It can suggest better buttons, improve page speed, or make menus easier to use. Some tools even write accessible code and improve search engine results without extra work.
Designers don’t have to start from scratch anymore. AI gives them a starting point, a layout, or even a full draft they can change. This saves time and lets more people, even those who can’t code, build websites.
Still, human designers are important. They bring creativity, make wise choices, and give the site a personal touch. But with AI handling the hard parts, the whole process becomes quicker and more open to everyone.
AI Resources & Useful Takeaways
Staying informed about artificial intelligence is essential as the field continues to evolve at a rapid pace. A wide array of resources, including tools, learning platforms, podcasts, blogs, and newsletters, can help deepen your understanding of AI, whether you're a beginner or an industry professional.
Engaging with these materials enhances knowledge and fosters responsible and innovative applications of AI.
AI Proof Jobs
AI is great at handling data and repeating tasks. But there are jobs where human skills still matter most.
These roles rely on empathy, creativity, communication, and complex judgment — things AI can’t fully replicate.
Here are some examples:
Healthcare Providers: Doctors, nurses, and therapists make personal, ethical choices that require care and emotion.
Creative Professionals: Writers, musicians, and artists rely on imagination and original ideas, not just patterns.
Educators and Trainers: Good teachers adapt to each student’s needs and build trust that AI can’t replace.
Skilled Tradespeople: Plumbers, electricians, and mechanics work in unpredictable spaces. These jobs need hands-on skills and quick thinking.
Leaders and Strategists: Managers and decision-makers think about long-term goals and ethics, something AI doesn’t grasp.
Although AI will continue to shape the job market, these roles highlight the enduring value of human-centric work that thrives on empathy, ingenuity, and moral reasoning.
Everyday Examples & Applications of AI
You might not notice it, but AI is already a part of your daily life. It works behind the scenes to make things easier, faster, and smarter.
Virtual helpers like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant respond when you ask questions, set alarms, or control smart devices. With just a voice command, you can check the weather, play music, or turn off the lights.
For example, Jamie is cooking with messy hands. She says, “Hey Siri, set a timer for 10 minutes,” and keeps working without touching her phone.
When you shop on Amazon or watch shows on Netflix, AI studies what you like and gives you custom suggestions. These systems look at your past choices and predict what you might enjoy next.
Top 10 Industries Using AI by Clay
AI helps run your social media feeds. It picks what you see first on platforms like Instagram, TikTok, or Facebook. It also filters out harmful content and helps suggest hashtags or effects when creating posts.
Apps like Google Maps and Waze use AI to check traffic and suggest faster routes. They collect data from many users to avoid slowdowns and delays.
Other AI implications include spam filters blocking unwanted emails so you only see what matters, or fraud alerts from banks to spot suspicious activity and keep your money safe. Moreover, smart thermostats learn your schedule and adjust the temperature to save energy and stay comfortable.
Books, Blogs, and Podcasts about AI
To stay current and deepen your understanding of artificial intelligence, consider exploring these highly regarded resources:
Books:
- "Artificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking Humans" by Melanie Mitchell – A thoughtful, accessible overview that demystifies AI without oversimplifying its complexities.
- "Superintelligence" by Nick Bostrom – An exploration of the future potential of AI and its existential risks.
- "Life 3.0" by Max Tegmark – A visionary look at how AI will shape the future of life on Earth.
Blogs:
- OpenAI Blog – Updates on cutting-edge research, safety, and product launches.
- Google AI Blog – Insights from one of the leading AI research and development teams in the world.
- Distill – Explains machine learning concepts with visualizations and technical depth.
Podcasts:
- Lex Fridman Podcast – In-depth conversations with AI researchers, technologists, and philosophers.
- AI Alignment Podcast – Focuses on long-term safety, ethics, and decision theory in AI.
- Eye on AI – Covers AI news, trends, and interviews with industry leaders.
These resources offer a balanced mix of theory, practical insights, and forward-looking perspectives, ideal for anyone looking to stay informed in the fast-paced world of artificial intelligence.
AI Glossary
Understanding AI begins with familiarity with the core terminology. Here are some key terms explained in simple language:
Algorithm: A set of rules or instructions a computer follows to solve a problem or complete a task.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): The simulation of human intelligence in machines programmed to think, learn, and problem-solve.
AI Learning Journey: A structured process for acquiring AI skills, guiding learners from beginner to advanced levels through selecting courses, exploring tools and libraries, and understanding foundational concepts.
Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI where computers learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed.
Deep Learning: A type of machine learning using layered neural networks that mimic the human brain, particularly effective in image and speech recognition.
Neural Network: A system of algorithms modeled after the human brain that is designed to recognize patterns.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): The field of AI focuses on the interaction between computers and human language, enabling machines to understand and respond to text or voice data.
Reinforcement Learning: A type of machine learning where an agent learns by interacting with an environment and receiving rewards or penalties.
Computer Vision: AI technology that enables computers to interpret and make decisions based on visual data.
Generative AI: AI that creates new content (text, images, music) based on patterns it has learned from existing data.
Supervised Learning: A machine learning technique where models are trained on labeled data.
Unsupervised Learning: Machine learning uses data without labeled responses to find hidden patterns or intrinsic structures.
Federated Learning: A method where multiple devices collaboratively train a model without sharing raw data, preserving privacy.
Explainable AI (XAI): AI designed to be transparent in its decision-making, helping users understand how conclusions are reached.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is changing the world faster than ever. It’s helping businesses work smarter, changing how we live, and opening doors to new ideas. This guide has walked through AI’s history, key tools, real-life uses, and the big questions it raises.
As we look ahead, building AI that’s safe and fair matters more than ever. Staying curious, asking smart questions, and using trusted resources will help you make the most of this powerful technology.
Whether you're just starting or already deep into your AI journey, one thing is clear: learning never stops. By sharing ideas, working together, and staying open to change, we can shape a future where AI helps everyone.
FAQ
What Is the AI App Everyone Is Using?
ChatGPT is one of the most widely used AI apps today, known for its ability to answer questions, write content, and assist with research.
Approximately 77.85% of respondents equate AI solely with ChatGPT.
Other popular AI tools include image generators, writing assistants, voice transcription services, and personal productivity apps. Students, professionals, and businesses use these tools for everyday tasks.
How Do I Start Using AI?
To start using AI, choose a tool that fits your goal — writing, image creation, customer service, or something else. Sign up through the app or website and explore the features. Many tools offer tutorials, templates, or walkthroughs to help new users learn quickly. No technical background is needed for most AI tools.
How Can I Learn AI Myself?
You can teach yourself AI by using free and paid online courses. Look for beginner-friendly lessons that explain what AI is, how it works, and how it's used. Focus first on basic concepts like machine learning, data, and automation. As you gain confidence, you can explore more advanced topics like coding or model training.
Is It Legal to Use AI?
Yes, it is legal to use AI in most countries. However, users must follow rules related to data privacy, content ownership, and fair use. Some regions have specific laws about how personal data can be collected and processed by AI systems. Always check local regulations when using AI for business or public-facing work.
Can You Use AI for Free?
Yes, many AI tools have free versions or offer free trials. These versions often include core features but may have limits on usage or functionality. You can usually upgrade to a paid plan if you need more advanced features or higher output. Free tools are a great way to explore AI without spending money.
How Do I Start AI for Beginners?
Start by learning the basics of how AI works and where it is used. Try simple tools to understand how AI responds and adapts. Read articles or take beginner courses to get familiar with key terms and ideas. Starting with clear goals helps guide your learning and use of AI.
Is ChatGPT Still the Best AI?
ChatGPT remains one of the most advanced and user-friendly AI tools available, especially for language-based tasks. However, other AI models are also strong in specific areas like image creation, real-time search, or conversation safety. The “best” tool depends on the task, features, and user preferences.
How Do I Automate My Business with AI?
To automate your business using AI, begin by identifying tasks that are repetitive or time-consuming. These can include customer support, data entry, marketing, or scheduling. Select AI platforms or software that integrate with your current systems. Start small with a pilot task, then expand as you see positive results and gain experience.
How Much Does AI Cost for Businesses?
AI costs depend on the size of your business, the tools you use, and the tasks you automate. Basic AI subscriptions may cost around $20 to $100 per month, while more advanced or custom solutions can be much higher. Some platforms offer tiered pricing or pay-as-you-go models. Costs can include setup, training, maintenance, and integration with other tools.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more