So, what is interaction design? It's a way of designing products and services that focus on how people interact with them. Interaction design, or IxD, helps shape how we use technology — whether it's a phone, a website, or an app.
It starts by understanding what users need and what motivates them. Designers use this knowledge to create simple, helpful interfaces that make tasks easier to complete. It uses interaction design frameworks and follows interaction design principles to guide this process.
Interaction design comes from human-computer interaction (HCI) research. But over time, it has grown into its own field with its own ideas and methods. It now explores interaction psychology and examines interaction paradigms to create better user experiences. Brand interaction design exploration helps companies understand how their visual identity can enhance these digital interactions.
What Is Interaction Design?
Interaction design is the study of how people interact with digital products and systems. It focuses on creating smooth, useful experiences that meet user needs in real situations. It applies interaction design and often applies cognitive interaction design to ensure the solution aligns with human behavior.
This field blends many areas, including graphic design, software engineering, psychology, product design, and more. It brings together different skills to better understand how people use technology. It also understands interaction semantics and analyzes interaction complexity to optimize systems. Brand interaction design integration ensures these diverse elements work together to support the overall brand experience.
The main goal of interaction design is to create experiences that feel easy, natural, and enjoyable. Designers work on websites, apps, smart devices, and even self-driving cars - anything that involves people using digital systems. It also practices interaction design through iterative development and research. It creates interaction feedback that improves satisfaction and retention.
Origins and Development of Interaction Design
Interaction design had its roots in the mid-20th century when scientists and engineers began creating machines that could interact with humans through visual feedback and interface elements such as displays or buttons - thus initiating the field of Human-Computer Interactions (HCI).
Since then, it has grown into an increasingly complex discipline that continues developing as technology advances at rapid speed - adopting new forms such as AI (Artificial Intelligence), VR (Virtual Reality), or AR (Augmented Reality). Modern interaction design now also explores interaction paradigms and considers interaction design ethics to account for evolving user expectations and social responsibility.
Brand interaction design has become an essential part of this evolution, helping companies create consistent experiences across all digital touchpoints.
Interaction Design
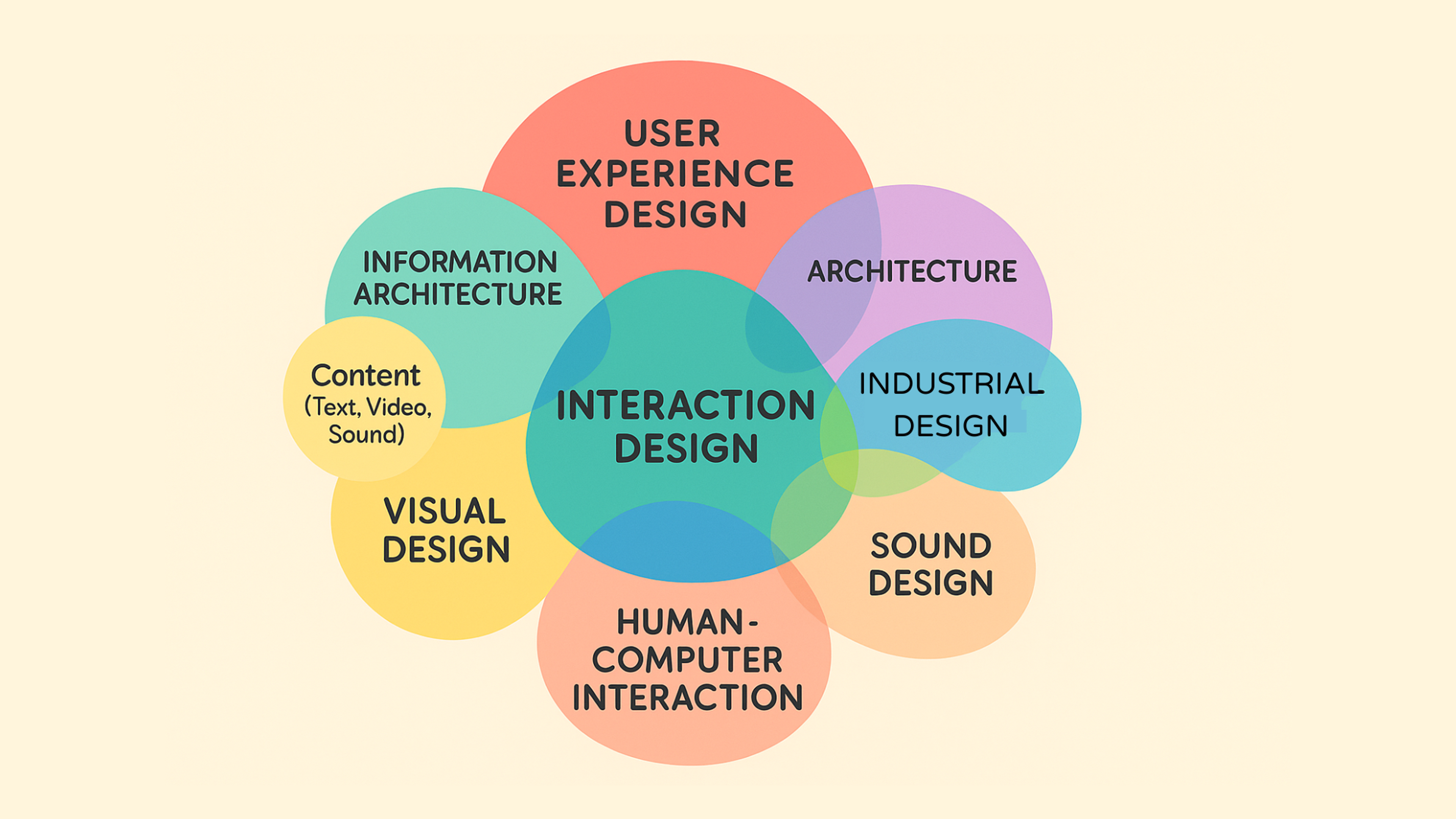
What Are the Benefits of Interaction Design?
Interaction design improves market success by making products easy to use and aligning system behavior with users' mental models.
Interaction design reduces frustration during the user journey and provides feedback that helps users learn and feel more confident.
When design work is driven by user-centered needs, goals, opinions, etc., it creates loyalty and satisfaction and increases user adoption. Good brand interaction design helps align these choices with the wider brand goals.
When good interaction design is applied, sign-up and purchasing actions in the system become more obvious. This, in turn, helps improve the system's usability and conversion rates.
Interaction Design Elements
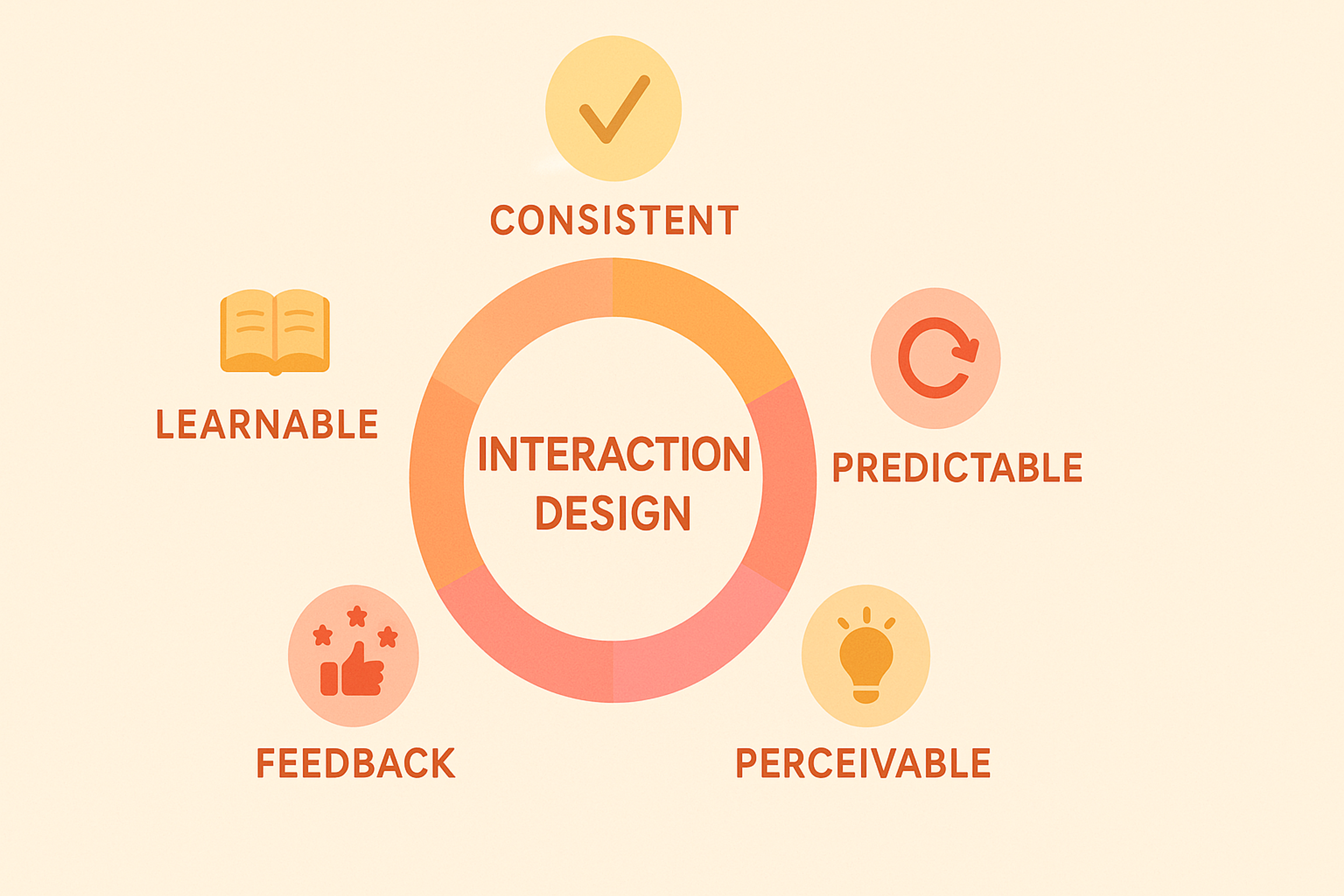
The Five Dimensions of Interaction Design
The model describes five dimensions that influence interaction with the interface.
1D - Words. Clarity is important, so the communication is concise - this applies to buttons and prompts.
2D - Visual representations include graphics, icons, and typography that enhance clarity and help with information scanning.
3D - Physical objects/space. This dimension involves the context and devices used (keyboard, screen, touch, touch environment).
4D - Time. This dimension involves response speed, transitions, and progress.
5D - Behavior involves the feedback, rules, and system states.
When designing significant user interactions, ensure the experience is solid across all five dimensions, not just in copy or layout.
Source: Anete Lūsiņa on Unsplash

Interaction Design vs UI Design
Interaction design involves a greater extent of the user's journey than UI design does.
- Interaction Design: defines behavior like what happens on click, swipe, hover, and includes things like transitions, micro-interactions, animation logic, and feedback.
- UI Design: defines the appearance, including color, typography, icons, and layout, for a unified visual system.
In smaller teams, it is common for the same person to do both, while in larger teams, the roles are usually split, with significant overlap in product design.
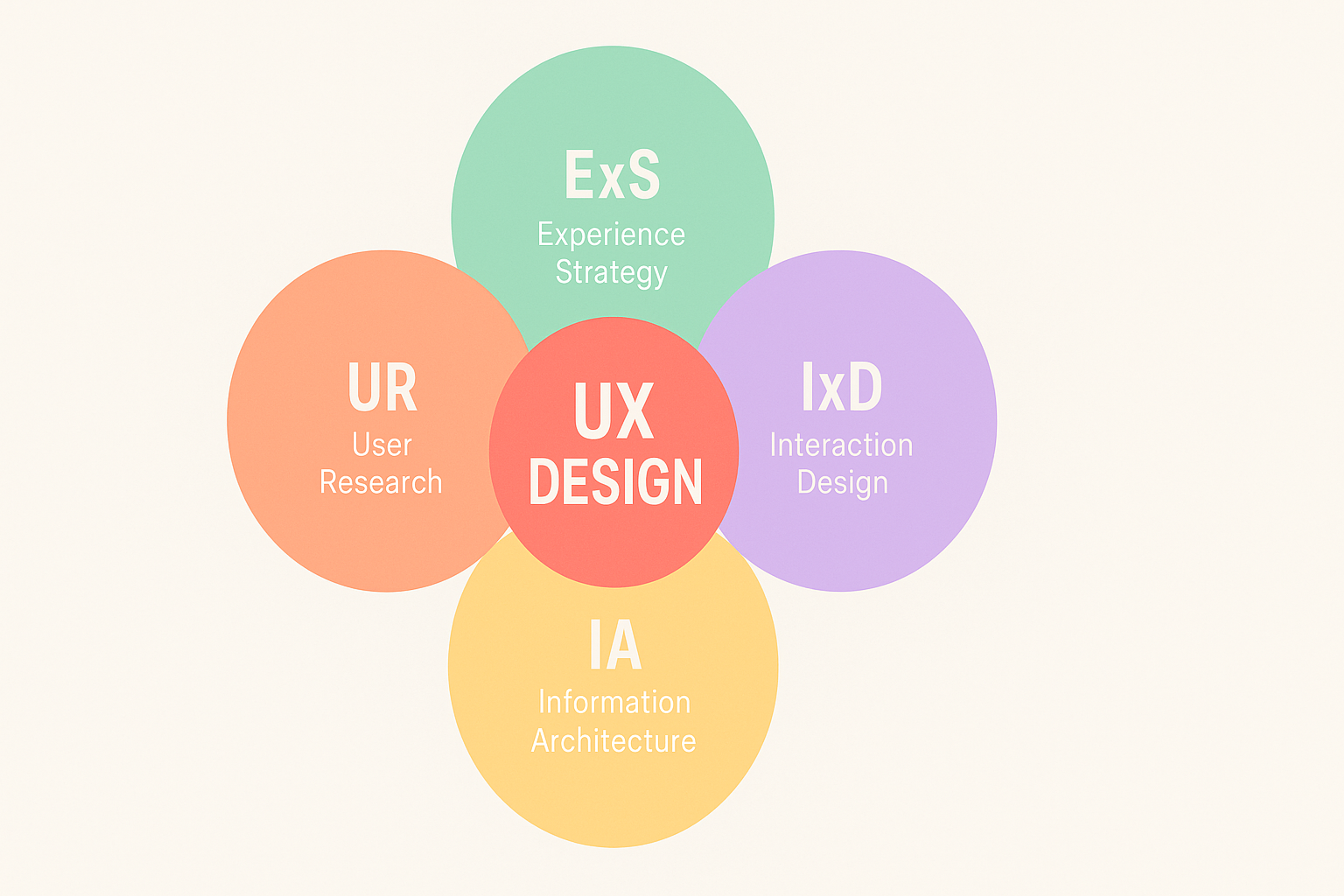
Interaction Design and User Experience
- Interaction Design: provides the answers to how the interface behaves, how things like clicks, swipes, inputs, etc. are initiated, how the system provides feedback, transitions, and changes state.
- UX is the umbrella of all things usability, accessibility, content, consistency, security, and branding alignment.
Interaction design is focused on understanding goals, tasks, and context to make interactions efficient and predictable. UX ensures the experience is clear, complete, and coherent.
UX Design
Who Are Interaction Designers?
Interaction designers combine design with psychology to shape people's interactions with digital products. They establish interaction behavior across a product, from idea to release, so primary tasks are evident, efficient, and consistent.
Some of the established traditions are:
- Task Analysis: focus on user objectives, steps, and areas causing issues.
- Prototyping: early testing of interactions with minimal risks.
- Storyboarding: mapping user flows and scenarios from start to end.
- Wireframing: organizing the structure of a screen and layout of interactions.
- User testing: confirm conduct with actual situations and repeat.
These practices improve interaction patterns and overall usability.
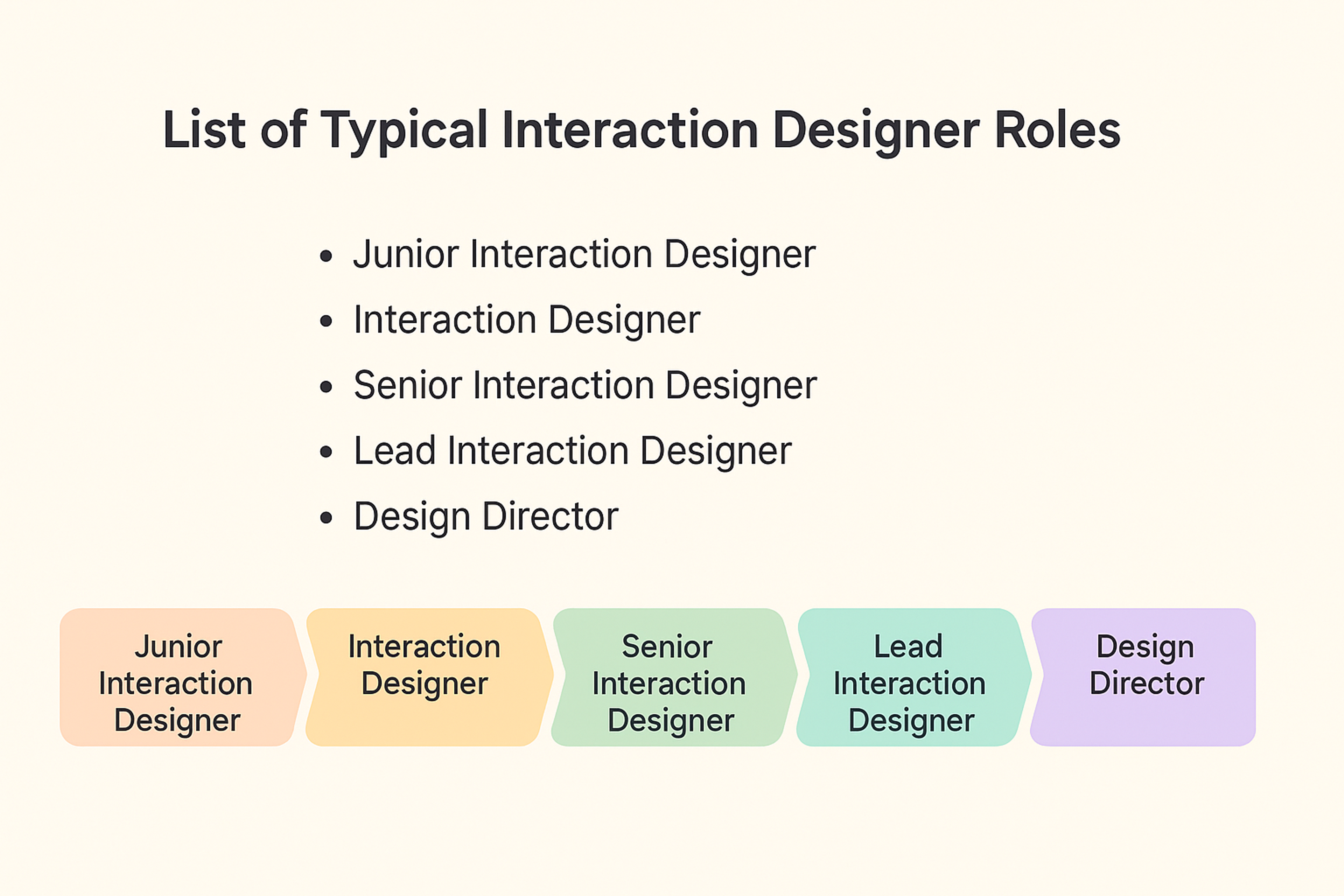
Typical Interaction Designer Roles
Standard Tools Used in Interaction Design
The most commonly used tools in interaction design include SketchApp, Principle, InVision Studio, Framer X, and UXPin, among many others - all designed specifically for UX/UI designers who need powerful but easy-to-use tools for prototyping user interfaces quickly without coding knowledge requirements.
These tools allow interaction designers to create interactive prototypes and collaborate to create desired user experiences while maintaining control over every aspect, from color schemas and typography elements to custom components and animations. These tools support teams that practice interaction design, apply interaction design, and use interaction design frameworks in their everyday workflows.
How to Measure the Success of Interaction Design?
Interaction design (IxD) is a subdivision of UX design that helps guarantee users reach their aims by properly utilizing the system. Ushering IxD’s influence on the business's financial outcome can assist in gaining approval from high-level decision-makers.
Establishing and reestablishing how effective interaction design is through measuring its impact and testing will indisputably prove its worthiness to stakeholders. Effective teams often perform interaction design pattern analysis to review what patterns worked and how they influenced success metrics.
The HEART framework is a beautiful mechanism to judge user experience design, although the attributes also apply to interaction design. For example, you can assess users’ satisfaction with surveys on customer happiness, net promoter score, and usability.
You should also consider how involved and engaged your users are by using interface data such as visit frequency or length of stay for each session. Lastly, observe the rate of new user adoption over time - an effective measure to monitor product or feature success!
Google's HEART Framework
Retention can be tracked with a dashboard that compares new vs returning users over time.
For interaction design, measure how well people complete tasks using behavioral metrics like completion time and error rate.
Validate a new product version with direct feedback and user research, then iterate using a structured design process based on the results.
Best Practices for IxD
Usability.gov encourages businesses to consider the following queries when creating digital products with interactive components. These prompts align with core interaction design principles and guide teams as they implement interaction design patterns thoughtfully:
- What instructions can a user give to engage with the interface?
- What design elements (color, shape, size) help users understand how the system functions?
- Before taking action, what kind of information do you provide so that people know anticipated outcomes?
- Are there restrictions in place to avoid mistakes and errors from happening?
- If an error occurs, does your program display useful messages for customers to figure out how best to fix it or why such an issue occurred in the first place?
- What feedback does a user get once an action is performed?
- How swiftly does the product respond to our actions?
- Are interactive elements easy to access based on their size and strategic placement of edges/corners?
- Is related information grouped into manageable chunks instead of inundating us all at once, and do we recognize these formats from other familiar sources?
By asking these questions, designers not only practice interaction design but also consider interaction design ethics — ensuring the experience is not only usable, but responsible, inclusive, and transparent. They explore interaction paradigms that guide users across modern interfaces with clarity and purpose.
Read more:
Conclusion
In conclusion, interaction design is an ever-changing field that requires an interdisciplinary approach, combining knowledge from various areas, such as graphic design, software engineering, and psychology.
By understanding users’ needs and expectations along with their context, you’ll be able to create meaningful experiences tailored specifically to them while providing real value and improving their day-to-day lives.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more