Flat design helps you create clean and simple user interfaces that are easy to use and nice to look at.
It uses open layouts with clear fonts, bright colors, simple icons, and images. This style removes extra details so users can focus on what matters most.
Flat design also makes it easier for developers to build and update websites or apps. It’s efficient, saves time, and works well across different screens.
In this article, you’ll learn the main rules of flat design and how to use them to create your own website.
Key Takeaways
Flat design focuses on uncluttered user interfaces using bold typography, open layout, simple shapes and lines, and uncluttered layouts with precise meanings.
Characteristics of flat design are as follows:
- Makes use of bold colors with ample negative space to enhance visual spacing.
- Utilizes simple icons with legible typefaces to reduce cognitive load.
- Removes visual elements such as shadows, textures, and more.
- Balances usability and aesthetics with visual hierarchy and contrast.
- Easier to develop and maintain, while also loading faster.
- Works on nearly any screen or device.
- Permits minimal interaction without distracting the user.
What Is Flat Design?
Flat design emerged as a response to skeuomorphic and heavily textured interfaces that mimicked physical objects through shadows, gradients, and realistic materials. In its modern form, flat design prioritizes clarity, legibility, and speed - while still using just enough visual cues to make interactive elements obvious.
Flat Design Example
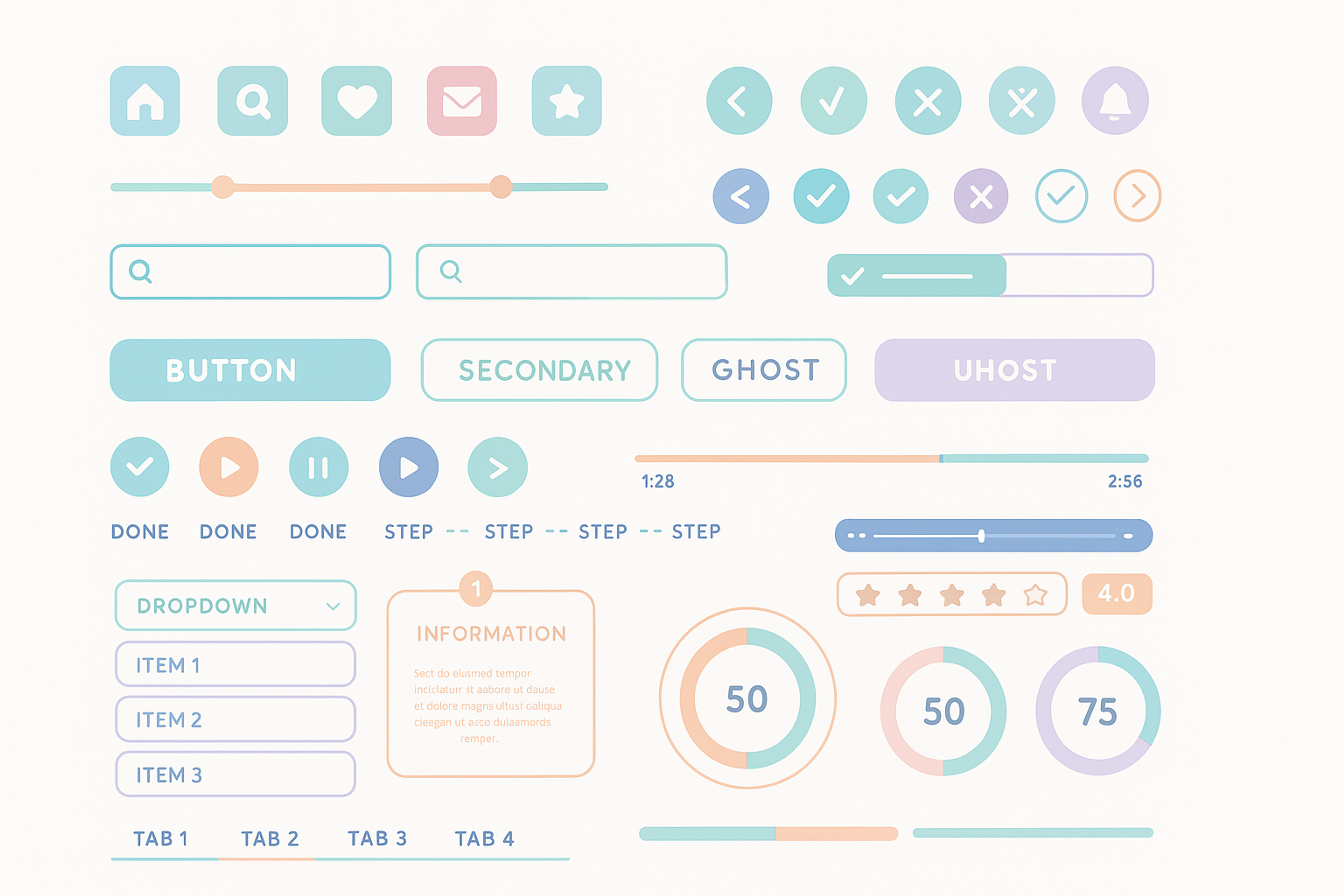
Apple popularized flat design with the release of iOS 7 in 2013. This update stripped heavy visual elements and focused on clean structure and simplicity. Flat design became a new standard for a variety of apps and websites.
Microsoft incorporated flat design in Windows 8 in 2012. Subsequently, Google applied flat design to its apps in 2014. A clean aesthetic with usability in mind is why web and UX designers use this style more often.
Flat Design Example

One of the many aspects of flat design that keeps it alive today is the resonance it has between functionality and visuals. It also has to do with usability and efficiency, which are highly valued when developers aim to create uncluttered and easy user interfaces.
Benefits of Flat UI Design
- Clear structure: Grid-based layouts make interfaces easier to scan and understand.
- Focus + efficiency: Removes irrelevant visuals, keeps attention on key actions and content.
- Better usability: Fewer decorative elements mean less clutter and faster decision-making.
- Simpler to build: Cleaner visuals are often easier and cheaper to implement in code.
- Faster performance: Lighter graphics can improve load speed and perceived responsiveness.
- Modern feel: A minimal, clean UI helps many brands look current while remaining functional.
Source: Canva
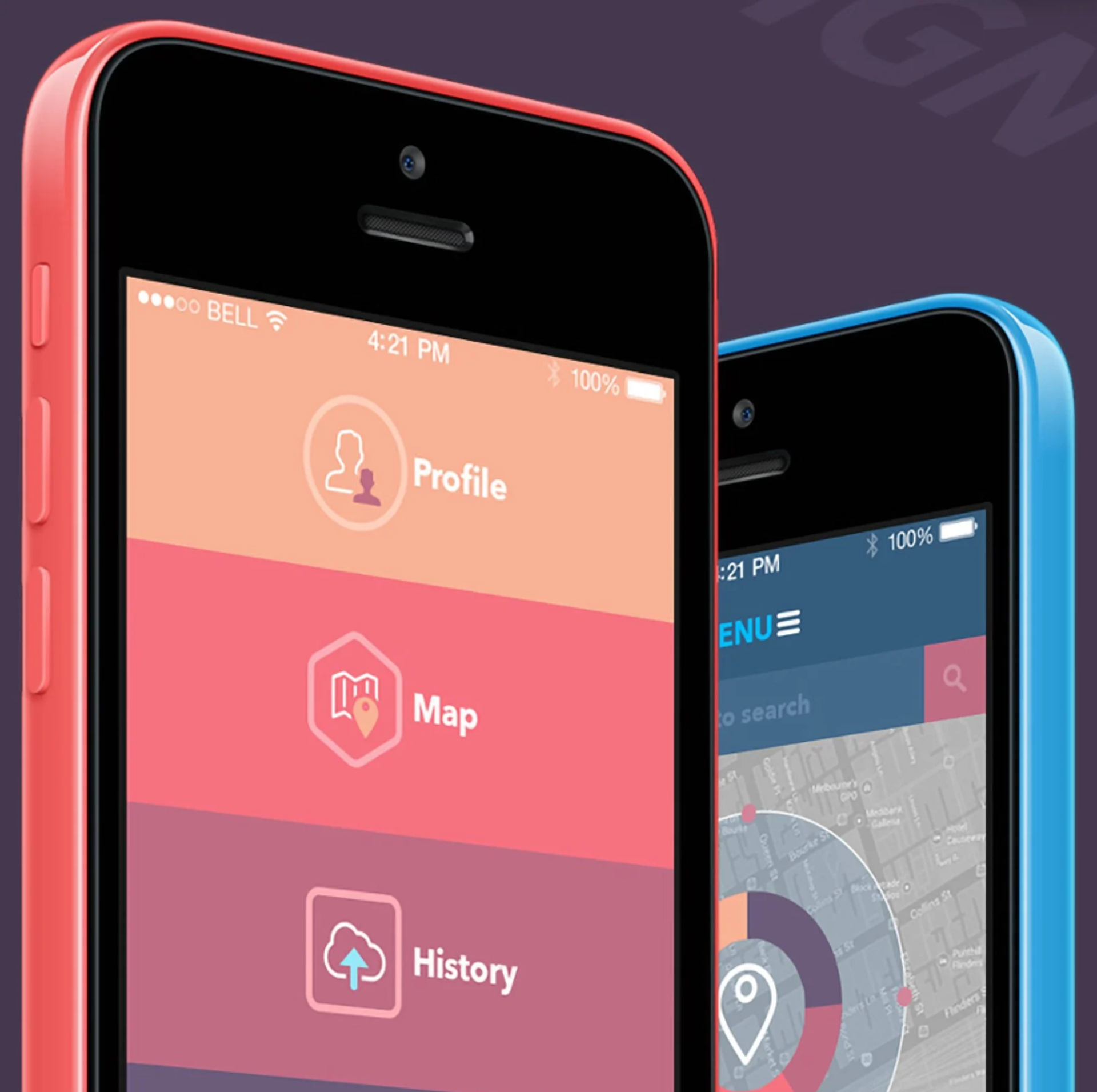
Material Design vs Flat Design
One of the essentials in technological visuals is using material and flat design. While Material Design uses depth, shadows, and movement, Flat Design uses simplicity and minimalism.
Material Design uses appropriate shadowing to help users understand and navigate easily. In the following sections, we will discuss the differences and strengths of the two designs.
Flat Design vs. Material Design

Key Differences between Flat Design and Material Design
Aesthetic Style
Everything in flat design is purely represented and does not have any shadow. It tries to utilize minimalism as much as possible. On the other hand, Material Design displays shadow and depth as it adds layers to illustrate a 3D object properly.
Use of Depth
Everything flat is simple and explained on a single page with no depth. Unlike flat design, material design has layers and shadows that pull the user's attention to emphasize other interface elements, adding depth to the design.
User Interaction
Activity and static engagement in flat design are minimal as few elements move. On the contrary, Material design offers rich interactivity with animations and transitions that improve user experience and bring the interface to life with a suggestion of responsiveness.
Typography & Icons
Both focus on seamlessly understanding typography and icons. In flat design, there is a bold structure with a variety of spacing, size, and alignment to make the design on other platforms appear as one.
Visual Impairment Feedback
With little to no animation, flat design aims for clarity and content at a glance. In contrast, Material Design expands the concept of interactivity by incorporating responsiveness needed to confirm actions taken with interactive elements - every button, toggle, and card displays some degree of responsive motion, animation, and action recognition.
Grid Systems
Unlike flat design, which often results in asymmetrical, uncontrolled layouts, Material design is centered on grid systems and layout structures, which are spaced, rule-bound child maps for arranging application and website content.
Complexity
Unlike flat design, which is more simplistic, material design is more complicated and relies on visual elements to enhance the interaction.
Material Design or Flat Design?
Flat design works best for fast, clean, content-first interfaces, while material design is stronger when you need clear interactivity, feedback, and structure.
Pure flat design can make it harder to spot what’s clickable, so add simple cues like subtle shadows or underlines.
The right choice depends on the product and UX goals, and many projects benefit from mixing both approaches.
Applying Flat Design Principles
While flat design lacks emphasis, it promotes user-centered design by integrating bright colors, uncomplicated typography, and other minimalistic elements.
An aspect of user experience design is flat design's grid-based layouts that enable quick and easy resizing and rearranging of elements and features for different devices.
Establishing Visual Hierarchy with Flat UI Design Elements
Establishing a visual hierarchy is a key principle of flat design. The influence of Swiss style on flat design is evident in its minimalist aesthetics, which prioritize contrasting color palettes, clean typography, and organized layouts. It involves creating a visual hierarchy among elements on the page or application to communicate their relative importance.
Flat Design Example
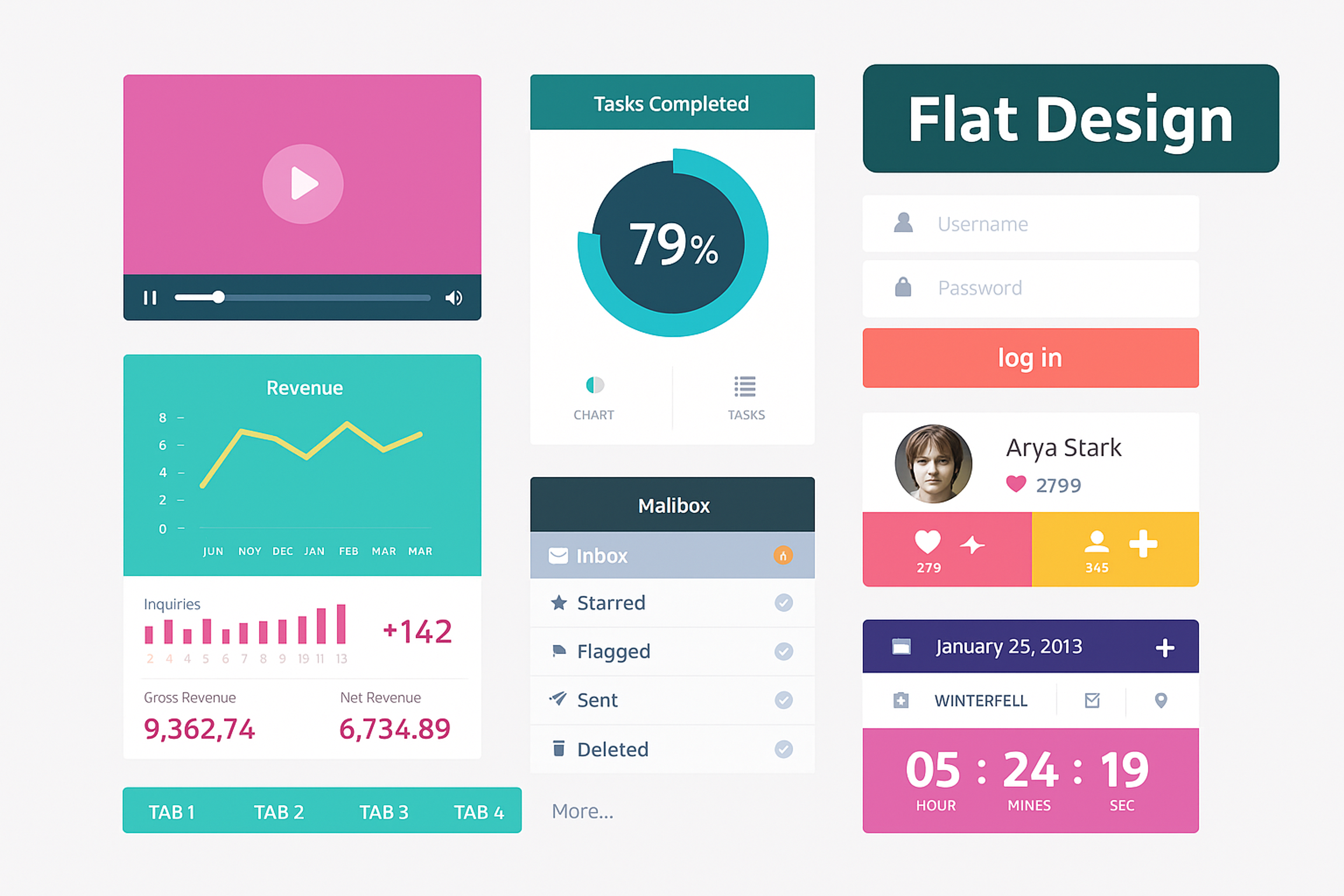
This includes using size, color, contrast, and other techniques to create a clear sense of order among elements on the page or application. By establishing a visual hierarchy, users can quickly and easily identify important information without becoming overwhelmed by too much information.
The most effective way to establish visual hierarchy is by placing important elements at the top of a page or app and less critical ones at the bottom. This guides users to focus on the top portion first before exploring further.
Designers can also use size, color contrast, typography, whitespace, and icons to emphasize key elements. For example, larger typefaces work well for headlines, while smaller ones suit body copy.
Similarly, dark colors can emphasize important elements, while muted colors are ideal for the background. Icons and images can highlight specific information without adding clutter, and whitespace helps create clarity by guiding users between elements.
Establishing visual hierarchy is essential in creating visually appealing and user-friendly interfaces, ensuring an intuitive experience for digital product users.
Emphasizing Clarity and Simplicity
Flat design prioritizes simplicity and clarity, using whitespace and a limited color palette to keep users focused.
Good flat UI relies on strong contrast, straightforward typography, and smart spacing so essential elements stand out and nothing feels crowded.
Use font pairing, weight (regular vs. bold), and a size hierarchy (large headings, smaller body text) to guide attention and make content easier to read.
Contrast, including color, should be used deliberately to highlight key actions without adding visual complexity.
Visual Design Elements by Clay
Utilizing Iconography and International Typographic Style
In flat design, icons and typography do the heavy lifting for clarity and usability.
Iconography: use simple, minimal shapes that stay readable on small screens, and place icons thoughtfully (often near headings) to reduce confusion.
Typography: rely on font choice, weight, size, and spacing to create hierarchy and emphasize key elements without extra visuals. Use larger text for titles and smaller for body copy so users can scan quickly.
Source: Brett Jordan on Unsplash

Incorporating Animations and Interactivity to Enhance User Experience
Adding flat design animations or transitions, along with user-driven elements, can make the entire experience of using a flat interface more pleasant and change the boring function into something more enjoyable.
In flat design, visual elements such as small shadows or underlined texts help the user understand where the "hot" links are and where the "cold" links are, thereby improving user experiences.
User interface (UI) design applies the motion of elements to make interfaces more attractive. It shifts users' focus from one aspect to another to guide and streamline the flow of interaction in the pages.
For instance, animations can provide gentle feedback when users move from one page to another or hover over sections.
Using animations to present the success or failure of a certain task is also helpful since people using the digital product can immediately understand whether they achieved the goal or not.
The app we created for JOKR includes interactive features alongside animations to improve the grocery shopping experience. The app also features easy navigation, delightful icons, and specialized personalized "smart baskets," which bolster the app's dynamic and usability.
JOKR Mobile App Design by Clay
Best Flat Design Examples
Here are some best examples of flat designs:
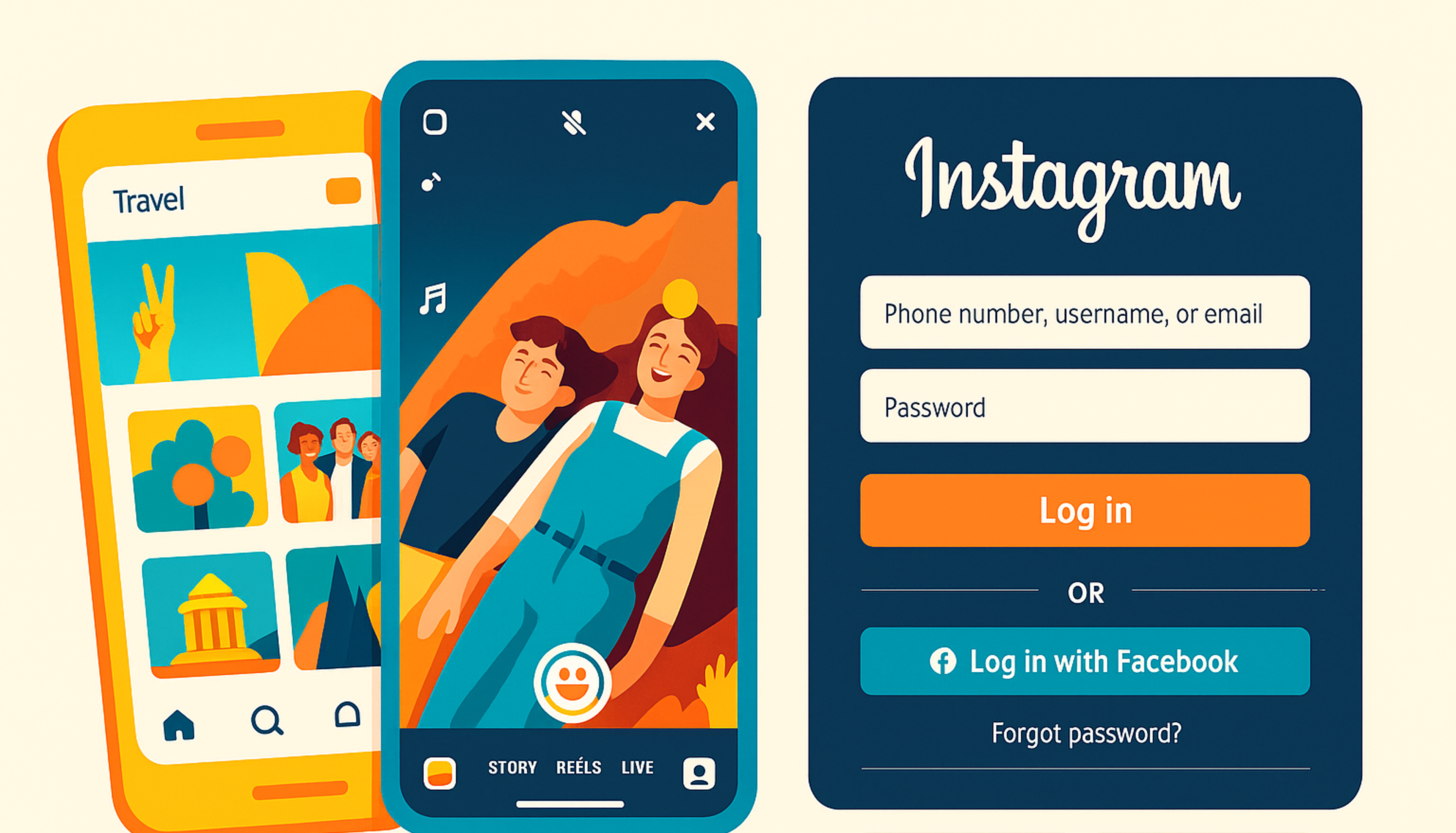
Instagram’s flat design, a visual style characterized by its clean interface and straightforward user flow, is evident throughout the app. The app’s minimalistic design enhances the visual impact of the photos and videos, with flat icons that ensure a smooth and enjoyable experience.
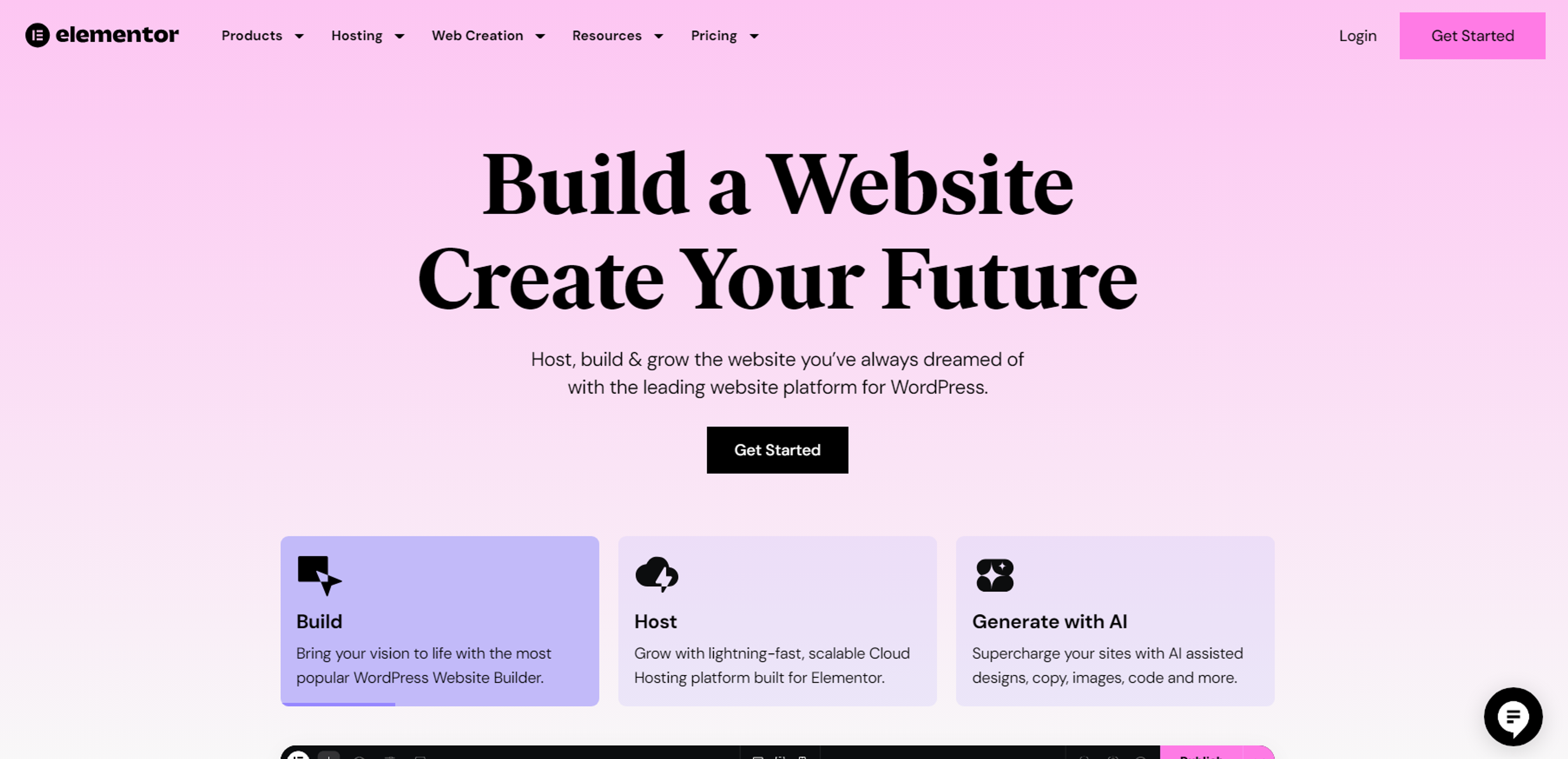
Elementor
Elementor, a drag-and-drop page builder, is an excellent tool for creating flat design websites. As a functional tool, Elementor enables designers to focus on the value provided to users through intuitive and clear interfaces.
Whether you’re a beginner or a professional web designer, Elementor’s flexibility and ease of use allow you to implement flat design principles effortlessly.
Source: elementor
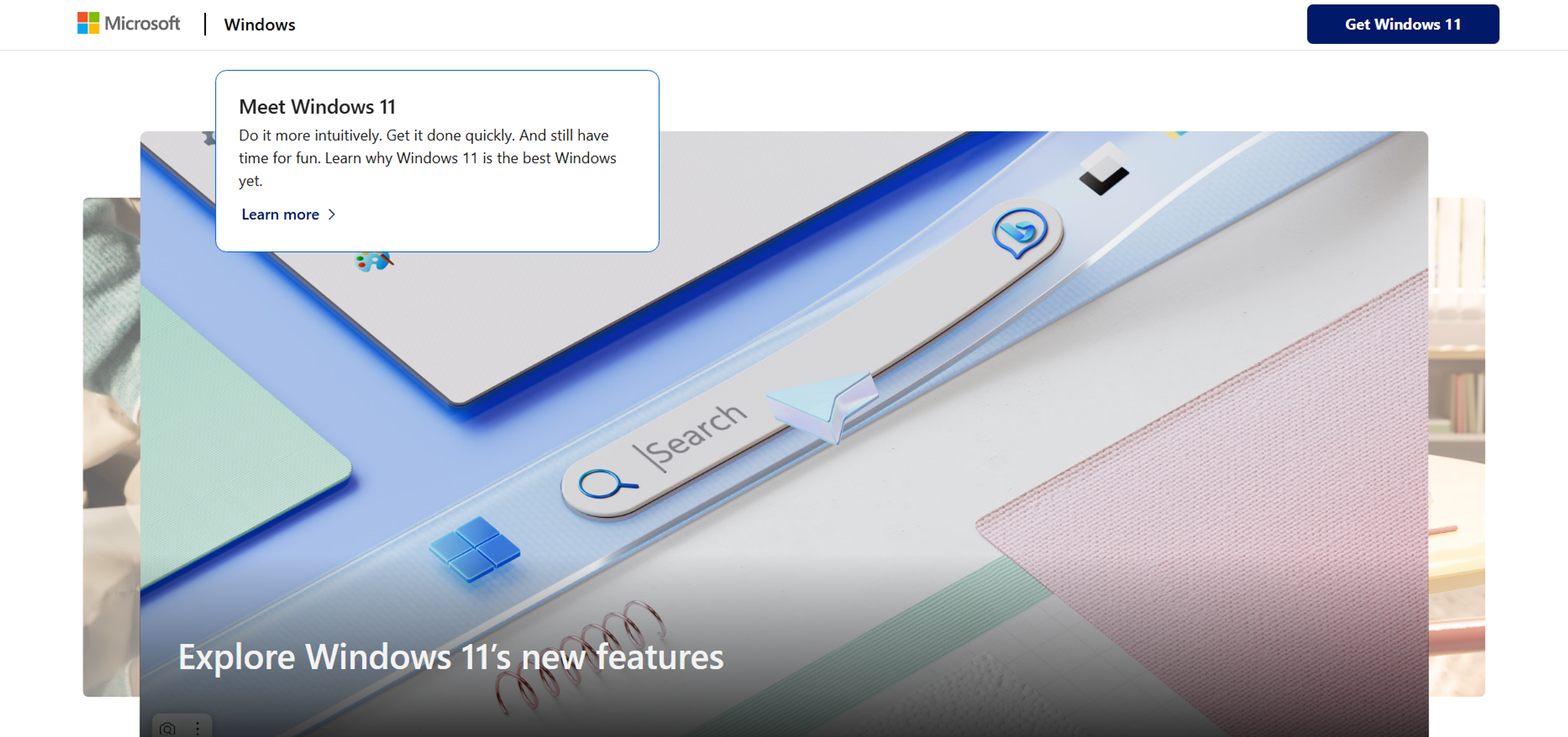
Microsoft's Windows 10 Interface
Microsoft’s Fluent Design System, which is built around flat design principles, has transformed Windows 10 into a user-friendly, visually appealing experience. Its flat elements, typography, and iconography keep the system clean and easy to navigate.
Source: microsoft
FAQ
Q: Why Is Flat Design Popular?
Flat design is popular because it improves user experience, loads quickly, and works well across all screen sizes.
Q: How Does Flat Design Compare to Material Design?
Flat design is minimal and two-dimensional. Material Design adds shadows and motion to create depth and richer interaction.
Q: When Should I Use Flat Design?
Use flat design when you want a clean, fast-loading, and intuitive user interface for content-focused websites or apps.
Q: How Does Flat Design Help User Experience?
Flat design improves user experience by removing distractions, creating clear hierarchy, and making interfaces easier to navigate.
Read more:
Conclusion
By leveraging flat design elements such as animations, interactivity, and consistent branding across platforms, designers can achieve visual simplicity while creating stunning flat design interfaces that are visually appealing and highly functional on any device.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more


