Mobile isn’t “just another” channel anymore. For many products, it’s the primary surface where people discover value, build habits, and decide whether they trust you.
That makes mobile work less about pretty screens and more about choices: what to build, how to ship safely, and how to improve fast after launch.
You’ll learn how to pick the right build approach (native, cross-platform, or PWA), plan an MVP that actually validates demand, design for touch and speed, set up a development process that avoids common traps, and launch with strong App Store presence.
App Creation

What Is Mobile App Design?
A mobile app is a product that lives inside constraints: small screens, touch input, intermittent connectivity, limited battery, strict platform rules, and users who quickly abandon when anything feels confusing.
The goal isn’t to “add more features.” The goal is to deliver a short path to value, then keep that path reliable as the app grows.
If your app feels fast, predictable, and safe, users return. If it feels slow, inconsistent, or surprising, they bounce even if the feature list is impressive.
A well-designed mobile app is not just about aesthetics. It’s about creating an intuitive and efficient user journey. This involves careful planning of the app’s layout, navigation, and interactive elements to ensure that users can easily find what they need and perform tasks without frustration.
By focusing on user-centric design, developers can create apps that are not only visually appealing but also highly functional and engaging.
App Architecture and Technology Stack
Choosing the exemplary architecture and technology stack is the first big step for any app development team. This choice shapes how well the app works, how fast it runs, and how easily it can grow later.
Developers remember that designing an app is different from traditional software. Where software may have complex features and extended timelines, apps zoom in on key features for faster launches.
Native vs. Hybrid vs. Web Apps
Users want to know immediately whether to build a native, hybrid, or web app. Native apps are made for a specific device, delivering the best performance and experience. Hybrid apps mix web and native code and run on various devices, but they might be slower.
Web apps, technically a type of hybrid, run in a browser on any operating system. They require less maintenance but can't use all device features.
Mobile Web, Hybrid Native, and Pure Native Development

Identifying Suitable Programming Languages and Frameworks
The final piece of the technology stack puzzle is choosing the best programming languages and frameworks for the app's needs and the platforms it will run on. This decision impacts performance, developer speed, and long-term sustainability.
For any mobile app, developing with native tools usually means picking up Swift for iOS or Kotlin for Android. Most developers still love these choices because they best suit the device's hardware.
On the other hand, a vast variety of hybrid frameworks can help. React Native and Flutter are the top players for cross-platform builds. Web tech like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript also still powers a surprising number of mobile apps.
Considerations for Scalability and Performance
Before you write a single line of code, map out how the app will grow. Scalability and performance matter even more if you expect big numbers in the future. Pick tools and services that stretch gracefully, whether adding new monthly users, layering in power features, or delivering fast and smooth interactions.
Dodge performance roadblocks by following best coding practices, optimizing resource use, and running complete tests. Check performance basics like real devices' load time, memory use, and battery life.
When you sort out these questions, you can build a rock-solid architecture and tech stack that meets today's needs and still shines tomorrow.
Mobile App Design
A mobile app's design can make or break the whole project. It's more than a pretty screen. Good design blends colors, size, and layout to pull users into a seamless flow, making sure they know what to do next and why.
Interaction Design for Mobile Apps
Interaction design, crucial in mobile app design, involves creating intuitive navigation systems for easy user access. It relies on understanding user needs and behavior, refined through feedback and testing. Using typography, color, and imagery, a clear visual hierarchy guides users and highlights essential elements.
Intuitive navigation through buttons and menus ensures simplicity and reduces user cognitive load. User feedback and usability tests identify areas for improvement, refining the design iteratively. Developers create functional, enjoyable apps by focusing on interaction design principles and user feedback, enhancing user experience and boosting market success.
Our mobile app for Joe & The Juice emphasizes the importance of interaction design through straightforward navigation and a seamless user experience. Users can effortlessly navigate the app using a visual hierarchy with vibrant colors, typography, and interactive elements.
The design prioritizes user-friendly features like simplified product search, loyalty programs, and contactless solutions, continuously refined through user feedback. This thoughtful organization of elements allows users to find what they need quickly and enhances the overall experience.
Source: Joe & The Juice mobile app design
How to Design a Mobile App
The most crucial step in the app development process is coding, iterative feedback, and editing the app. This is where one of the app parts is created, and the appropriate development is selected to integrate all those components so that this part can be done efficiently and, even more so, satisfy the active nature of the project.
Agile vs. Waterfall Methodologies
Workflows and project success greatly depend on the methodology adopted. Consequently, the project manager should wisely choose Agile or Waterfall methodologies.
Agile is preferred mainly because flexibility in the organization time of the project is essential for delivery, amending and con, and constant interaction within the project's lifetime.
It divides the project into several phases, during which only the previously identified components are being worked on. In contrast, Waterfall is old-fashioned.
After each project phase is over, it is necessary to wait until the last phase is over before starting on the second phase. It is most suited for projects where requirements are already apparent, and the likelihood of changes is low.
Version Control and Code Management
Version control and code management are critical for optimizing the middle stage of development. Tools such as Git help developers change documents, work together, and save the history of code changes.
Thanks to this practice, teams can work together smoothly, reducing the chances of disagreements and restoring previous versions, which is possible when needed.
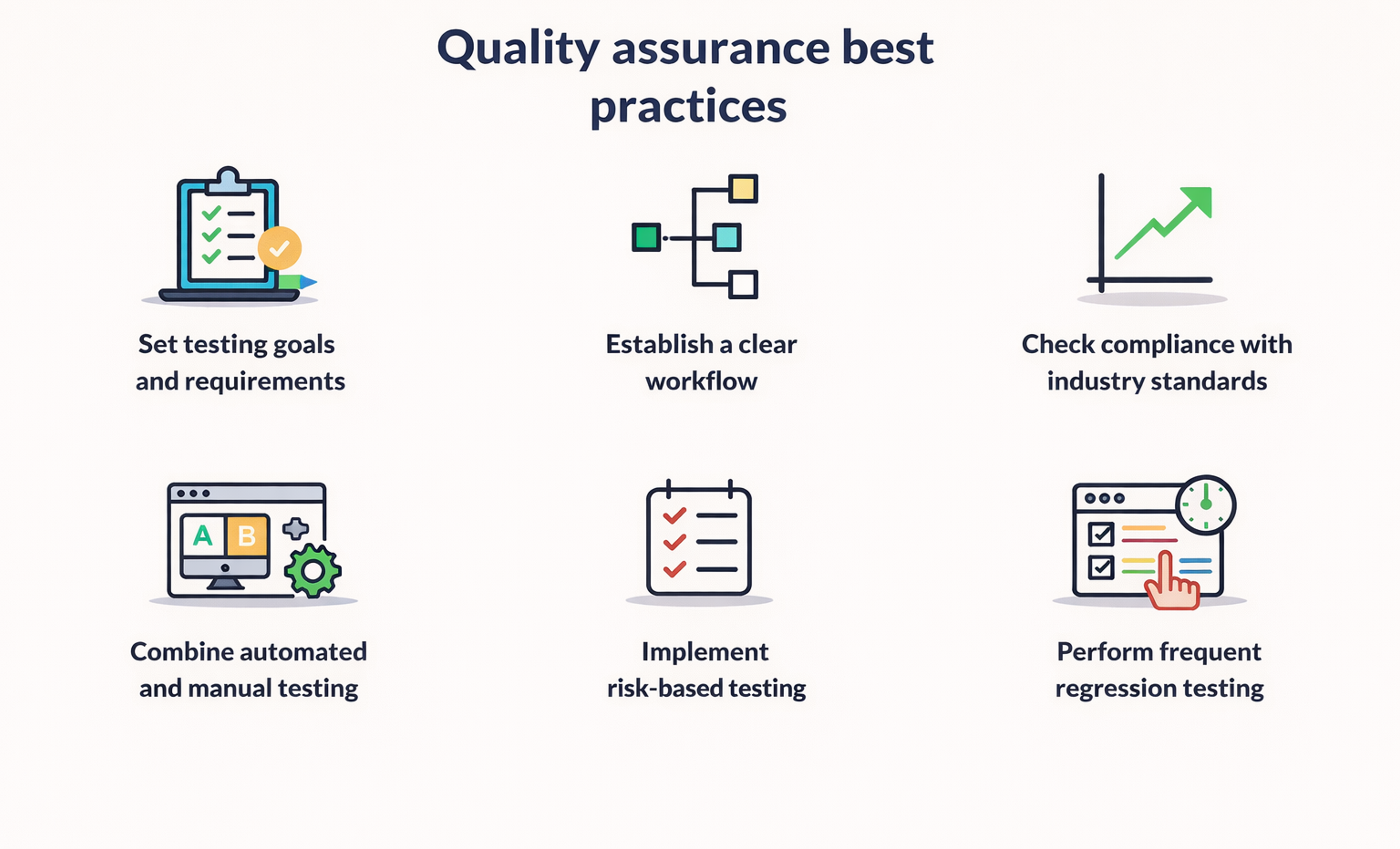
Testing and Quality Assurance
Systematic testing and QA must be observed and employed to deliver a credible, bug-free application. Testing must incorporate many tests, such as unit tests, integration, and user acceptance tests, to fix problems early.
This process can be done more efficiently and comprehensively using Automated testing. Last, relevant QA activities are performed on specific methods or applications to be released to the consumers to ensure that they conform to the defined non-functional requirements.
Including these elements as part of the development process also helps take a pragmatic and ordered approach to developing the application, resulting in successful collaborative creation and improvement processes.
Quality Assurance Components
App Store Optimization (ASO)
App Store Optimization (ASO) reassures mobile application developers and marketers that such mists can be cleared and that their apps are made conspicuous in the app markets, including the Apple App Store.
It is essential for the developers not to rush into the competition and focus on pain points optimization; instead, optimize the most critical parts of the app for the developmental expectations.
Crafting Compelling App Titles and Descriptions
An appropriately crafted app title and description need no introduction since they capture the user's attention and the app's offering. App titles should be particular, catchy, and warm, including main keywords for search purposes.
The body's objective is to present the application, concentrating on its highlights, pros, features, and functionalities, and motivating the users to install and use it.
Choosing the Right Keywords
This is usually the most efficient process of improving the app's position in the app stores regarding search features. Use a keyword tool, do the best keyword research, and look for keywords that users usually search for in the application category you are creating. These keywords should be placed in the app title and metadata in the description to boost the app's chances.
Creating Attractive App Icons and Screenshots
The icon and high-quality software images are paramount for attracting prospective users. An attractive and unique app icon can capture the audience's attention and make them click.
Also, screenshots related to the app showcasing the user interface and its features and benefits provide a sample of the app's use, which would encourage downloads.
Thus, by concentrating on these App Store Optimization aspects, developers can improve the app's visibility, attract more users, and enjoy growth and success in the ever-evolving app market.
Mobile Apps Best Practices
Designing and developing a successful mobile app requires more than just clean code and eye-catching visuals. It’s about building something that feels intuitive, performs reliably, and meets user expectations from the first tap. Here are a few essential best practices to keep in mind:
Here are the most important best practices to focus on when creating a successful mobile app:
- Prioritize User-Centered Design: Design with real user needs in mind. Understand their behavior, goals, and pain points to build an intuitive, helpful app.
- Optimize for Performance and Speed: Users expect fast, smooth apps. Keep load times short, reduce friction, and ensure performance across devices and networks.
- Design for Touch and Simplicity: A clean, touch-friendly interface makes it easier for users to navigate. Use large tap targets, clear CTAs, and a logical layout.
- Test Continuously and Gather Feedback: Regular usability testing helps you catch bugs, improve UX, and adapt to user needs before small problems become big ones.
- Keep Permissions Minimal and Transparent: Only request necessary data, and clearly explain why you need it. This builds trust and supports user privacy.
Focusing on these five areas will ensure your mobile app delivers a high-quality, user-friendly experience that keeps people coming back.
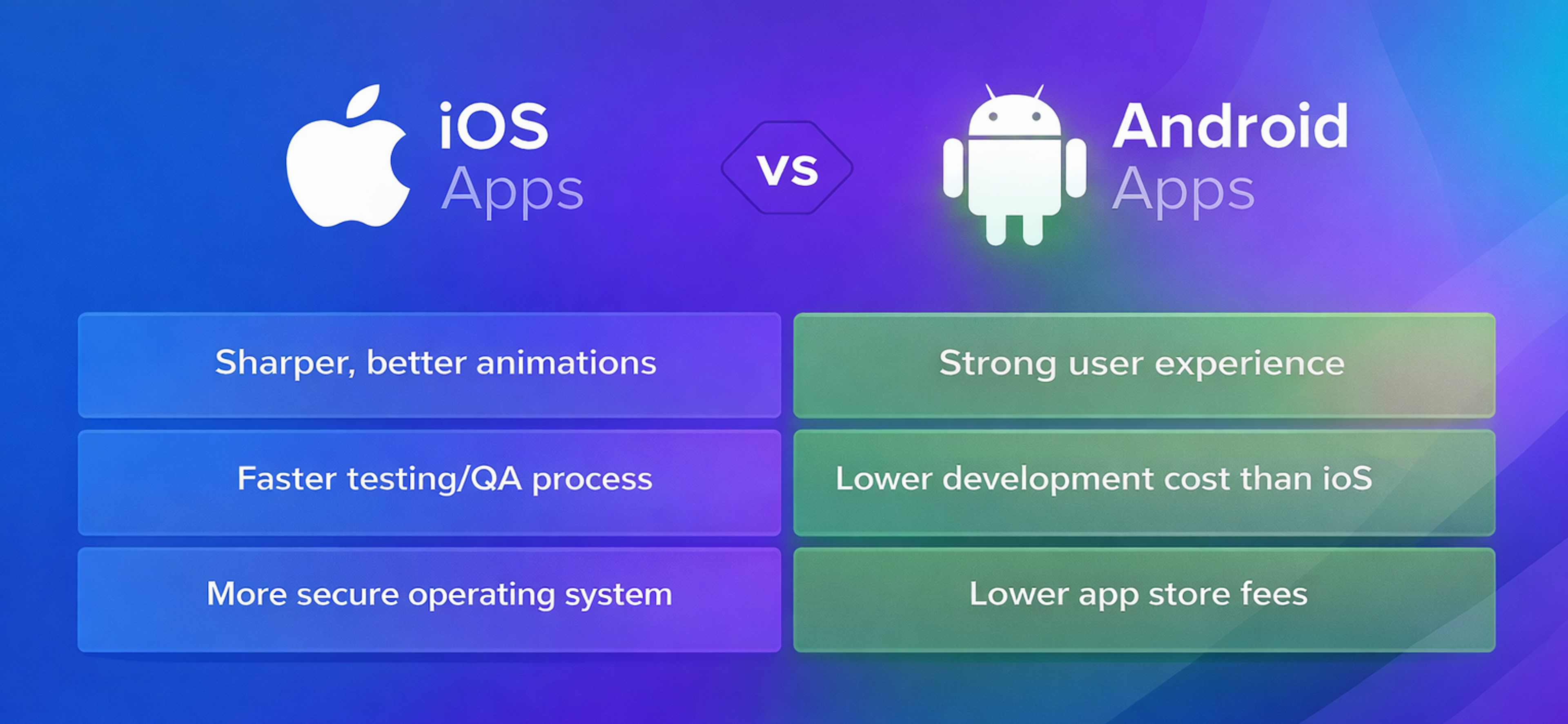
iOS App Development vs. Android App Development: What’s the Difference?
When building a mobile app, you can't skip deciding whether to use iOS or Android. Sure, both platforms look appealing, but every app maker needs to notice a few hidden differences.
iOS App Development vs. Android App Development
Development Environment
Making an iOS app means you'll mostly be inside Xcode, Apple's official tool. You'll program in Swift, or if you've been coding for a while, you might still use Objective-C. For Android, it's more straightforward.
You'll use Android Studio and Kotlin (the new favorite) or Java (the long-time standby). Each platform gives you its special toolbox. Knowing what's in that box will save you many headaches later.
Design Guidelines
Apple and Google have strict rules about how your apps look and feel. For iOS, it's more about strict control — elements like buttons and animations are predictable and clean. The design favors a few big, clear spaces instead of a flashy layout.
On Android, you get a bit more wiggle room, but you still follow Material Design rules, which means layering and directional cues are essential. If you don't pay attention to these guidelines, the apps will feel awkward on the platform.
But for Android, Material Design centers on the interface, where animated guides appear, gliding toward buttons, tabs, and menus to make touch targets light up and to make the animations ring louder in the user's mind.
Market and User Demographics
Also, the intended audience varies. iOS users in the U.S. and Western Europe are toward the upper-income marks, which opens doors for app makers to charge for features and content.
Android's user data, in contrast, shows a deeper global reach, especially in Asia, Africa, and Latin America, meaning app content, tools, and pricing must flex to match vastly differing user needs and spending habits.
App Store Policies and Monetization
Apple's App Store and Google Play set the ground rules for how apps are cleared and how developers can make money. Apple's approval process is tight; it guides developers step by step, which takes longer but can prevent scandals. Google Play is more liberal.
Developers send in their apps, often get a rapid look, and can press "publish" sooner. The trade-off may be that violations creep in on Google Play, while Apple carefully polishes what shows up in its storefront.
Excellent Examples of App Design
Flower Kiss Mobile App Design
This flower app shines with flat design, showing how a clean, minimal look can speed up load times and make online flower shopping a breeze. Colors, shapes, and crisp type draw quick attention, giving a smooth, user-friendly experience.
The flat style has made a comeback in recent years, and this app is proof of its power. This project is a clever reference if you're designing a marketplace or want a no-frills shopping journey.
Flower Delivery Mobile App Design

Done! Goals App
Done! Goals is a light, tidy app that helps users grow healthier habits by tracking personal targets without fuss. The flat design and bright cards let users focus on progress instead of distractions.
You can set daily or weekly builds, count streaks, and see charts and lines that add color to any achievement. Custom reminders let you make goals for fitness, habits, projects, or any area you want to improve. Overall, Done! Feels smooth and welcoming, encouraging users to keep moving toward daily wins.
Done App

Alto’s Odyssey
Alto's Odyssey is a gorgeous endless runner that invites you to glide across sweeping dunes while sandboarding. You'll travel through dreamy deserts, hidden temples, and colorful canyons, beautifully rendered in simple, elegant graphics. The game is alive with moving clouds, shifting sunlight, and gentle storms, making every moment feel fresh.
An easy one-finger tap keeps you moving, and a tranquil music score keeps things mellow, letting you lose yourself in the flow. Whether you're playing for a quick bike to the store or a long outdoor break, it strikes the perfect balance between chill and challenge.
Alto's Odyssey
FAQ
Should I Build For iOS Or Android First?
Build first for the platform where your highest-value users are. Consider your target region, revenue model, and audience preferences. Expand to the other platform once product-market fit is proven.
How Long Does App Development Take?
App development timelines depend on features, polish, and team capacity. Simple apps may take a few months, while complex builds can run a year or more. Cross-platform frameworks and progressive web apps often reduce time-to-market.
What’s The Difference Between Cross-Platform And Native?
Native development builds apps specifically for one OS, offering the best performance and access to device features. Cross-platform development reuses most code across iOS and Android, speeding delivery but with some trade-offs in flexibility or optimization.
How Do I Improve Approval Odds In App Stores?
To increase approval odds, follow app store guidelines, ensure stability, and be transparent with data use. Test on real devices, avoid misleading claims, respect intellectual property, and make sure privacy prompts and metadata match the app’s behavior.
Read more:
Conclusion
A successful mobile app isn’t built by stacking features. It’s built by making a few smart decisions early, designing for real-world usage (states, touch, performance), shipping with a feedback loop, and improving continuously after launch.
If you want a practical next step: decide your build path, define the job-to-be-done, outline an MVP with one clear value moment, and design the critical flows plus their states. That combination gets you to a confident launch and to a product that can grow.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more