Color theory explores how harmonious color combinations evoke emotions and visual appeal. It involves understanding the relationships between colors on the color wheel, including primary colors (red, blue, yellow) and secondary colors (orange, green, purple).
Neutrals like black, white, gray, and brown serve as accents or backgrounds. By mastering these principles, designers can create visually attractive and effective websites.
What Is Color Theory?
Color theory is a framework of guidelines and concepts that govern how colors interact in visual media, from painting and graphic design to digital interfaces.
It explains why certain hues complement each other, how combinations can evoke specific moods, and how we perceive balance and contrast in a composition.
The Importance of Color Theory in Web Design
Grasping color theory is vital when you’re building a website or crafting any user interface. It lets you guide visitors’ eyes to key elements, reinforce your brand’s personality, and create an emotional connection that keeps people engaged. By choosing the right primary and secondary hues, you establish visual hierarchy and design harmony, ensuring your content feels both coherent and compelling.
Color theory transforms a simple layout into an immersive experience when applied thoughtfully. A well-balanced palette makes navigation intuitive and fosters a sense of trust and familiarity. Website designers who master these principles can turn every page into a vibrant invitation for users to explore, interact, and return.
Color Wheel Illustration by Clay
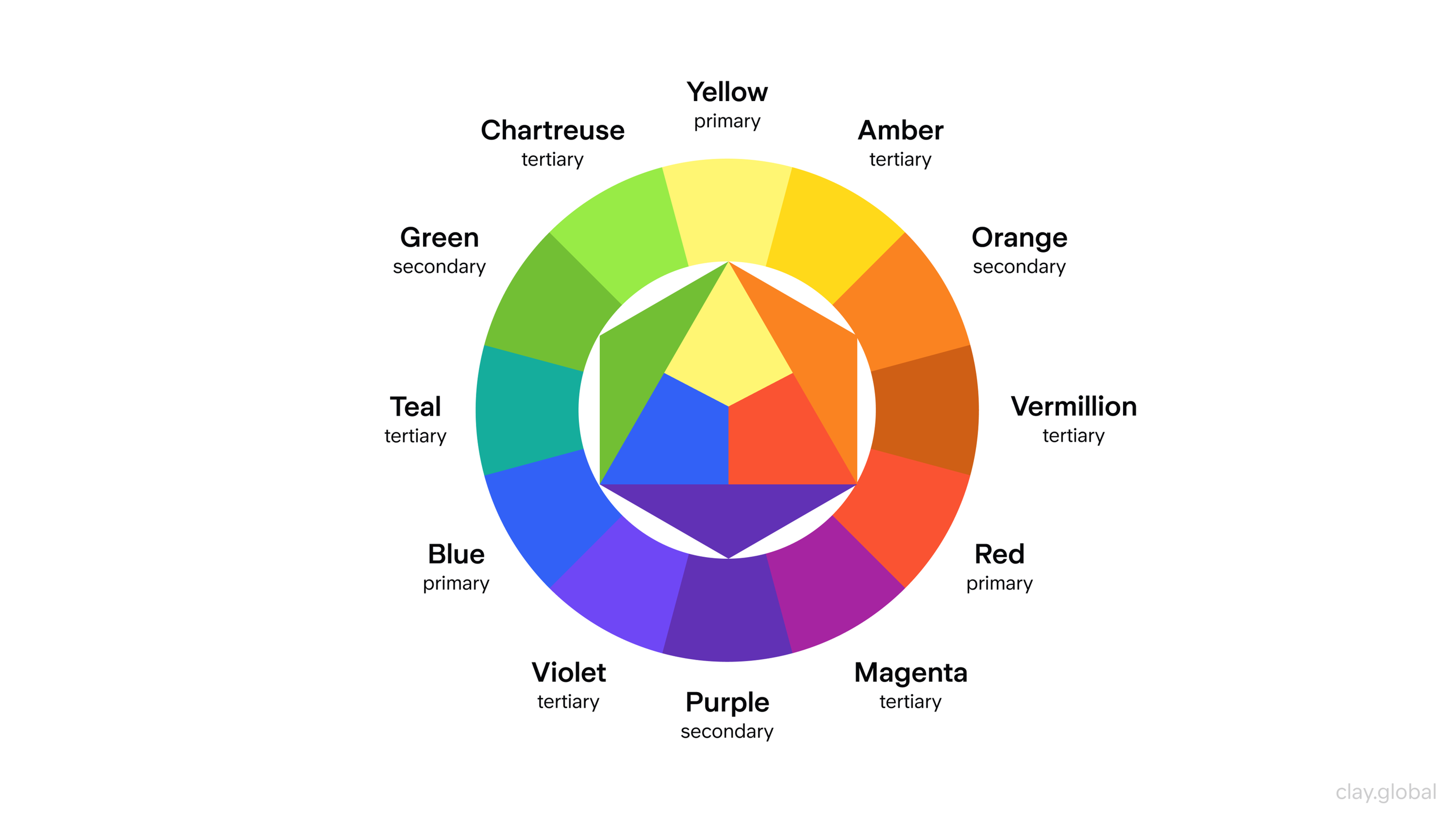
Color Theory Terms and Fundamentals
Primary Colors
Red, yellow, and blue are Primary colors. Since primary colors are the first colors you learn to use, you have to use them to learn to use the other colors in the rainbow.
Each primary color is separated from the others on the color wheel. If you combine primary colors, you can get the other colors in the rainbow (or, as they are called in color mixing, secondary colors). You can further build your palette with tints and shades to alter your colors.
Secondary Colors
If you combine primary colors, you get secondary colors: orange (red + yellow), green (blue + yellow), and purple (red + blue).
With secondary colors, you gain greater range and diversity, helping create balance in your color combinations.
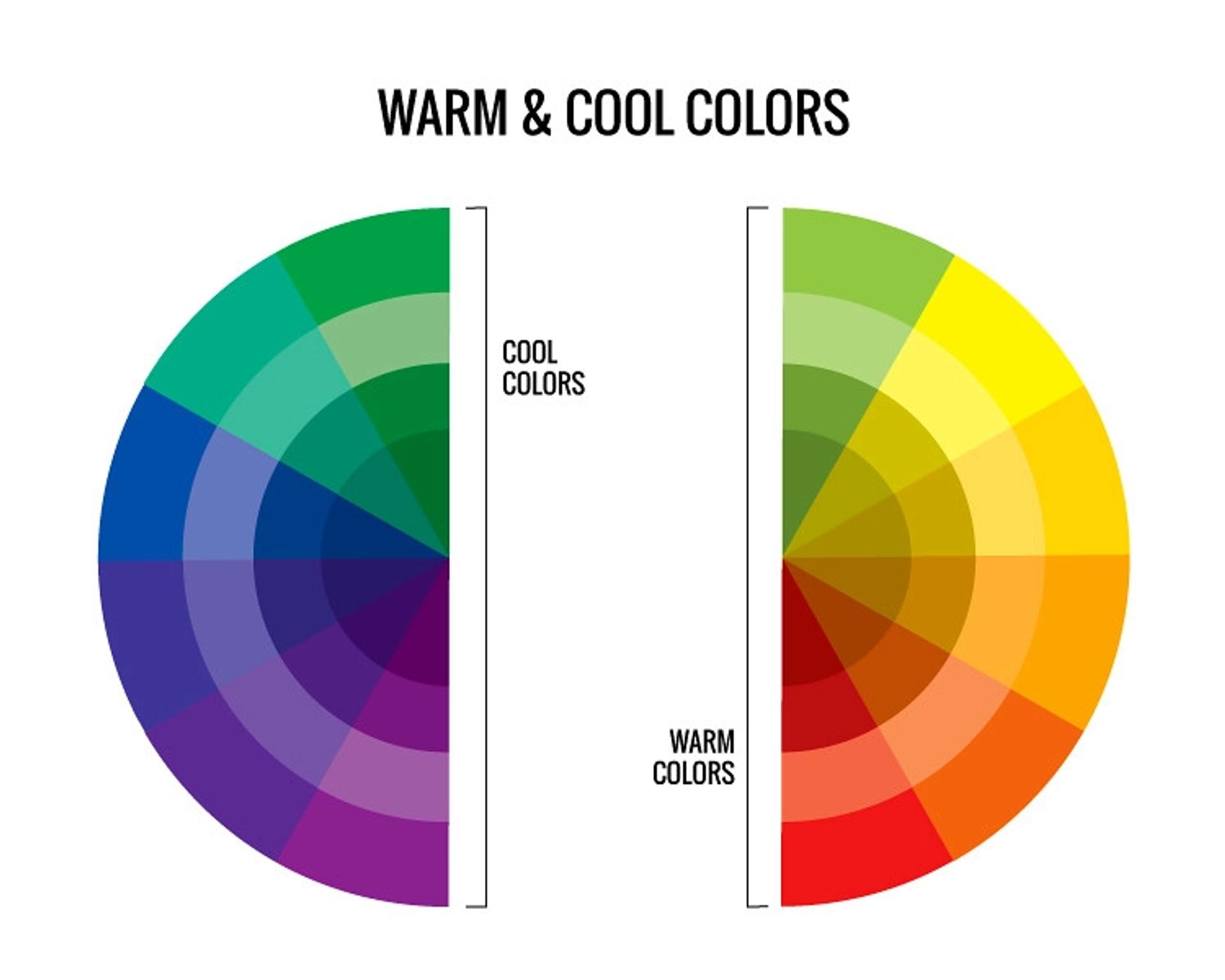
Color Warmth
Colors can be classified as warm or cool. Warm colors include red, orange, and yellow, and can even include a warning light because they are energetic and inviting.
They are also used in cool colors, such as blue and purple, which can create a calm or formal feeling. When only warm or only cool is used in a color palette, it can create colors that are too intense or too cool, or a lack of color. A combination of both can create a better balance.
Source: Flickr
Shades and Tints
A color + black = a shade. A color + white = a tint. By using many tints and shades of a color, you can learn how it behaves and also learn when it is better to bring in other colors to create a greater contrast.
Source: Flickr
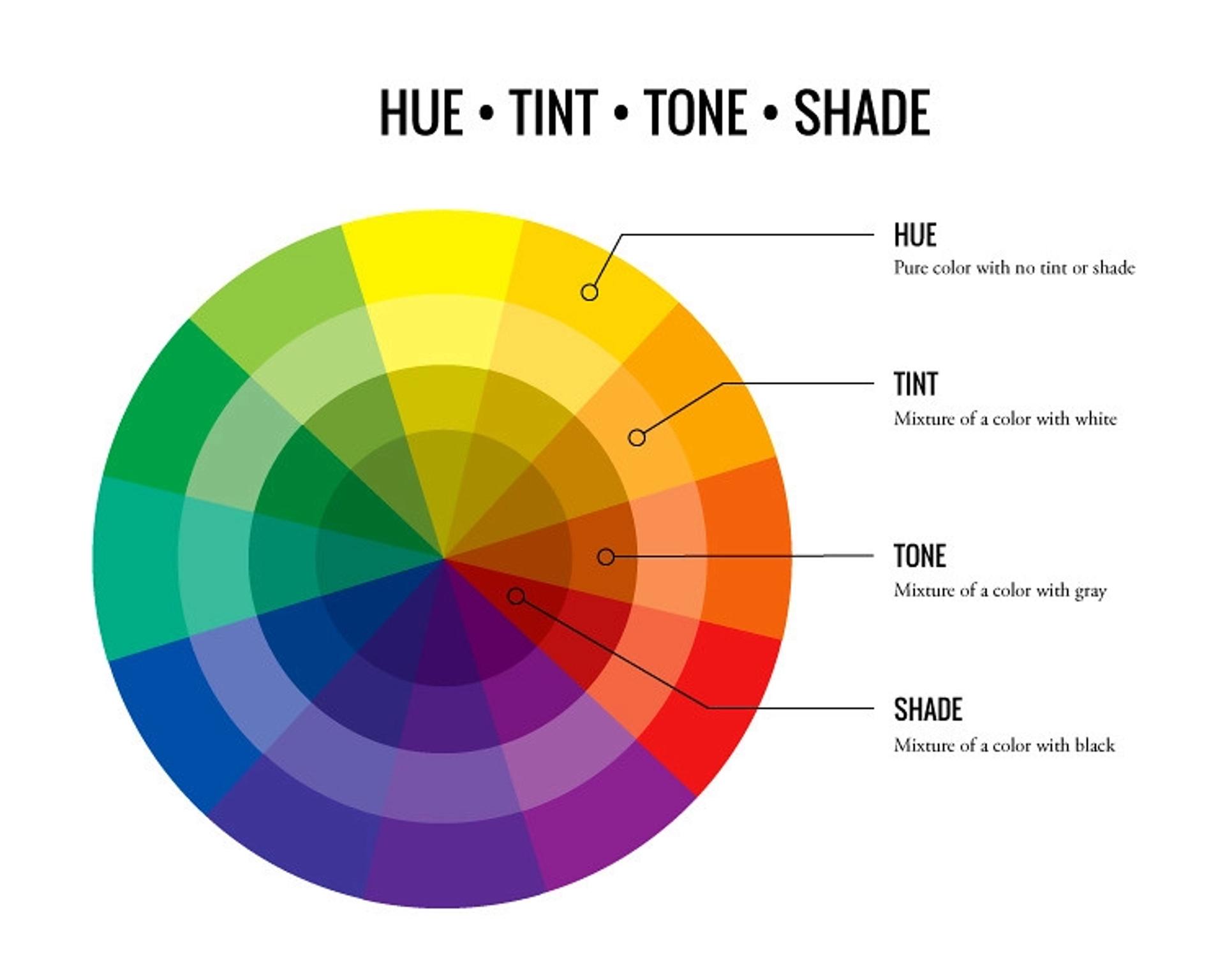
Hue, Lightness, Saturation, Gradient and Contrast
To an artist, hue is just where a color sits on the wheel. Think of it as the shortcut to knowing which family the color belongs to — even if it’s been tinted, shaded, or brightened, the hue still hints at the main character underneath.
Brightness is more flexible. It can refer to tints, like when we add white to a color, or shades where black or gray is mixed in. Some folks use brightness and lightness in the same conversation, and as long as everyone knows we’re counting how much light reflects off the surface, they’re basically interchangeable.
Saturation measures the intensity of color. Decreasing it makes the color less bright and duller, while increasing it makes it more vibrant. This could be considered a measure of how thickly concentrated this stuff is, so "saturation" fits. As you add more drops of food coloring to water, its color becomes saturated.
Source: Pinterest
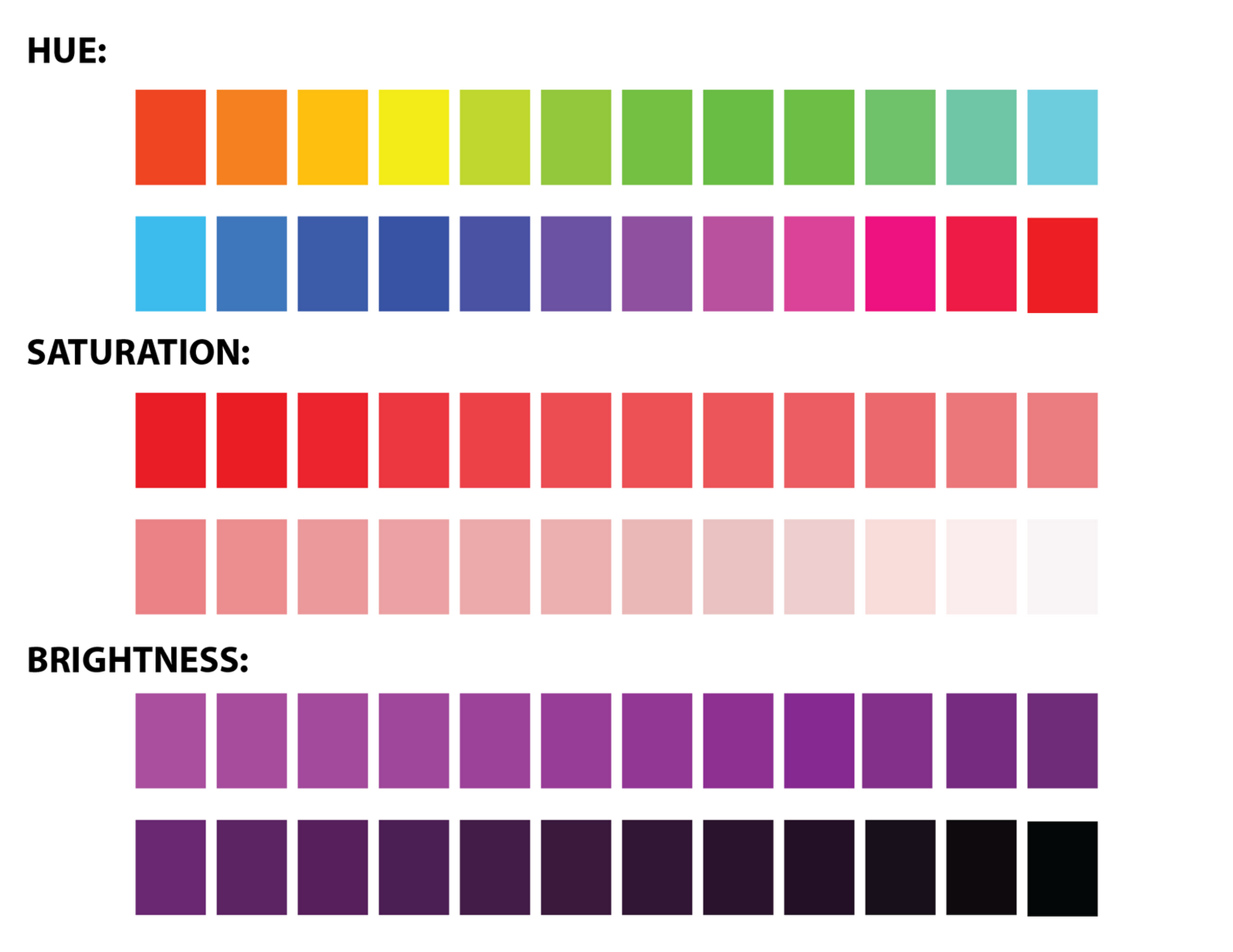
Contrast measures how distinct elements in two colors are from each other. Text on webpages usually needs to have high contrast against backgrounds, leading to web design trends in which most websites are either a "Light Theme" or "Dark Theme."
One scenario comprises a light background with black or dark font. Another consists of a dark background, white font, and very light text.
Gradients play a crucial role in digital art and design, seamlessly blending hues, lightness, and saturation to create visually appealing transitions. Artists utilize gradients to add depth and dimension to their work, achieving smooth shifts from one color to another.
Using Color Theory in Web Design to Create Effective Color Palettes
How to Use the Color Wheel
The color wheel is a simple but powerful tool to help you choose colors that look great together. Here's how you can use it to make your design pop:
- Set the right mood – Warm colors like reds, oranges, and yellows bring energy and excitement, while cool colors like blues, greens, and purples feel calm and soothing. Think about the vibe you want for your website or brand, and choose colors that reflect that feeling.
- Create contrast with complementary colors – Complementary colors are opposites on the wheel, like blue and orange or red and green. These combinations create a bold contrast, making elements stand out — perfect for buttons or key calls to action.
- Go for harmony with analogous colors – Colors next to each other on the wheel, like blue, blue-green, and green, blend seamlessly and create a calm, unified look. These are great for backgrounds or for the design to feel cohesive and easy on the eyes.
- Try triadic or tetradic schemes – A triadic color scheme uses three evenly spaced colors around the wheel, giving you balance and vibrancy without feeling too chaotic. A tetradic scheme (four colors in a rectangle) can add depth, but be mindful to balance the tones so it doesn’t get too busy.
- Play with saturation and brightness – The strength of a color can change its impact. Softer tones are great for background elements, while more vibrant colors are perfect for things you want to draw attention to, like headlines or buttons.
By using the color wheel as your guide, you can easily create designs that are visually balanced and emotionally engaging, while staying true to your brand's personality.
Primary Colors vs Secondary Colors
There are three primary colors: yellow, blue, and red. They cannot be made by mixing other colors.
Secondary colors are colors that can be made by mixing primary colors. For example, blue and yellow make green, and yellow and red make orange. Purple, red, and blue make purple.
Primary colors feel more bold than secondary colors. Use primary colors alongside secondary colors to create contrast and/or harmony.
Contrasting colors are opposite of each other on the color wheel. Analogous colors are next to each other on the color wheel.
Source: Practical Ecommerce

Color Harmony
Color harmony refers to the way colors work together to create a visually appealing effect. It is a crucial aspect of color theory, as it can make or break the success of a design. When colors are in harmony, they create a sense of balance and order, making the design more pleasing to the eye and easier to navigate.
Principles of Color Harmony
There are several principles of color harmony that designers can use to create effective color combinations:
- Balance: Balance refers to the way colors are distributed in a design. A balanced color scheme creates a sense of stability and equilibrium. For instance, using a mix of primary and secondary colors can help achieve a balanced look.
- Contrast: Contrast is about how colors interact with each other. High-contrast colors, like complementary colors, can create a sense of energy and excitement, while low-contrast colors can evoke calmness and serenity. For example, pairing a dark background with lighter shades of text can enhance readability.
- Emphasis: Emphasis involves using colors to draw attention to specific elements in a design. Warm colors, such as red and orange, can create a sense of emphasis and urgency, while cool colors, like blue and green, can create a calming effect.
- Unity: Unity is about how colors work together to create a cohesive and harmonious look. A unified color scheme ensures that all elements of the design feel connected and consistent, enhancing the overall user experience.
Creating Color Harmony
Creating color harmony involves selecting colors that work well together and applying the principles of color harmony. Here are some tips for achieving this:
- Use the color wheel: The color wheel is an invaluable tool for creating color harmony. It shows the relationships between primary, secondary, and tertiary colors, helping designers select harmonious color combinations.
- Select colors with similar hues: Colors with similar hues can create a sense of harmony and cohesion. For example, using different shades of blue can evoke a serene and cohesive look.
- Use warm and cool colors: Combining warm and cool colors can create a balanced and dynamic design. Warm colors, like red and orange, can add energy, while cool colors, like blue and green, can provide a calming effect.
- Experiment with different color combinations: Don’t be afraid to experiment with various color combinations. Trying out different schemes, such as analogous or triadic color schemes, can help you find the perfect harmony for your design.
Types of Color Schemes
Choosing the right color scheme can make or break your design. Here are some color schemes you can try, depending on the mood or effect you're aiming for:
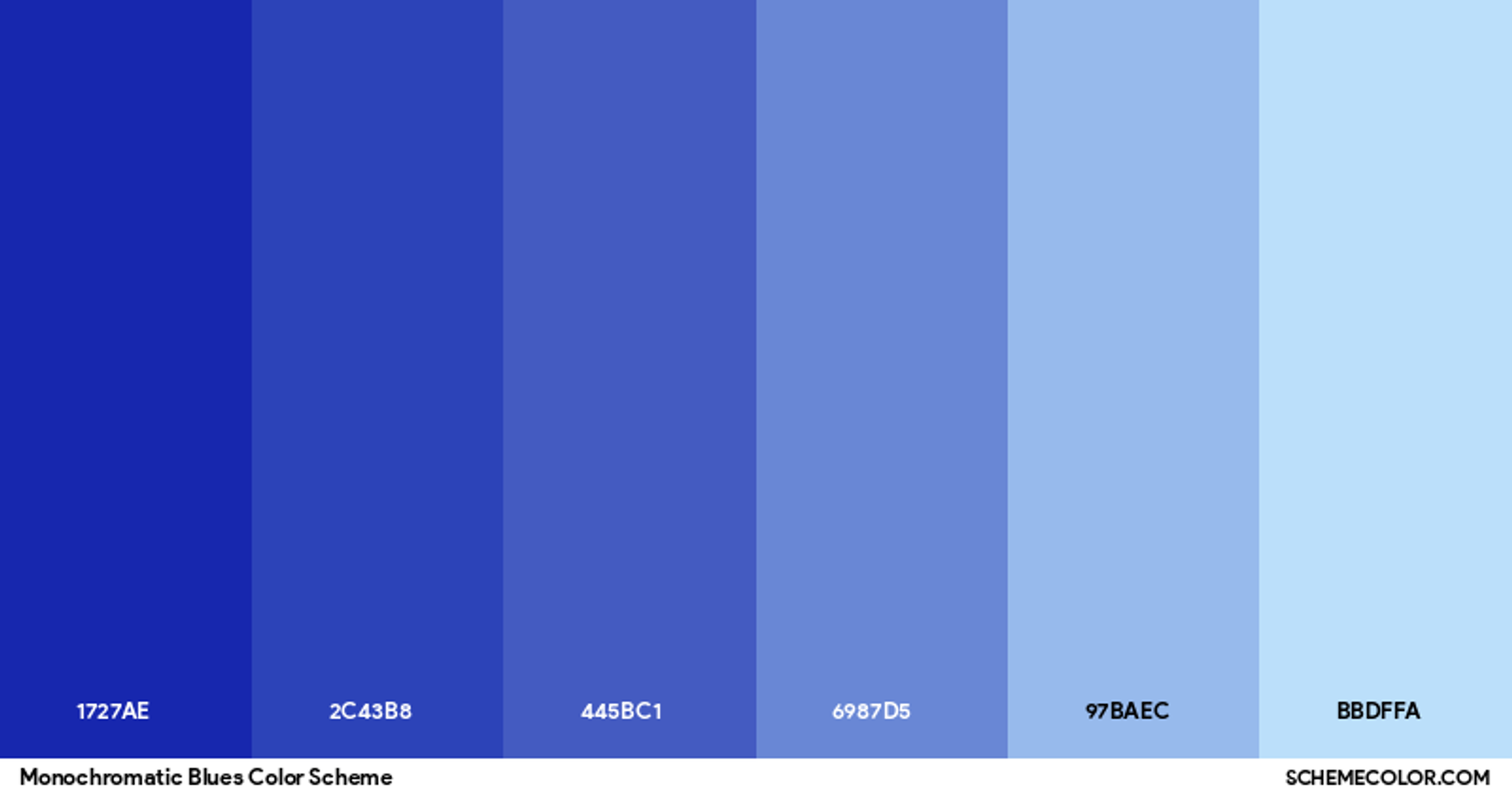
Monochromatic Color Scheme
Monochromatic is one color plus its tints, shades, and tones. Tints are created by adding white, shades by adding black, and tones by adding gray. This is a simple way to create a clean, consistent look.
Source: Scheme Color
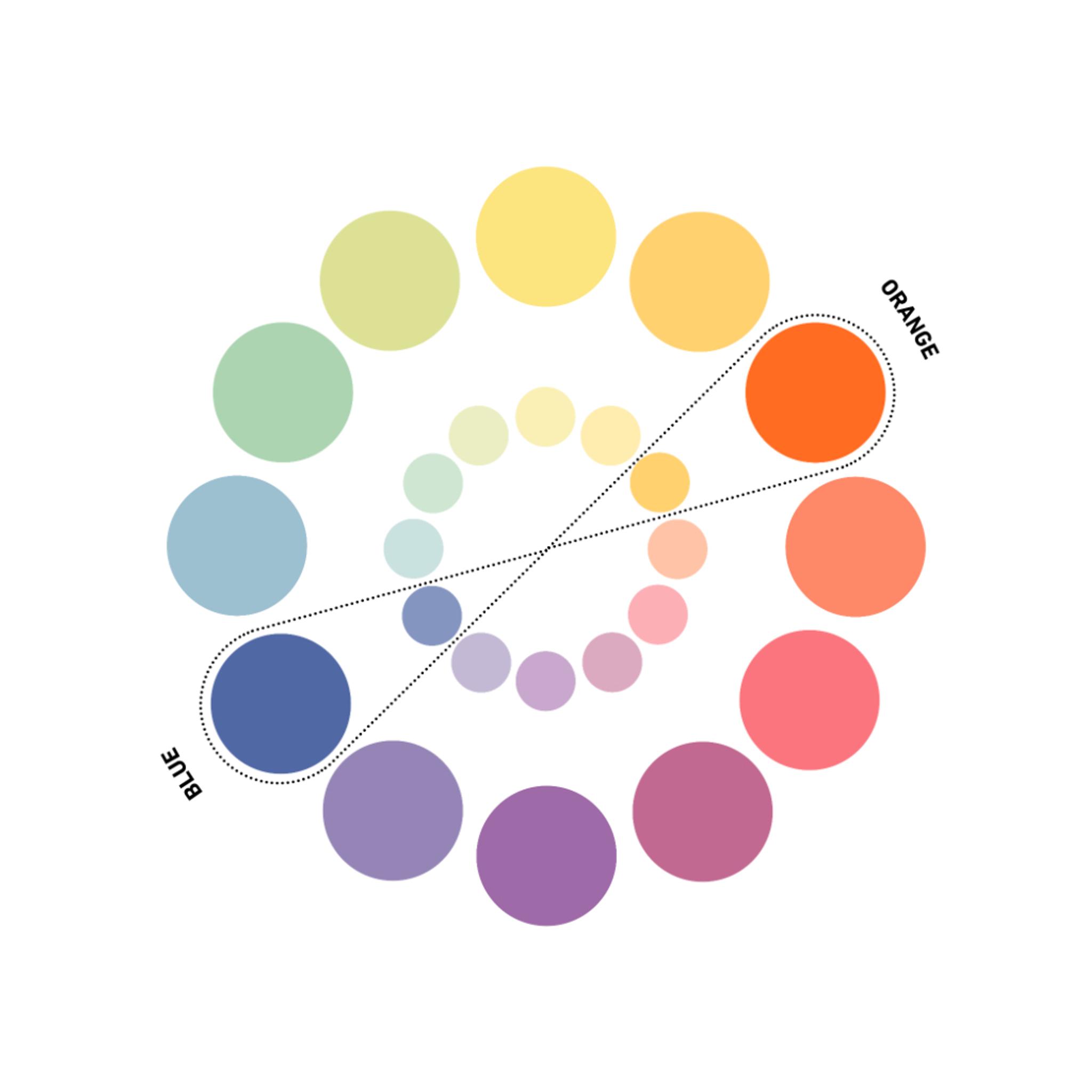
Complementary Color Scheme
Complementary colors are colors that are opposite each other on the color wheel, creating a strong contrast.
This is perfect for headlines and call to actions. Use complementary colors carefully. It can be overwhelming to look at. Adding whites, blacks, or grays can tone down the overwhelming look.
Source: Shutterstock
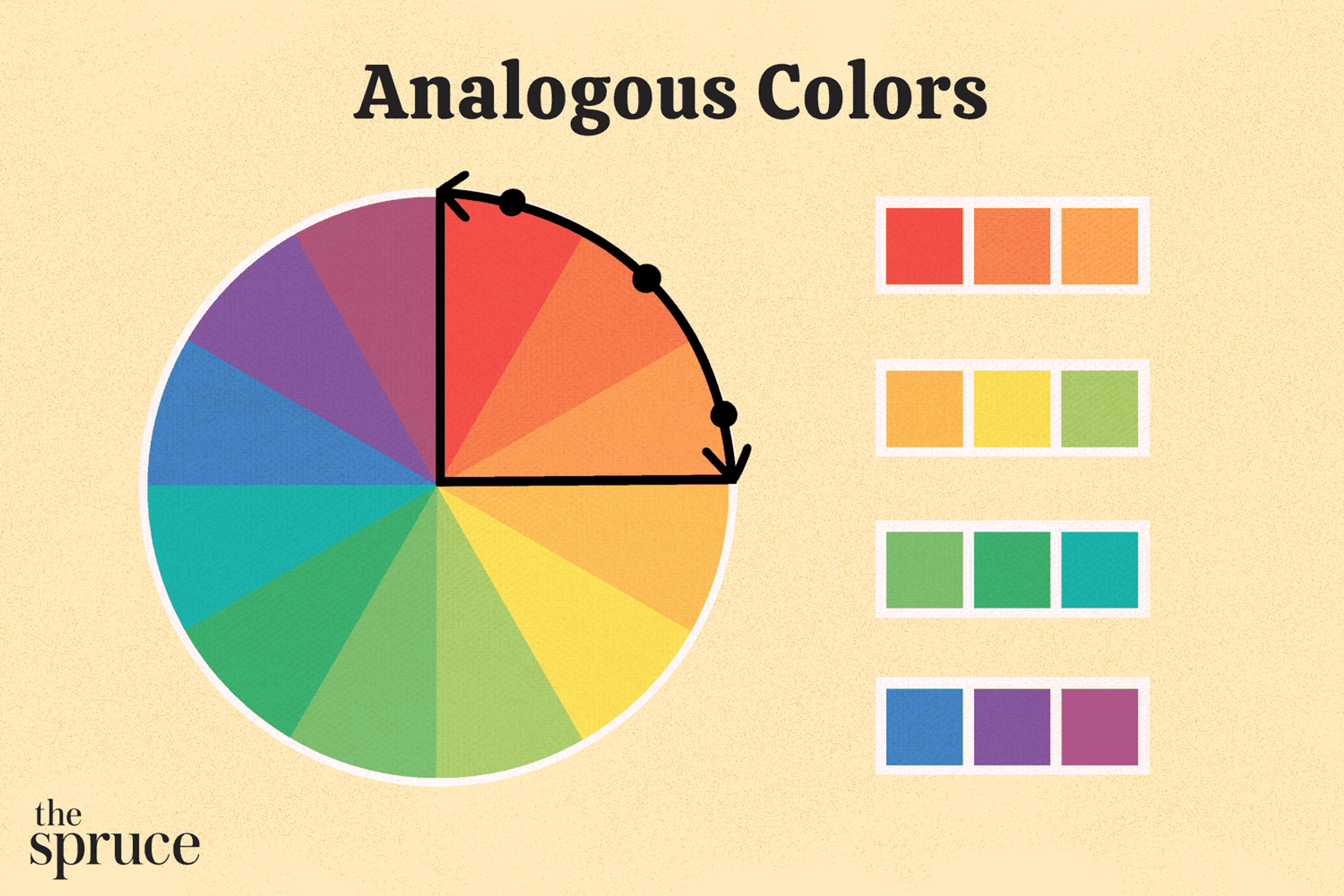
Analogous Color Scheme
Analogous colors are neighbors on the color wheel — think blue, blue-green, and green. When used together, these colors blend effortlessly and wrap your design in a calm, unified hug. This color scheme works beautifully when you want a soft, tranquil mood.
Use it for backgrounds, logos, or any layout that needs to feel collected without any loud surprises. The design reads as one smooth connection because the colors slide into one another without obvious borders.
Source: The Spruce
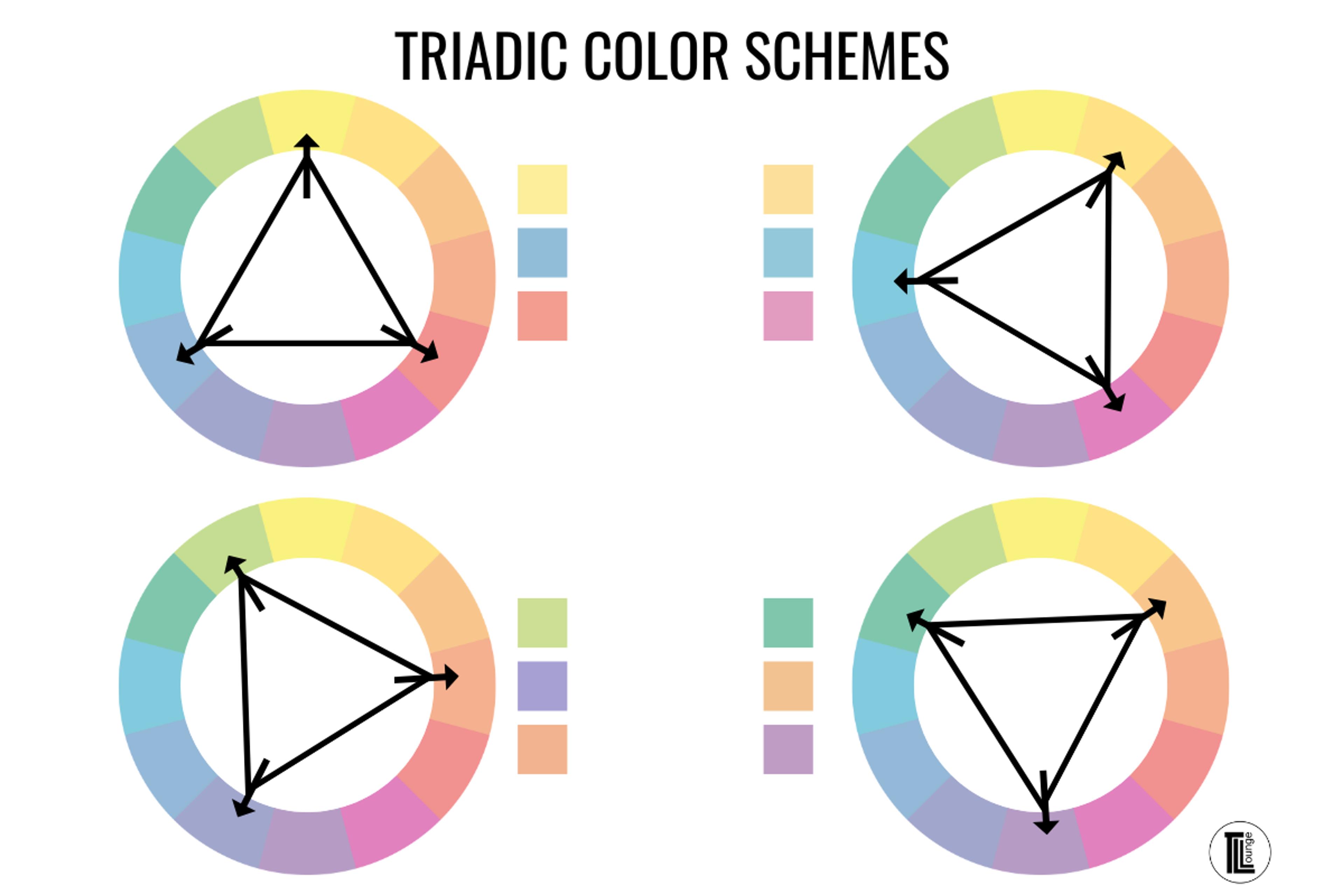
Triadic Color Scheme
Pick three equally spaced colors on the wheel to make a triadic color scheme, like red, yellow, and blue. This trio gives your design a pinch of contrast, a splash of brightness, and a comfy sense of balance. A triadic scheme can bring zest without tipping into chaos.
The colors play nicely, so everything stays anchored and lively simultaneously. Just keep the brightness of each color reasonably even, and the whole design will feel like a well-rehearsed performance instead of a free-for-all.
Source: The Lens Lounge
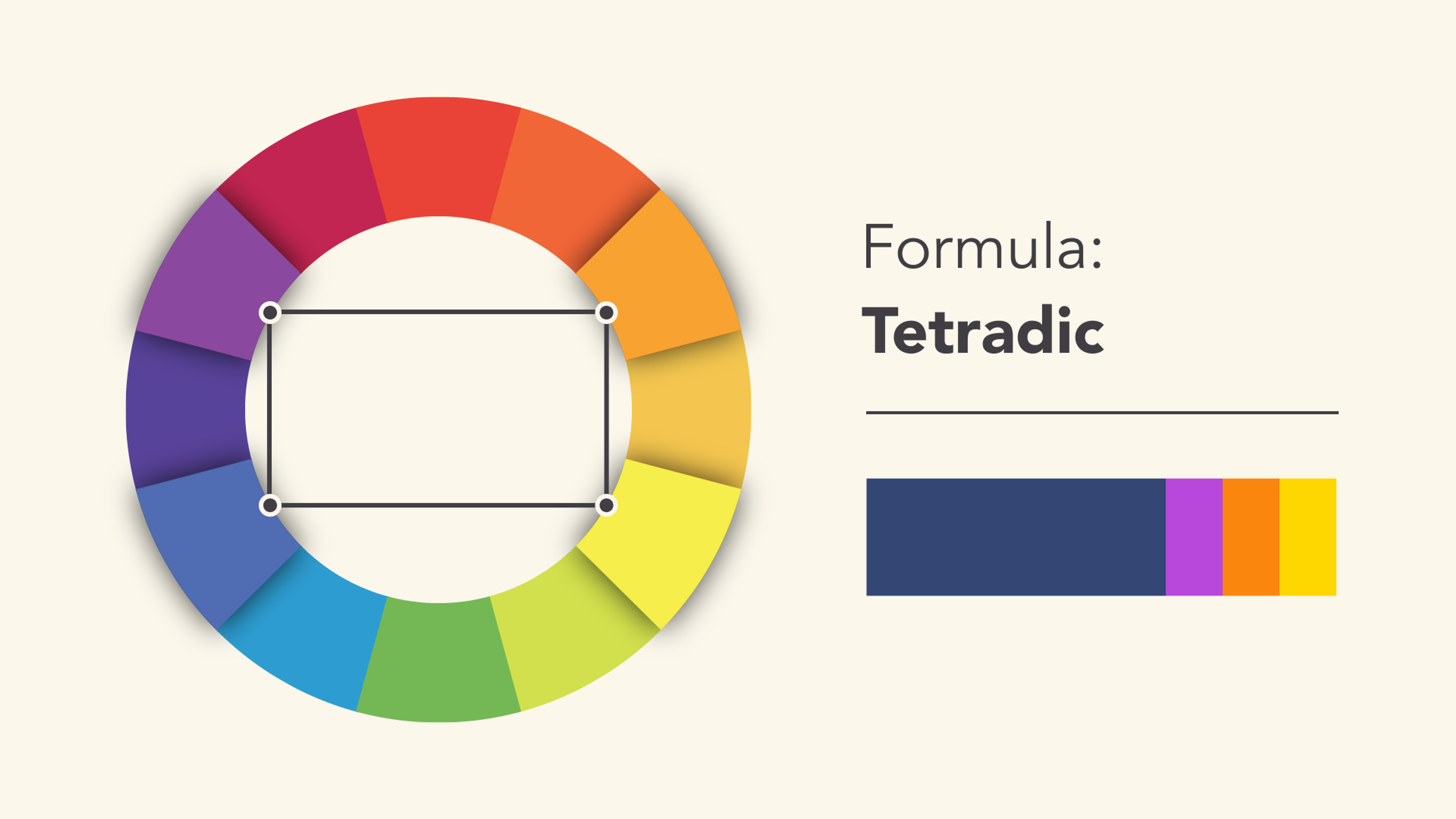
Tetradic Color Scheme
A tetradic color scheme pulls together four colors split into two sets of complementary pairs. This tactic is perfect for designs that crave variety yet still want to sing in harmony.
You gain wiggle room to swap in surprising colors, but keep a close eye on the balance. If one color threatens to hog the spotlight, the whole scheme clutters. Nail that balance, however, and a tetradic palette reveals layers of depth without shouting its secret.
Source: BINUS International
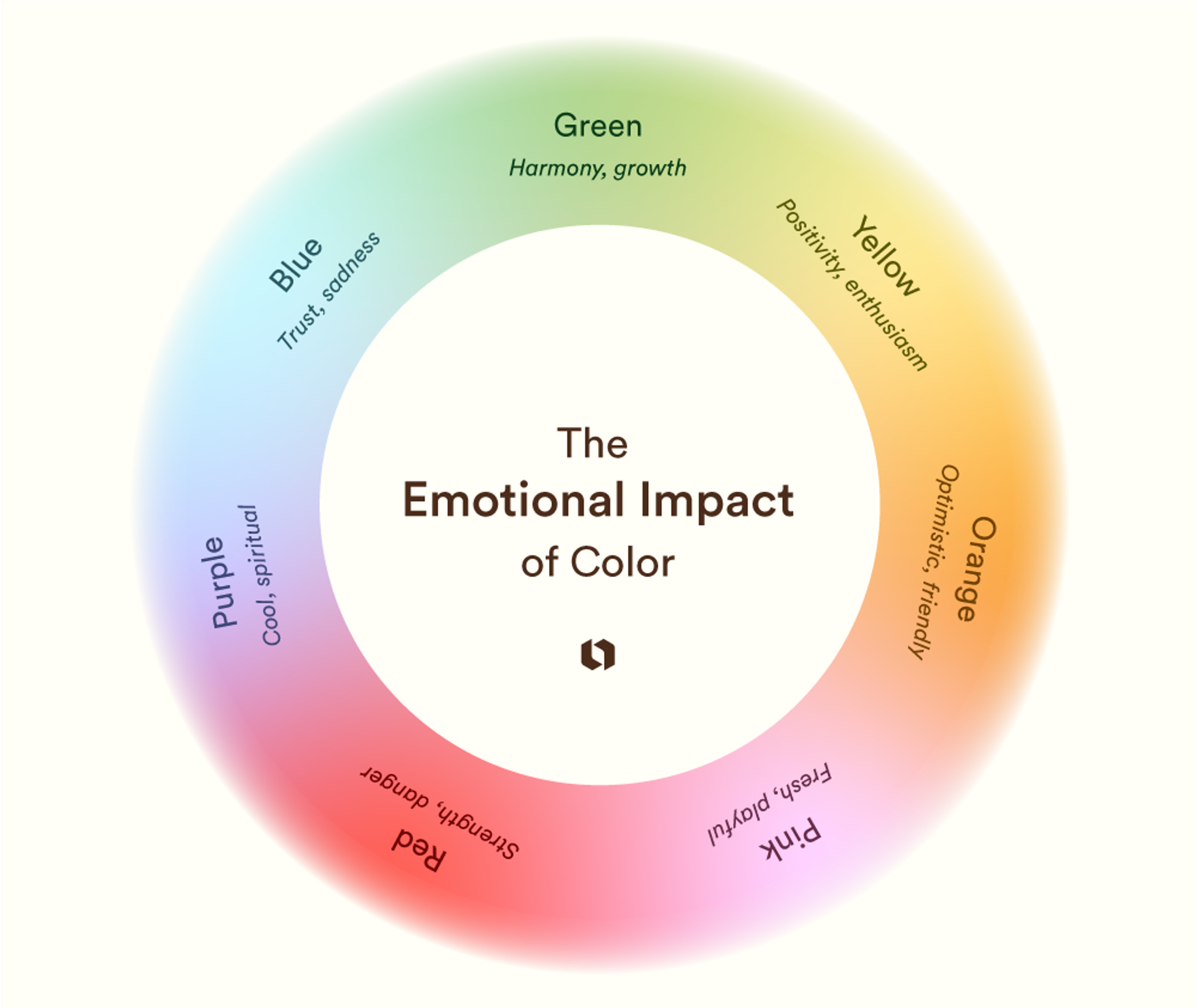
How Different Colors Trigger Emotions
Blue can create feelings of trust. Hang the color blue in places where you want calm feelings. Use red to create a sense of energy or urgency. Red can also create feelings of warmth and friendliness.
Yellow can also create feelings of warmth and friendliness. Green colors can evoke feelings of nature and growth. Purple can evoke feelings of luxury and is also linked to creativity. These feelings are linked to the colors. It is a general starting point.
Source: Looka
Phenom
Our design for Phenom’s website effectively uses vibrant shades of blue to create a trustworthy and dependable brand image. The coolness of blue provides a relaxing feel for users, making the site both inviting and professional.
By increasing the saturation, the design ensures the blue appears lively and dynamic, avoiding a pale or sad tone. This strategic use of blue demonstrates how color can enhance user experience and reinforce brand perception, making the website both aesthetically pleasing and emotionally engaging.
Phenom Website by Clay
Nike
Nike uses a monochromatic color scheme with different shades of their iconic orange. This creates an energetic and dynamic feel that aligns with their brand image.
Source: color-hex
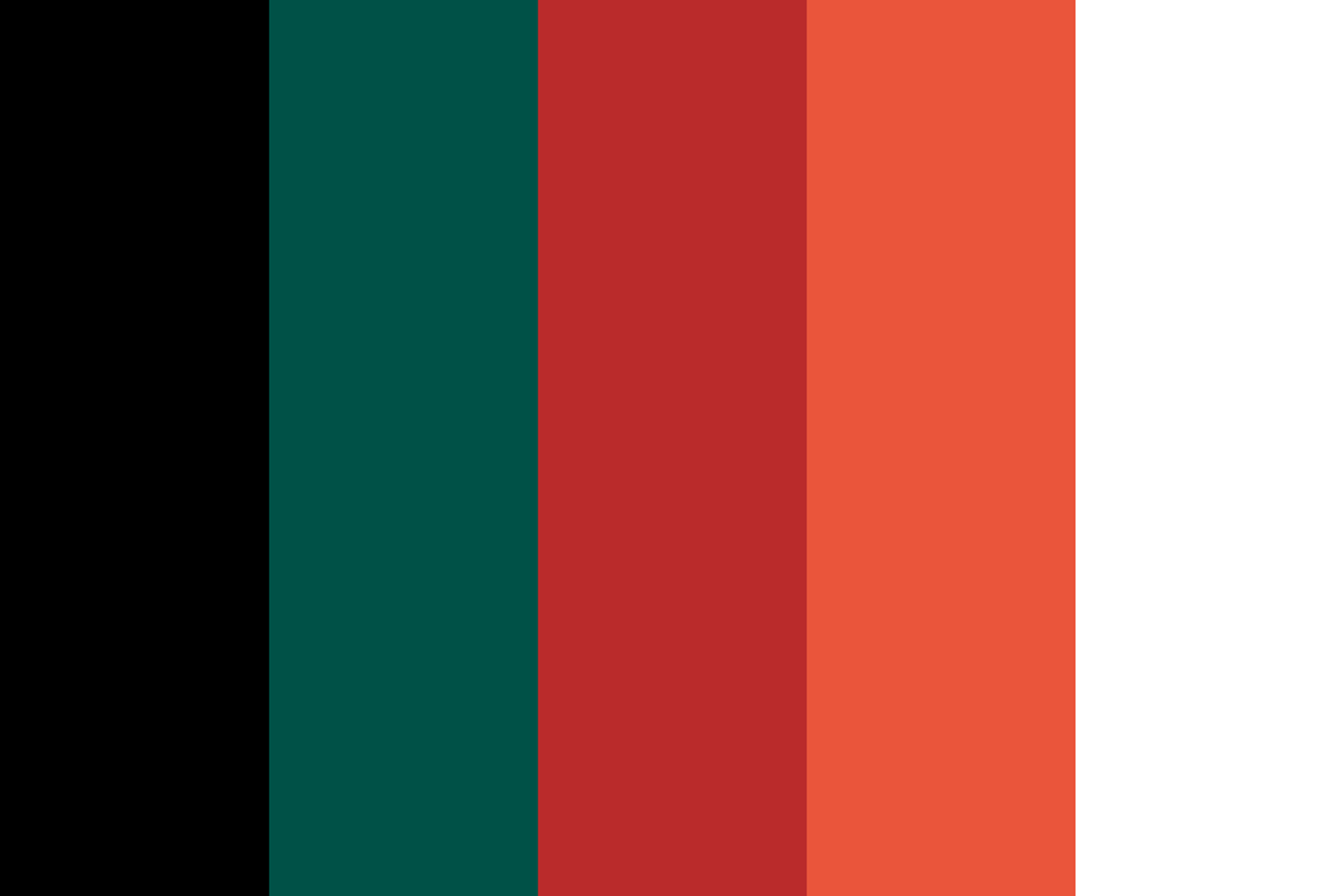
Spotify
Spotify employs complementary colors - green and pink - for its logo and branding. The contrast between these two vibrant colors immediately catches the eye and creates a strong visual impact.
Source: color-hex
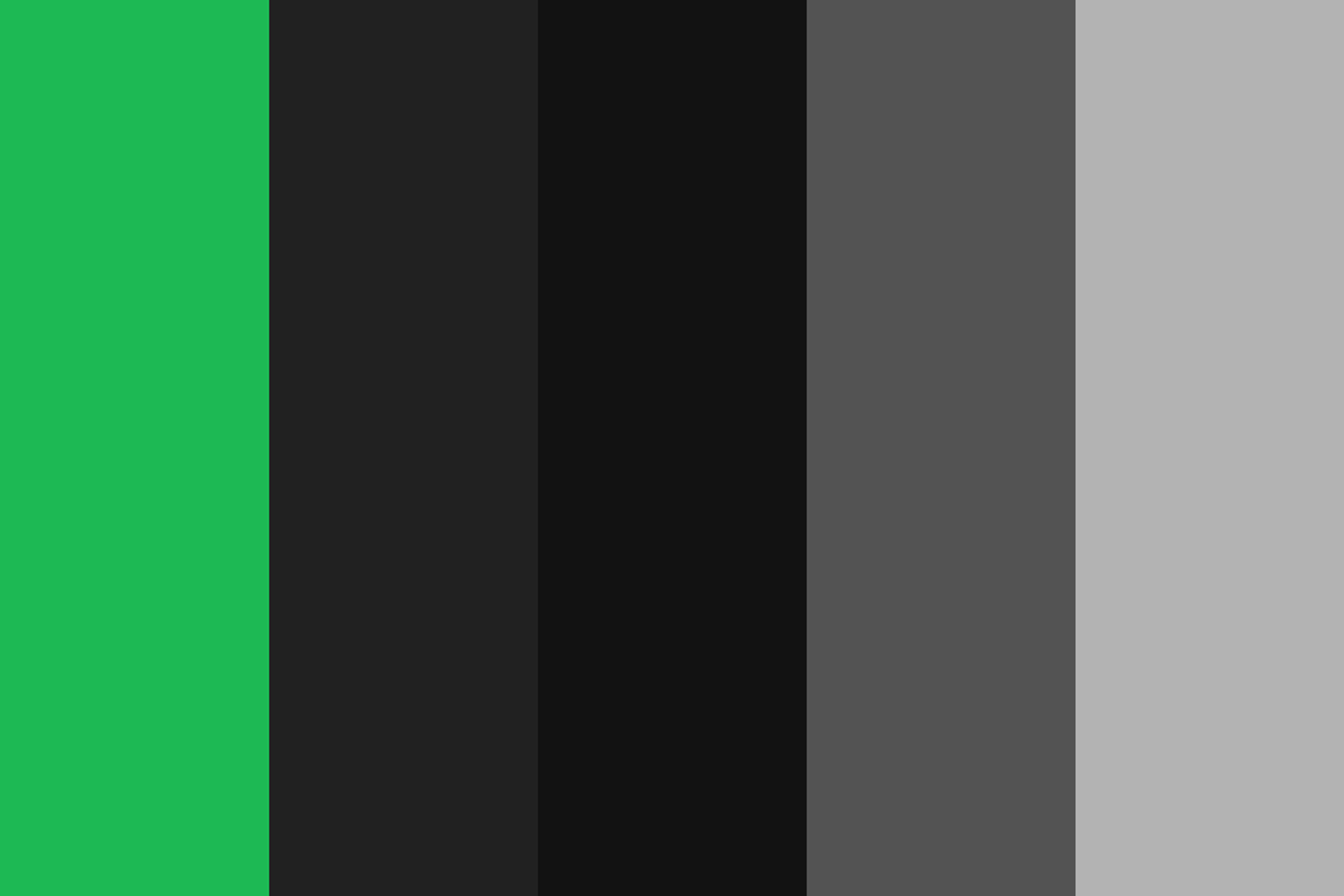

Airbnb
Airbnb uses an analogous color scheme with different shades of blue and green. These calming colors evoke a sense of relaxation and trustworthiness, aligning with the brand's focus on travel and hospitality.
Source: Pick Color Online
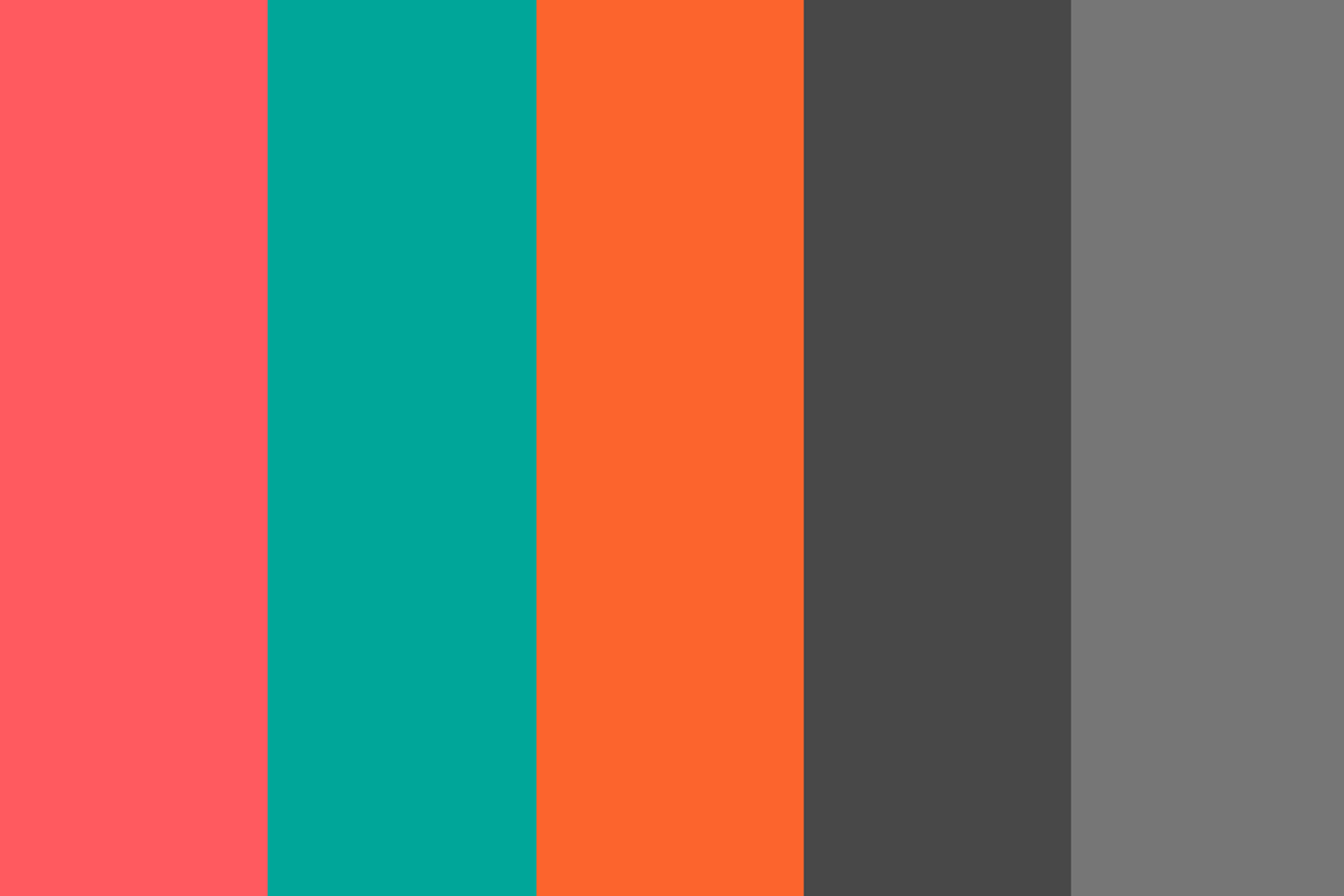
What Are the Three Systems of Colors that Designers Use?
Designers typically work with three main color systems to create vibrant and balanced designs, depending on the medium they’re working with:
1.
RGB (Red, Green, Blue). This system is used for websites, apps, or digital displays. It blends red, green, and blue light at different levels to produce a wide range of colors. Since it’s based on light, it’s often referred to as the “additive” color model, meaning colors are created by adding light together.2.
CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Key/Black). Designers use the CMYK system for print projects like brochures or posters. It’s based on mixing four ink colors - cyan, magenta, yellow, and black - so it’s called a “subtractive” model. By subtracting light using these inks, designers can create the rich colors seen in printed materials.3.
HSL (Hue, Saturation, Lightness). This system is based on how we naturally see and think about colors. HSL looks at three things: Hue (the actual color), Saturation (how intense or faded the color is), and Lightness (how light or dark the color is). Designers often use HSL in digital tools because it’s an intuitive way to adjust and play around with colors without getting too technical.
Source: Doozy Tools
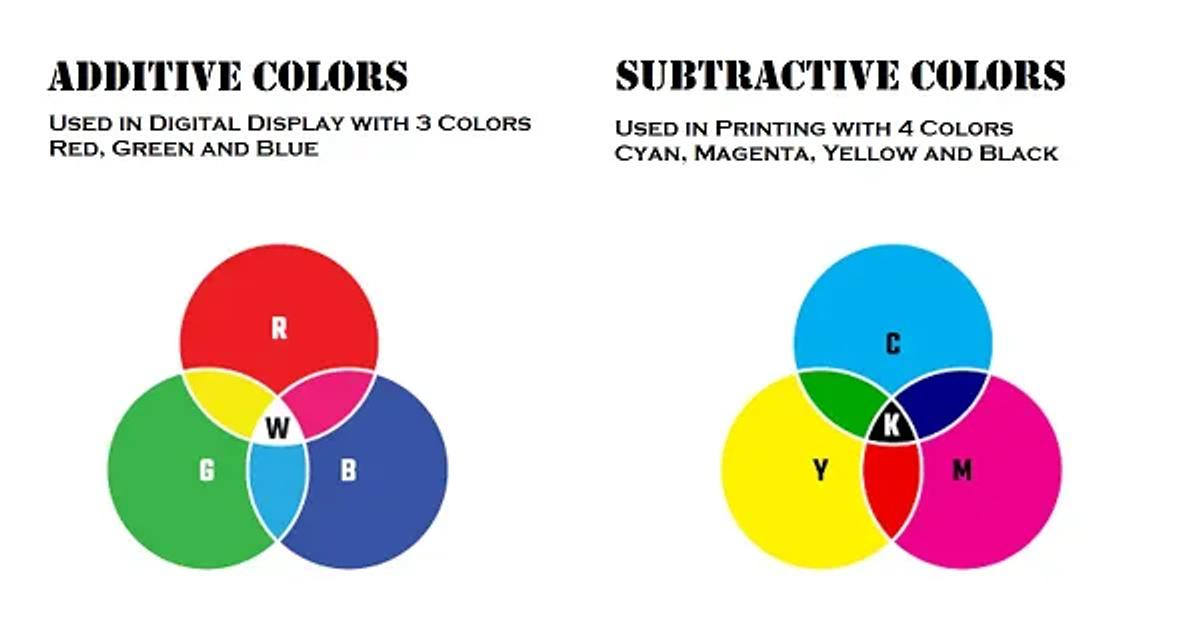
Understanding these systems helps designers achieve color harmony in their projects.
What to Consider When Choosing Web Design Colors
Consider emotion. How do you want your audience to feel? To ensure the site is recognizable, keep your colors consistent with your brand. For readability and visual hierarchy, prioritize contrast: ensure that text and important UI elements stand out clearly against the background.
Source: Wikimedia Commons

Practical Tips for Using Colors Effectively in Website Design
- Limit your color palette to 3-4 main hues to avoid overwhelming users with too many shades.
- Complementary or analogous colors may be used for high contrast or a more cohesive design.
- Consider the emotional associations of different colors and choose accordingly based on your brand and target audience.
- The balance between cool and neutral background colors can be struck by using white space (empty places) that enables other elements on the web page to stand out very well.
- Ensure that your color scheme looks good on various devices and screens to be visually appealing and accessible to all people.
- 60-30-10 Rule. This principle suggests using one dominant color, which occupies 60% of the whole design, a secondary color taking up 30%, and an accent color covering only 10%. Such an approach creates a balanced and consistent color combination without overloading users with too many colors or creating visual chaos.
Source: Flowmapp

Applications for Developing Color Palettes
Quite often, choosing a color palette can be daunting for designers. However, thanks to numerous online tools available today, this task has been made easier since you can generate harmonious combinations of colors on websites easily.
Adobe Color CC (formerly Adobe Kuler) is one such tool. You can create custom palettes based on complementary, monochromatic, or triad rules. In addition to this feature, it provides HEX codes –a six-digit code representing each specific color- which makes implementation into web design simple.
Another useful tool is Coolors.co. It generates random color palettes and allows you to tweak them until you find one that suits your needs. The site also has other utilities, such as exporting palettes in different formats and saving them for later use.
Eagle is a powerful digital asset management tool designed for designers, creatives, and teams to efficiently organize, search, and manage visual assets. It supports a wide range of file formats, including images, videos, fonts, and 3D models, making it a versatile tool for UI/UX designers, illustrators, and content creators.
FAQ
Can I Do Color Analysis Myself?
Yes. You can do a basic color analysis by checking how your skin, eyes, and hair interact with warm or cool tones. Online tools and seasonal color guides help, though a professional gives more precise results.
What Is The 60 30 10 Rule For Color Palette?
The 60-30-10 rule is a design principle where 60% is the dominant color, 30% is the secondary color, and 10% is the accent color. It creates balance and visual harmony.
Can ChatGPT Do A Color Analysis?
ChatGPT can’t visually analyze colors but can explain color theory, suggest palettes, and guide analysis methods. For exact results, use digital tools or professional consultations.
How Do I Find My Color Palette Free?
You can find your palette free with online generators, mobile apps, or seasonal color quizzes. Uploading a photo or experimenting with digital palettes can reveal flattering combinations at no cost.
Read More
Conclusion
Understanding the principle of color harmony and the application of online tools will enable designers to effectively utilize colors to enhance the user experience on a website.
Limit your color palette, try it on different devices, and use white space effectively to create balance. With these tips, you can create a stunning color scheme that looks great and strengthens your brand identity.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more