Product designers and UX designers both create great user experiences, but they work in different ways. Understanding these differences helps you pick the right career path and helps companies hire the right people.
Product designers think about the big picture. UX designers focus on how users interact with products. Both roles are important, but they approach problems from different angles. This guide explains everything you need to know about both careers.
What Is a Product Designer?
Product designers use many disciplines to ensure that the product they are working on is created as planned. Product designers use many disciplines, including industrial design, to ensure that the product they are working on is created as planned. They also deal with any issues that arise during the development process quickly so that the product is not delayed or ruined.
User Experience Design vs Product Design

Product designers don’t do it all alone. They need to think about the best solutions to the problems. It can include creating different teams and assigning them to other issues so that the product can stay on schedule.
The product designer will follow the product through the whole process and work with different teams to ensure everything is going as planned, whether it’s the designers, developers, marketing team, or any other department involved.
Product Designer Responsibilities
Product designers have many responsibilities, from concept and strategy development to design and prototype building. They must be creative and knowledgeable to create compelling products that meet customer needs.
The key responsibilities of a product designer include the following:
- Identifying user requirements
- Developing user interfaces
- Creating visual designs
- Testing prototypes and iterating on designs
- Possessing technical skills in areas such as manufacturing, software development, and engineering
They must work closely with the product team to meet all design goals. Product designers are the masters of problem-solving. They wear many hats and use their creative thinking to develop solutions to any issues that arise during development - from UX design to UI visuals, coding, and project management. A product designer does it all!
To ensure success, they assemble effective teams that create various test plans and wireframes and undertake A/B testing until they reach an optimum outcome. In essence, a product designer bridges the gap between idea generation and production execution, making them invaluable assets for any business endeavor.
Product designers are the champions of the product, guaranteeing that it meets all requirements in cost, functionality, and relevance. Moreover, they collaborate with developers throughout the launch to guarantee a successful deployment and cooperate with marketing teams to maintain alignment between brand identity and product design. Ultimately, their goal is to ensure that all stakeholders remain satisfied with every aspect of the product.
What Is a UX Designer?
User experience designers think about giving users the best user experience when using a product. They have a strong focus on interaction design, which involves creating specific user interactions and micro-interactions that enhance product responsiveness and intuitiveness. UX designers focus on creating a product that lets users quickly and intuitively achieve their goals.
It is done by understanding the users, what they want from the product, and how they will use it. Using this information, the UX designer can design the product and give people the best experience by improving usability and accessibility for the product’s target users.
The UX designer will follow the product’s development from the research stage to the prototyping stage, release stage, and after. The UX designer will help improve the product based on user feedback.
It causes the UX designer to work on the product throughout the process to ensure usability, providing users with the best user experience during the design process.
UX Designer Responsibilities
UX designers (who also differ from UI designers) are responsible for ensuring that a product or service is easy and enjoyable to use. They create designs that consider user needs, wants, behaviors, and preferences. This includes researching users' goals and motivations while using a product or service.
UX designers must also design an interface that allows users to access information quickly and perform tasks without difficulty navigating through the website or app.
UX Designer Responsibilities by Clay
Additionally, they need to ensure that their design is accessible to all users regardless of physical ability or technological capabilities. Ultimately, UX designers strive to create products and services with maximum usability so that customers have a positive experience when interacting with them.
As a UX designer, one has the opportunity to engage in activities such as:
- Collecting user feedback and assessing user experiences
- Formulating customer pathways toward their desired goal
- Synthesizing data into personas for a better understanding of target audiences
- Generating wireframes and prototypes to visualize concepts
- Collaborating with UI designers on designing aesthetically pleasing visuals
- Cooperating with developers for functional project management and execution.
What Are the Similarities Between Product Designers and UX Designers?
Product designers and UX/UI designers both play vital roles in the development of digital products. Both disciplines have similar goals: creating user-friendly interaction designs that meet customer needs while achieving business objectives.
However, there are subtle differences between product design and UX design: product designers focus on creating products from the ground up, emphasizing aesthetics. In contrast, UX Designers strive to improve existing products by enhancing usability and increasing user satisfaction.
Product Designers vs UX Designers
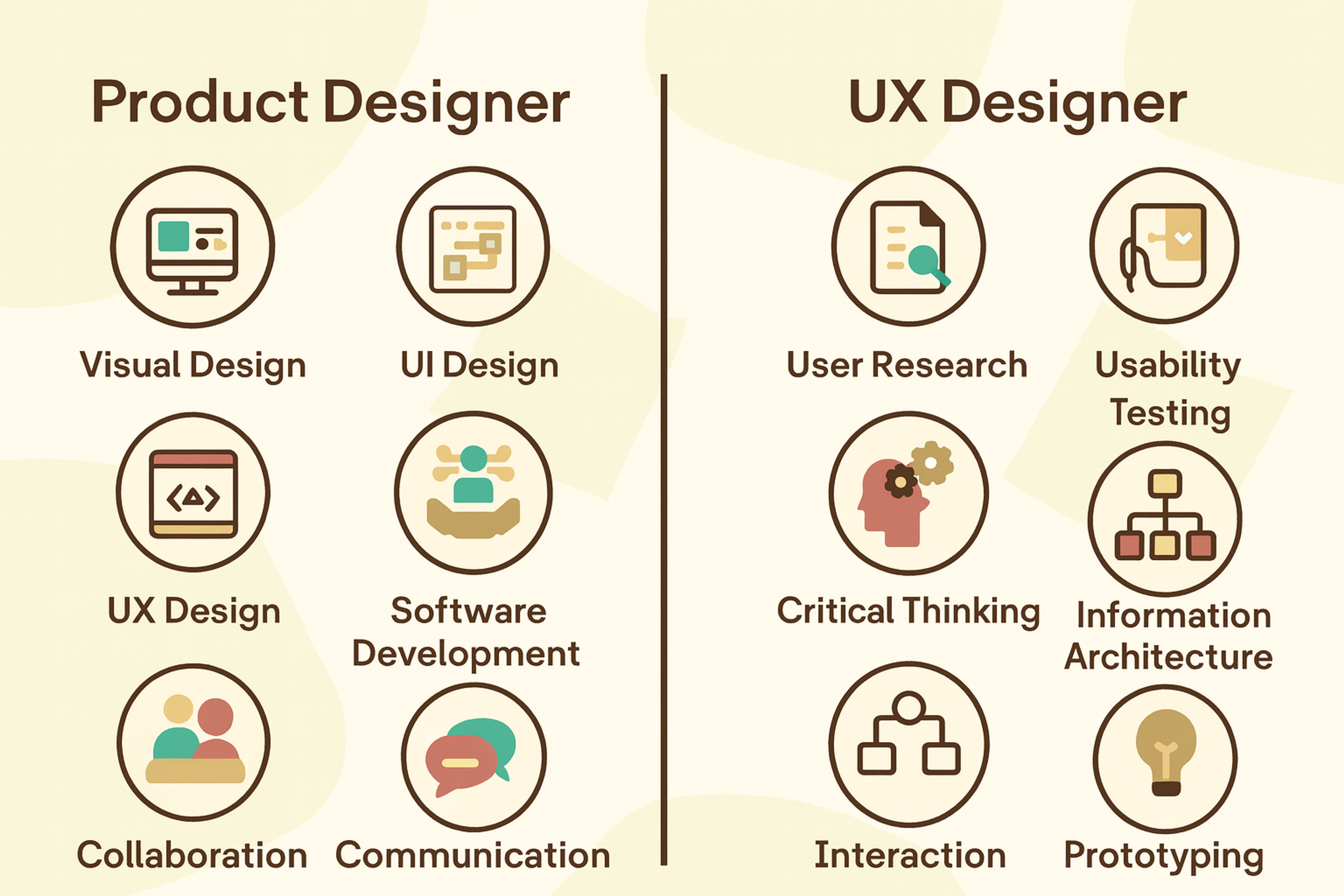
Despite these differences, product and UX designers share many similarities regarding their roles and responsibilities, such as researching users’ needs, creating wireframes or prototypes for testing during the design process, conducting usability tests, gathering stakeholder feedback, etc.
Ultimately, both fields are essential components of successful product development as they provide insights into how customers interact with products so that companies can create better experiences for their users.
Product Designer vs UX Designer
The responsibilities might look similar, but there is an easy way to see the difference. While the UX designer focuses on ensuring the product is usable and provides the best user experience to the target users, the product designer focuses on the bigger picture. The product designer thinks about how well the product will do and its purpose.
The UX designer is more responsible for the product's user experience, but the product designer thinks about the business and how the product will affect it. The product designer needs to be more flexible, as they need to deal with a broader range of problems and propose solutions.
The product designer and UX designer need to work together to ensure that a product provides value to users and is helpful and successful. Each designer needs the other to achieve their goals and create a successful outcome.
The clear difference between the product designer and the UX designer is that a product designer has more responsibilities that vary greatly. In contrast, the UX designer mainly focuses on the product's usability.
Product Designer vs UX Designer Salary
When comparing product designer and UX designer salaries, there are a few key differences, though both roles generally offer competitive pay. The salary for both positions can vary based on factors like experience, location, industry, and company size.
Product Designer Salary
A product designer is responsible for designing a product’s overall user experience, including its interface, functionality, and how it fits into the overall business strategy. Because product designers handle both visual design and the functionality of the product, their salaries tend to be on the higher end of the design spectrum.
- Average Salary: According to Glassdoor, the average annual salary for a product designer in the United States is around $85,000 - $120,000 depending on the region, experience, and expertise.
- Experience: Junior product designers typically start around $65,000 - $75,000, while experienced product designers can earn upwards of $130,000 - $150,000 annually.
UX Designer Salary
UX designers, on the other hand, focus primarily on improving the overall experience of the user, ensuring that the product is user-friendly, functional, and meets user needs. They collaborate with product designers, developers, and product managers to create intuitive interfaces and experiences.
- Average Salary: According to PayScale, the average salary for a UX designer is around $70,000 - $110,000 per year.
- Experience: Entry-level UX designers typically start at $55,000 - $70,000, while senior-level professionals can earn around $115,000 - $130,000 annually.
5 Ways Product Designers Differ from UX Designers
1.
Focus on Functionality vs. Experience: product designers typically concentrate on the overall functionality and feasibility of the product, whereas UX designers prioritize the user experience, ensuring that the product is intuitive and enjoyable to use.2.
Scope of Work: product designers often work on the broader aspects of design that encompass product strategy, development, and visual aesthetics. In contrast, UX designers dive deep into user research, wireframing, and prototyping, focusing on how users interact with the product.3.
Skill Set: while both roles require understanding design principles, product designers often possess a wider range of skills, including product management and engineering know-how. UX designers usually excel in usability testing and user-centered design methodologies.4.
Iterative Process: product designers may engage in an iterative design process that includes feedback from multiple stakeholders, including marketing and sales teams. UX designers, however, predominantly rely on user testing results to refine and enhance the user interface.5.
End Goals: product designers aim to create a successful product that meets business objectives. In contrast, UX designers strive to optimize the user journey, ensuring satisfaction and accessibility throughout the interaction with the product.
Essential Skills for Product and UX Designers
What Skills Does a Product Designer Need?
Product designers should be able to work efficiently and collaborate with different teams to ensure the product’s success. Product designers often collaborate with visual designers to ensure the product is both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Product designers must have excellent communication skills and adapt to varying communication styles. Understanding business needs and processes and seeing the bigger picture when following the development process of a product. Product designers need to be flexible, able to adapt to different situations, and able to propose solutions to various problems during development. Product designers need to be capable of using modern software to aid other teams during product development.
Product designers must have an eye for detail and understand the user experience. They must be able to analyze customer feedback and incorporate it into their design thinking process. They also need to think strategically about how their plans can shape the future direction of a product or service.
Product designers must be able to utilize various tools such as Sketch, Photoshop, Illustrator, and other design software to create prototypes and visual assets. Furthermore, they should have a strong knowledge of web technologies such as HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript to develop compelling user experiences across desktop and mobile devices.
Source: KOBU Agency on Unsplash

Product designers should be highly organized and have excellent communication skills to work effectively with stakeholders at all organizational levels.
They must also stay up-to-date with the latest trends in product design so that they can bring fresh ideas into their design process. Additionally, they must possess problem-solving skills to identify challenges and find appropriate solutions quickly.
What Skills Does a UX Designer Need?
- UX designers need to understand the UX design process and be able to create customized design processes for different products to improve the product's probability of success.
- Use user testing feedback to improve a product to give users what they want.
- UX designers have to be able to user research and analyze the information to understand users, their pain points, and what they want.
- Know how to use modern design tools to create designs and prototypes to speed up the design thinking process.
- A UX designer needs to know how to give users the best user experience and make it easy to achieve their goals using the product.
UX designers need to use various tools to effectively create intuitive and user-friendly products and services. The most common tools include wireframing software, prototyping tools, usability testing tools, and analytics tools.
Wireframing software helps create the initial structure of any product or service. It provides a visual representation of the project and helps define the overall user experience by providing a basic outline of how a product should look and feel. Popular wireframing tools include Sketch, Adobe XD, InVision Studio, Figma, Balsamiq Mockups, and Moqups.
Wireframe for UX Projects by Clay
Prototyping is another vital tool for UX designers. It helps turn designs into interactive models that can be tested by real users to measure their reactions to the design.
These prototypes can also be used to communicate ideas more effectively between stakeholders. Popular prototyping tools include InVision Studio, Axure RP Pro, Adobe XD, ProtoPie, and Marvel App.
Usability testing involves assessing how easily users can complete tasks using the design elements of a particular product or service. This helps identify any areas that could cause confusion or frustration to users when using the design features. Popular usability testing tools include UserTesting, Loop11, Chalkmark, Optimal Workshop’s Treejack & Chalkmark, and WhatUsersDo.
Finally, analytics provide key insights into how well a product is performing with its users and allow you to identify areas in which further improvements can be made to optimize the user experience. Popular analytics tools include Google Analytics, Mixpanel, and Heap Analytics.
Building Your Design Career
Essential First Steps
Develop core skills by mastering fundamental design tools and methods regardless of which path you choose. Build a portfolio with case studies that show your problem solving process and impact. Gain real experience through internships, freelance projects, or volunteer opportunities.
Join design communities by participating in local meetups, online communities, and professional organizations. Stay current by following design trends, tools, and methods through blogs, courses, and conferences.
Long Term Career Development
Both career paths offer opportunities for growth into leadership, consulting, entrepreneurship, or specialized expertise. The key is building strong foundational skills while staying curious and adaptable as the field evolves.
Success in either role requires continuous learning, user empathy, and the ability to communicate design value to diverse stakeholders. Whether you choose product design or UX design, focus on solving real problems for real people while contributing to business success.
FAQ
Is UX Designer The Same As Product Designer?
No. A UX designer focuses on user research, flows, and usability. A product designer covers that plus product strategy, prioritization, and partnering with engineering and business to ship outcomes.
Which Is Better, Product Design Or UX Design?
Neither is “better.” Choose UX design if you prefer research and interaction design depth; choose product design if you want end-to-end ownership that mixes UX, UI, strategy, and delivery.
Who Earns More, UX Designer Or Product Designer?
Comp varies by region and level, but product designers often earn slightly more because the role spans research, design, and product strategy. Seniority and company stage have a bigger impact than title alone.
Is UI/UX Under Product Design?
Often yes. Many teams use “product design” as the umbrella that includes UX research, interaction design, visual/UI, prototyping, and design ops, all aimed at shipping product outcomes.
How Much Do UX/Product Designers Make?
Ranges vary widely by location and seniority. Entry-level roles may earn modest salaries. Senior/staff designers at tech companies can earn significantly more with bonuses and equity. Compare local market data and level guides for precise ranges.
Read more
Conclusion
Product designers and UX designers both play crucial roles in creating successful digital products. Product designers take a strategic, business focused approach while UX designers specialize in user research and experience optimization.
Understanding these differences helps you choose the right career path and ensures teams have the right mix of skills for project success. Both roles require creativity, problem solving abilities, and user empathy, but they channel these qualities in different ways.
The most successful design organizations use both perspectives, creating products that satisfy user needs while achieving business objectives. Whether you pursue product design or UX design, focus on developing strong foundational skills while staying curious about the broader design landscape.
Your choice between these paths should align with your interests, strengths, and career goals. Both offer rewarding opportunities to impact how people interact with technology while building meaningful, sustainable businesses.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more


