UX design moves fast. Every year brings new trends that change how people use websites and apps. Smart designers track these changes to build experiences that truly connect with users.
What Is UX Design?
What is user experience design? At its heart, it’s the practice of making interfaces that revolve around real users and their goals. From the moment someone first encounters your service to the final click or tap, good UX guides them smoothly through each step.
Don Norman, the father of user-centered design, revolutionized how we think about interfaces. His work at Apple in the 1990s established that design should adapt to human behavior, not force humans to adapt to technology.
Jakob Nielsen pioneered usability testing in the early days of the web. His research at Nielsen Norman Group shows that users scan web pages in an F-pattern and make decisions in just 50 milliseconds.
When you focus on creating positive interactions, you boost customer loyalty. Putting people at the center sparks innovation and keeps users engaged.
UX Design by Clay
Designing for usability goes deeper than surface convenience. You must understand your users completely. How will they approach a task? Where might they get stuck? What features can smooth out rough spots?
UX designers use powerful tools to craft interfaces that work. They start with data analysis and user feedback. Figma has become the industry standard, with over 4 million designers using it daily. Adobe XD offers seamless integration with Creative Suite workflows. Sketch remains popular for its symbol libraries and plugin ecosystem.
Wireframing comes next. Designers sketch page layouts without specific content. This stage sets the framework for everything that follows.
Prototyping transforms static sketches into clickable models. Tools like Marvel and Principle let designers experiment with interactions before writing production code.
Usability testing involves real users. It reveals where people stumble and which parts feel natural. Companies like UserTesting and Lookback provide platforms for remote user research.
A/B testing compares two versions side by side. By measuring real responses, designers learn which layout drives better engagement. Every stage aims to help customers achieve goals with minimal effort.
The Evolution of UX Design
UX design has transformed dramatically. Key developments changed how we interact with technology.
The 1980s brought graphical user interfaces. Susan Kare designed the original Mac icons, turning computers from specialist tools into everyday devices. Icons, windows, and menus made computing accessible.
The 1990s introduced web design challenges. Pages needed to be fast loading and intuitive navigation. Alan Cooper invented the persona method during this decade, helping designers understand their users better.
Today's UX professionals have AI and machine learning. These technologies analyze user data to reveal behavior patterns. GPT-4 now helps designers generate content variations. Claude AI assists with user research analysis. Midjourney creates visual mockups in seconds.
Machine learning enables interfaces that adapt to individual needs. Netflix's recommendation algorithm analyzes viewing patterns to suggest content. Spotify's Discover Weekly uses AI to find new music based on listening history.
The shift toward data-driven design creates natural, engaging experiences. Products anticipate user needs before people even realize them.
Looking forward, UX will continue evolving with emerging technologies. The story that began with simple icons has grown into a dynamic field where every advance promises fresh ways to delight users.
Previous Dominant Trends in UX Design
Over the past decade, UX design has undergone significant transformations driven by technological advancements and shifting user expectations. In the early 2010s, skeuomorphism dominated the design landscape, with interfaces mimicking real-world objects to create familiarity.
However, this soon gave way to flat design, championed by companies like Apple and Microsoft, emphasizing simplicity, clean lines, and a minimalist approach.
As mobile technology proliferated, responsive design became crucial, ensuring that interfaces were adaptable to various screen sizes and devices. This period also saw the rise of touch interfaces, demanding designers rethink usability for tap, swipe, and pinch gestures.
By the mid-2010s, Google's introduction of material design brought depth and motion to flat design principles, creating more intuitive and visually appealing interfaces. At the same time, the importance of micro-interactions and animations became evident, adding layers of feedback and delight to user interactions.
Iphone Icons

The mid-2010s saw micro-interactions gain importance. These small animations added feedback and delight to user interactions. They made interfaces feel more human and responsive.
The late 2010s integrated AI and machine learning into UX. Personalization became standard. Voice interfaces gained popularity through smart speakers like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant.
Inclusivity and accessibility became priorities. The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) provide standards for inclusive design. Dark mode reduced eye strain and saved battery life.
AR and VR started pushing interaction boundaries. These technologies created new possibilities for immersive experiences.
User Experience Trends
Modern trends reflect our changing technology landscape. UX professionals must stay current to keep users satisfied.
Cross-platform Compatibility
Mobile design takes priority. Everything must work perfectly on smartphones and tablets. This means responsive layouts, touch-friendly interfaces, and fast loading times.
Users expect seamless experiences across all devices. Whether they start on a phone and finish on a desktop, the transition should feel natural. Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) bridge the gap between web and mobile experiences.
Motion Design
Motion design applies animation principles to user interfaces. It creates immersive experiences that guide attention and provide feedback. Well-crafted animations make interactions smoother and more enjoyable.
Motion serves function beyond visual appeal. Loading animations tell users a process is running. Hover effects show interactive elements. Transition animations help users understand navigation changes.
Tools like After Effects and Principle help designers create sophisticated motion graphics. Lottie allows animations to work across platforms with small file sizes.
Personalization and User Behavior
Types of AI Recommendations

We're approaching highly personalized experiences. AI analyzes user data to customize content, features, and messaging. This goes beyond simple recommendations to predictive analytics that anticipate needs.
Machine learning algorithms study browsing patterns, purchase history, and interaction data. They create unique experiences for each user. Amazon's recommendation engine drives 35% of its revenue through personalization.
Behavioral analytics tools like Hotjar and Mixpanel reveal how users actually interact with interfaces. Heat maps show where people click and scroll. This data drives design decisions.
Conversational Interface
Chatbots and voice interfaces let users interact through natural language. Advanced natural language processing makes conversations feel almost human.
ChatGPT demonstrated conversational AI's potential. Companies now integrate similar technology into customer service and product discovery. These interfaces feel intuitive because they mirror human communication.
Voice User Interfaces (VUIs) continue growing. Smart speakers, car systems, and mobile assistants all rely on voice interaction. Designers must consider audio feedback, error handling, and conversation flow.
Source: Mojahid Mottakin on Unsplash
The Future of UX Design: Predictions for 2026 and Beyond
UX designers are creating increasingly personalized experiences. AI-driven automation provides custom recommendations for individual users. Voice interfaces become more critical as smart devices proliferate.
Motion design and augmented reality will create engaging experiences. UX researchers become crucial for understanding user behavior and preferences.
UX Design Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI transforms how designers work. Machine learning analyzes usage data to improve products automatically. Companies use AI insights to tailor content and features to individual preferences.
Stable Diffusion generates images from text descriptions. This helps designers create visual concepts quickly. AI writing tools help generate microcopy and error messages.
How Generative AI Helps UX Professionals
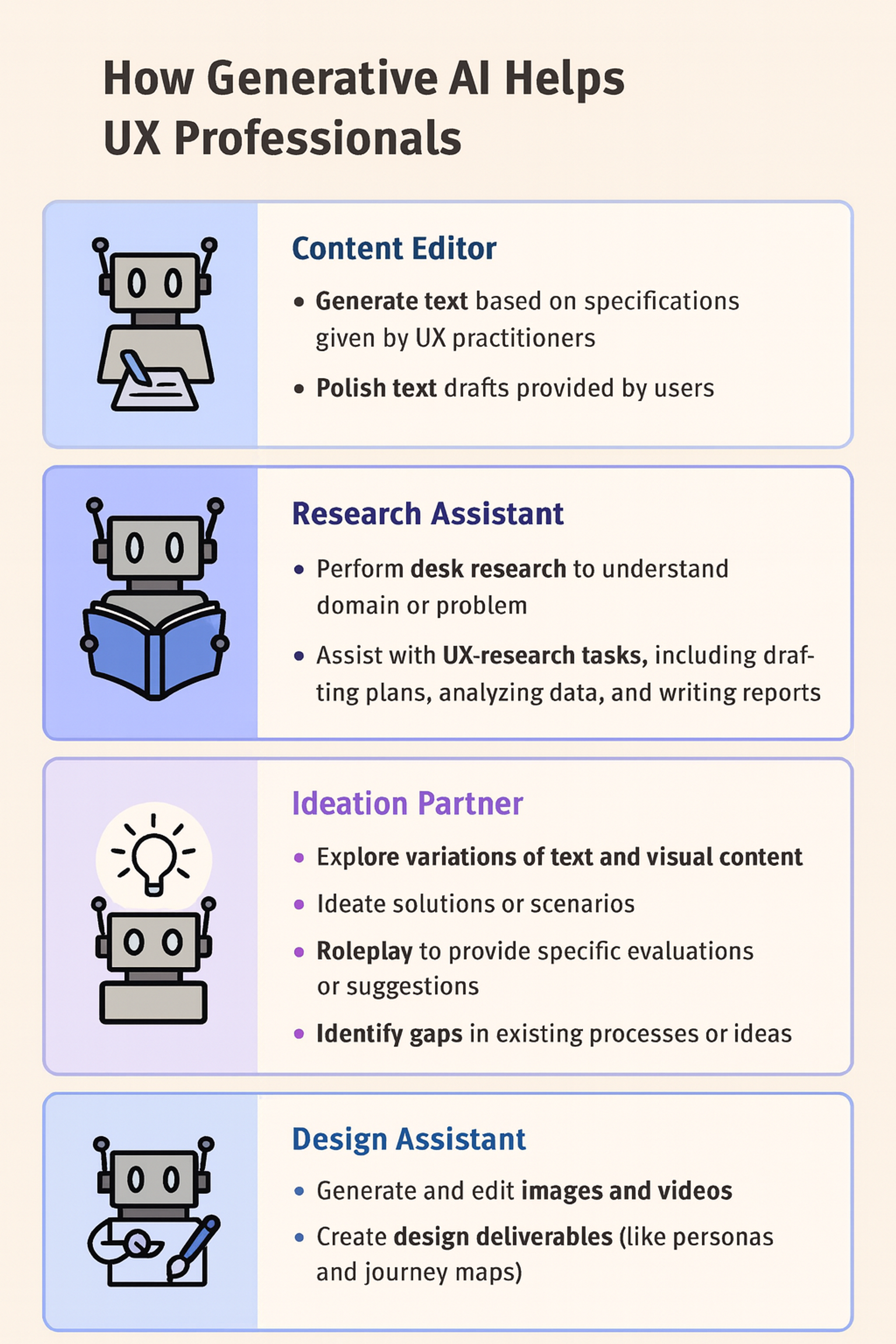
AI impacts motion design by creating realistic animations. Automated testing tools can spot usability issues before human testing begins, speeding up the design process while improving quality.
Predictive analytics anticipate user needs. If someone typically orders coffee at 8 AM, the app might show coffee shops first thing in the morning. This level of anticipation creates magical user experiences.
Voice User Interface Design (VUIs)
VUIs let users interact with products through speech. Natural language processing understands user input and responds accurately to voice commands.
Amazon Alexa pioneered consumer VUI adoption. Google Assistant and Siri followed with their own approaches. Each platform has unique design patterns and capabilities.
VUIs make experiences more interactive and intuitive. Users complete tasks without looking at screens. This helps while driving, cooking, or when hands are busy.
Companies use VUIs for customer service, food ordering, music playing, and information searching. The technology learns from user behavior to provide better recommendations over time.
Our research into Snapchat highlights the innovative use of voice user interfaces (VUIs) to enhance user interactions with digital products through natural language. By implementing VUIs, users can navigate and perform tasks using voice commands, making the experience more interactive and intuitive.
Integrating natural language processing and AI-based technologies enables personalization of user experiences by learning user behavior and preferences to deliver tailored content and recommendations, ensuring a seamless and efficient user experience.
Snapchat VUI Design by Clay
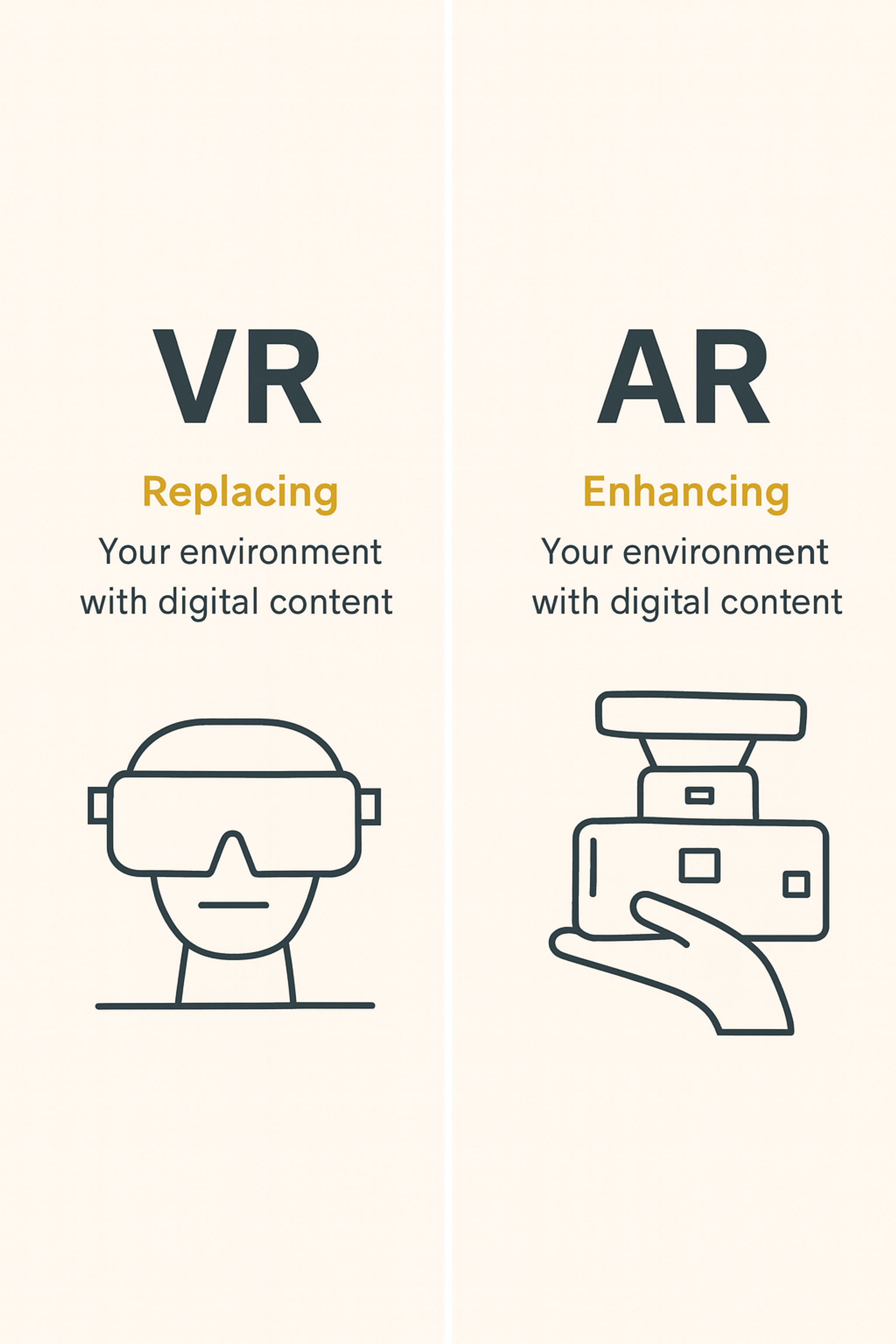
Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR & VR)
AR overlays digital elements onto the real world. Users interact with virtual objects in their physical environment. This creates blended reality experiences.
Retailers use AR for virtual try-ons. IKEA's app shows how furniture looks in your home. Sephora lets customers test makeup virtually. These applications reduce returns and increase confidence.
Navigation apps use AR to show directions overlaid on live camera views. Pokemon Go demonstrated AR's entertainment potential. Apple's Vision Pro and Meta's Quest headsets push AR/VR boundaries.
VR creates fully immersive digital environments. Real estate companies offer virtual property tours. Car manufacturers let customers explore vehicle interiors before buying.
Motion controllers and haptic feedback make VR feel real. Users can touch and manipulate virtual objects. This technology will improve as hardware becomes lighter and more affordable.
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT connects physical objects to the internet. This creates seamless experiences across multiple devices. Smart homes demonstrate IoT's potential for unified control.
Amazon Echo connects with Alexa-enabled devices throughout homes. Users access content from any device without switching applications. Everything works together as a connected system.
Smart thermostats learn user preferences and adjust automatically. Fitness trackers sync with health apps. Connected cars integrate with smartphones for navigation and entertainment.
UX designers must consider how people move between connected devices. The experience should feel continuous, not fragmented across different interfaces.
Microinteractions
Microinteractions are small moments when users engage with digital products. These subtle details make experiences more delightful and human.
Examples include button color changes on hover, pull-to-refresh animations, and notification sounds. Well-designed microinteractions provide instant feedback and prevent errors.
Loading spinners tell users that processes are running. Form validation shows errors immediately instead of after submission. These small touches reduce frustration and improve satisfaction.
Microinteractions guide users through complex processes. They make technology feel more responsive and alive. As interfaces become more sophisticated, these details become increasingly important.
Accessibility
Accessibility ensures everyone can use digital products regardless of ability. Voice recognition helps users with physical impairments navigate without traditional inputs. Eye-tracking technology provides alternative interaction methods.
WebAIM's accessibility guidelines help designers create inclusive experiences. Screen readers need proper markup to function correctly. High-contrast color schemes help users with visual impairments.
Accessibility benefits everyone, not just users with disabilities. Captions help in noisy environments. Voice controls work hands-free while driving. Good accessibility creates better experiences overall.
Accessibility Elements by Clay

Sustainability in UX Design
Environmental awareness drives sustainable design practices. Digital products should minimize energy consumption throughout their lifecycle.
Efficient coding reduces server energy usage. Optimized images load faster and use less bandwidth. Dark mode saves battery life on OLED screens.
Sustainable design considers hardware longevity. Products should encourage repair over replacement. This reduces electronic waste and environmental impact.
Sustainability in UX Design
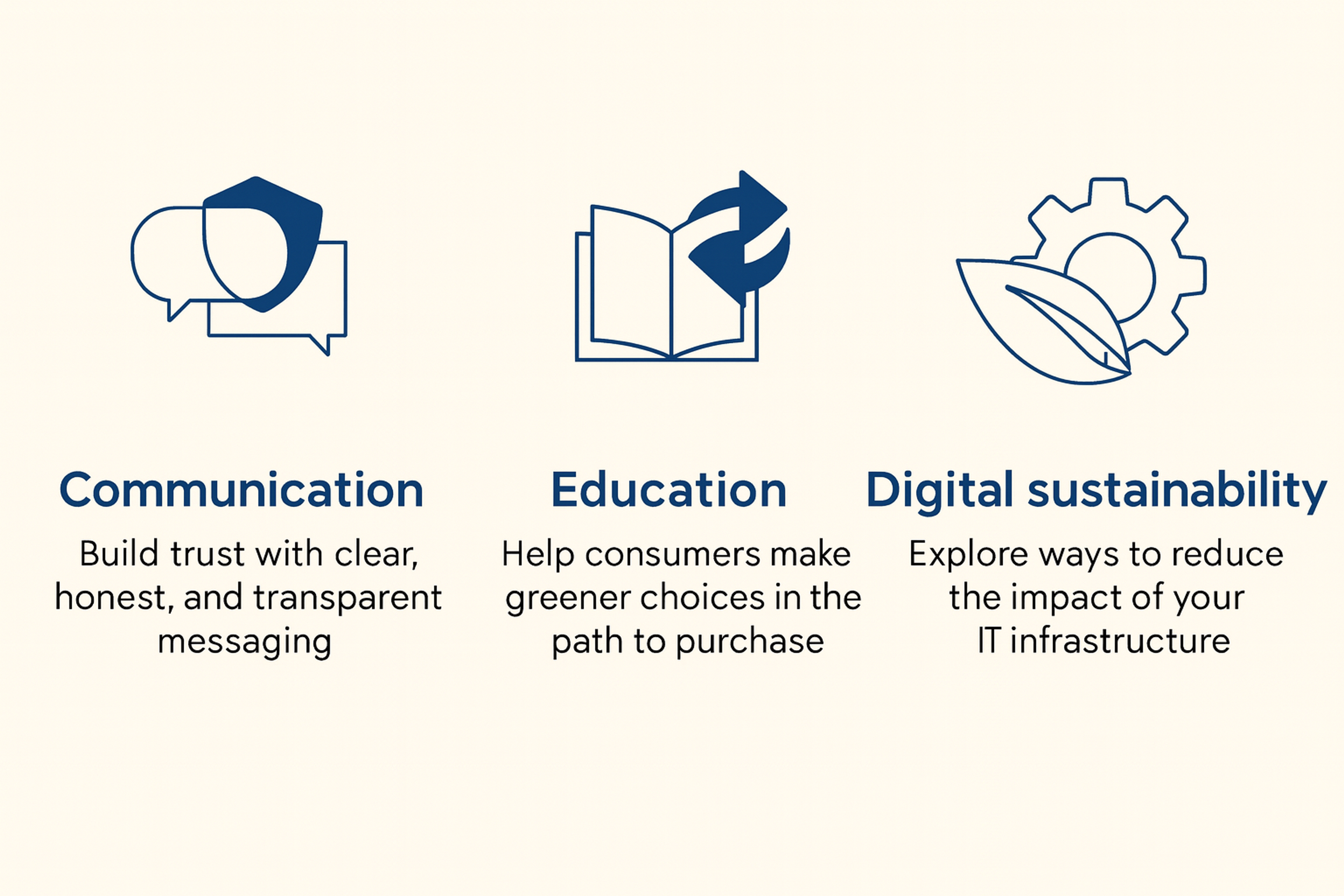
Users increasingly care about environmental responsibility. Companies that demonstrate sustainability commitment build stronger brand loyalty. Green design becomes a competitive advantage.
Data-Driven UX Design
Data transforms guesswork into evidence-based decisions. Analytics reveal user behavior patterns and pain points. A/B testing compares design variations to find what works best.
User journey maps show where people drop off. Heat maps reveal which elements get attention. Surveys gather qualitative feedback about user preferences.
Personalization relies on data analysis. The more a system knows about users, the better it can serve their needs. This creates more relevant and engaging experiences.
However, data must balance with creativity and intuition. Numbers tell part of the story, but empathy and innovation remain essential for great design.
Remote Collaboration Tools
Remote work changed how design teams operate. Cloud-based tools enable real-time collaboration across distances. Multiple designers can work on the same project simultaneously.
Figma pioneered collaborative design editing. Miro provides digital whiteboards for brainstorming. Slack and Microsoft Teams handle communication and file sharing.
Project management tools like Asana and Trello keep teams organized. Video calls replace in-person meetings for feedback and discussions.
Remote collaboration requires new skills and processes. Clear communication becomes more important when teams aren't co-located. Documentation helps maintain project knowledge.
The Metaverse and Web 3.0
The Metaverse creates persistent virtual worlds where users interact in real-time. This opens new possibilities for social interaction, entertainment, and commerce.
Web 3.0 emphasizes decentralization and user control. Instead of centralized platforms, users own their data and digital assets. This shift requires new approaches to user experience.
UX designers must understand these emerging platforms. Virtual world interfaces need different design patterns than traditional screens, and spatial computing changes how we think about navigation and interaction.
Blockchain technology enables new ownership models. NFTs represent digital property rights. Cryptocurrency changes how people pay for products and services.
These technologies are still developing, but early adopters are already experimenting. Designers who understand these platforms will have advantages as they mature.
Read More
Conclusion
The future of UX design combines human needs with advancing technology. AI enables personalization at scale while maintaining human-centered principles, and voice and gesture interfaces create more natural interactions.
Success requires staying current with emerging technologies while focusing on fundamental user needs. The best designs will always put people first, regardless of the technology behind them.
UX designers who adapt to these changes while maintaining user focus will create the most compelling experiences. The future belongs to those who can balance innovation with usability, complexity with simplicity, and global reach with personal relevance.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more