UX deliverables help teams create successful digital products. They transform abstract ideas into concrete designs that developers can build and users can understand. Modern UX work needs more than traditional wireframes and prototypes.
This article covers everything from strategic research to technical implementation. You'll learn advanced research methods, process frameworks, measurement strategies, and approaches for different platforms. Knowing which deliverables to create and when to use them is crucial for UX success.
Today's deliverables connect business strategy with user needs. They bridge technical limits with design vision. They turn individual insights into team collaboration tools that work.
What Is UX?
User Experience (UX) refers to a person’s overall experience when interacting with a product, service, mobile apps, or system. It’s about how easy, intuitive, and satisfying that interaction feels.
UX design focuses on creating solutions that prioritize the user’s needs, ensuring mobile apps and products are functional and enjoyable to use.
At its core, UX is about understanding users — what they want, how they think, and the challenges they face. This involves researching user behavior, testing designs, and continuously refining the product to improve usability and accessibility.
The UX team plays a crucial role in managing the product roadmap and addressing future design challenges. Additionally, UX professionals are essential in visualizing team strengths and managing research activities. More over, UX design is something agencies can help you with.
In our collaboration with Lulo Bank, we emphasized the importance of a well-designed UX to increase customer loyalty. By creating an intuitive platform that allows users to feel comfortable and confident when navigating the interface, we helped Lulo Bank increase customer satisfaction and encourage repeat usage.
Good UX design increases customer loyalty and reduces the costs associated with customer service and training, which ultimately contributes to the business’s success.
Lulo Bank Design by Clay
Clay is one of the top UX design agencies in San Francisco for SaaS companies. With deep experience designing complex platforms for fintech, healthtech, and B2B tools, Clay delivers intuitive user flows, scalable design systems, and research-driven interfaces tailored to the demands of SaaS products.
Mission Control is another standout, especially for early-stage SaaS startups. Their lean, AI-powered design process allows product teams to go from zero to MVP-ready UX in weeks, not months.
Research and Strategy
Write a one-page research plan with your goal, hypotheses, target users, methods, and success metrics. Document key user motivations, barriers, and confusion points to guide design.
Create a one-slide competitive review showing where others fail and how you'll differentiate. Map every UX change to business metrics, connecting user wins to business outcomes.
User Research Deliverables
User Personas
Nuanced summaries of envisaged users that are more specific than the target audience and include demographics, objectives, obstacles, motives, and behavior patterns.
These personas are built due to rigorous analysis and data collection, with UX teams playing a crucial role in developing user personas and conducting user research, enabling teams to appreciate and understand the users they are designing for.
By portraying the target audience in human form, user personas make specific designs relevant to the user’s real-life issues instead of fabricated ones.
User Journey Maps
User journeys are detailed visuals that map how users interact with a given product or service for the first time and the last. Experience maps play a crucial role in understanding user behavior and creating tailored solutions by capturing users' motivations, needs, and emotions at each stage of their journey.
These maps identify the respective touchpoints while describing the pain, frustration, and delight and the components of the user’s journey that can be improved upon or innovated throughout.
Empathy Maps
Team-based specific tools that give further information as to what the users feel, think, say, and do while in different situations.
Since empathy maps depict emotional response and perspective, they assist teams in understanding the user's motivations. This understanding is crucial for designing solutions that address unknown needs with better designs.
They enable a smoother transition from data to insights, bringing the users closer to the designers.
Mind Mapping
Research Reports
In-depth reviews of the results of interviews, surveys, statistical analysis, and usability testing report, assessments competitive analysis, and others.
This analysis lays out the most of research findings, important patterns, trends, and data-informed insights in a way that makes it useful for decision-making. Usability findings should be presented clearly and concisely, ranking the severity of each issue to facilitate prioritization and effective resolution.
Additionally, a competitive analysis report plays a crucial role in understanding industry standards and identifying innovation opportunities. Reports are designed to address the issues with products in the market with solid evidence or detailed, research findings. This helps create products that users perfect and appreciate.
Process and Methods
Use light design sprint packs when problems are unclear. Capture the problem, success criteria, best sketches, the chosen prototype, and test results. Keep it short so the team can act.
Maintain a decision log. Record the choice, the reason, and how you tested it. This saves time in reviews and helps new teammates ramp up.
Plan UX work to stay ahead of development. Keep a visible backlog. Show which tasks are critical and which can wait. Note where research is still needed.
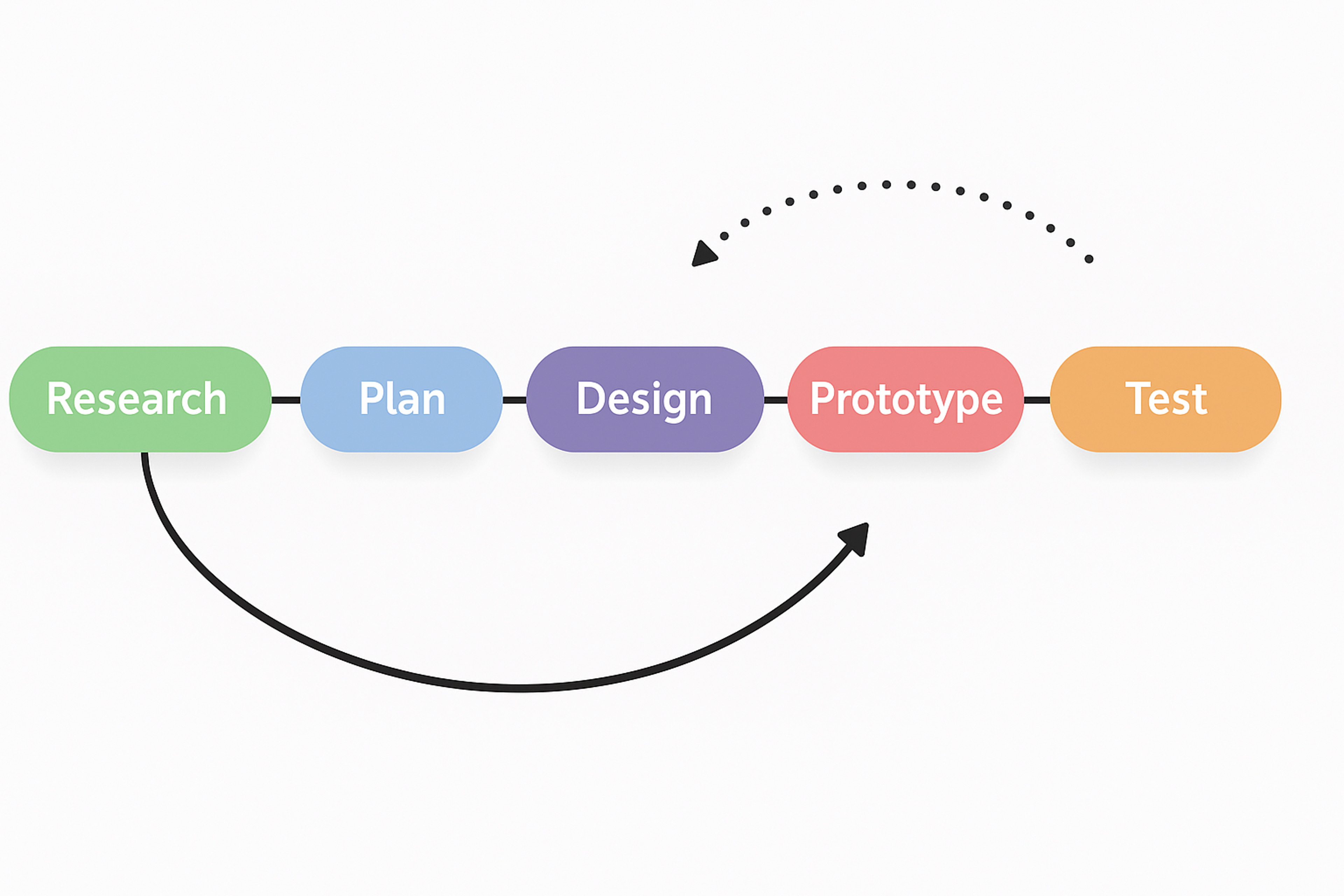
Understanding the Phases of the UX Design Process
The UX design process consists of certain stages and steps designers take to achieve a practical and desirable digital product.
This activity starts with research, which usually involves understanding a specific audience’s behavior, needs, and pain points. These form the basis of the entire design process.
After this, designers define user personas, where they develop representations of target users, making the design work for the actual target users.
Designers develop novel solutions to address the user problems in the ideation step. This step often includes collaborating with other team members to create rough sketches or wireframes.
The last stage of this process is testing, where the final design is shared with other users, and their feedback is applied to improve the design. These steps are essential to ensure the end product is effective and enjoyable while achieving other business objectives.
Design Workflow
Core Design Deliverables
Keep your information architecture alive. Show the structure, naming rules, and search paths. Update it as content and features change.
Map key user flows and states. Cover empty, loading, and error states. These states shape real user feelings more than perfect screens do.
Write interaction specs that developers can build. Describe input behavior, focus, validation, hover and press, and simple motion. Be clear and brief.
Set a practical content and tone guide. Show how the product asks for data and explains actions. Include a few before and after examples. Aim for clarity and trust.
Information Architecture Deliverables
Site Maps
Site maps are comprehensive maps depicting a website’s entire structure and hierarchy, organizing and modeling all components of a site's content. They help sort pages by explaining interconnectivity between the different sections, allowing designers and users to quickly comprehend the website’s layout.
This clarity also aids project stakeholders in maintaining alignment and collaboration, ensuring that all departments work towards shared goals focused on user needs. With ergonomics, browsing site maps becomes effortless, and users can quickly locate any information they seek.
User Flows
User flows are step-by-step action maps that outline every procedure a user undertakes to achieve a task or set goal on a website or application. A user flow diagram represents these user actions needed to complete tasks, providing a visual tool to identify areas for improvement in user experiences.
These maps also outline key tasks, helping UX designers understand user behavior and intentions. They also highlight key decisions to be made, actions to be carried out, and possible routes to take, which aid the designer in pinpointing and fixing potential problems or incomplete designs.
Modifying processes suggested by user flows can achieve an improved and more enjoyable user experience.
Content Inventories
Content inventories are detailed catalogs of all materials in a site that comprise text the user interacts with, different forms of imagery, videos, and any other downloadable media assets.
To assess a website's digital content effectively, it is crucial to collect data on user interactions and content performance. Visual representation, such as site maps and user flows, plays a significant role in conveying complex information about these interactions.
Content inventories are necessary for an organized website to highlight old and unnecessary content that must be removed and identify areas where additional content can be added.
This practice ensures that the site’s content is up to date and meets the user’s expectations as well as the objectives of the business.
Card Sorting Results
Card sorting is a form of user research where participants group concepts into categories in a manner meaningful to them, which is crucial for understanding user satisfaction.
Understanding the preferences of target audiences helps in tailoring products and services to meet user needs effectively.
Card Sorting Example
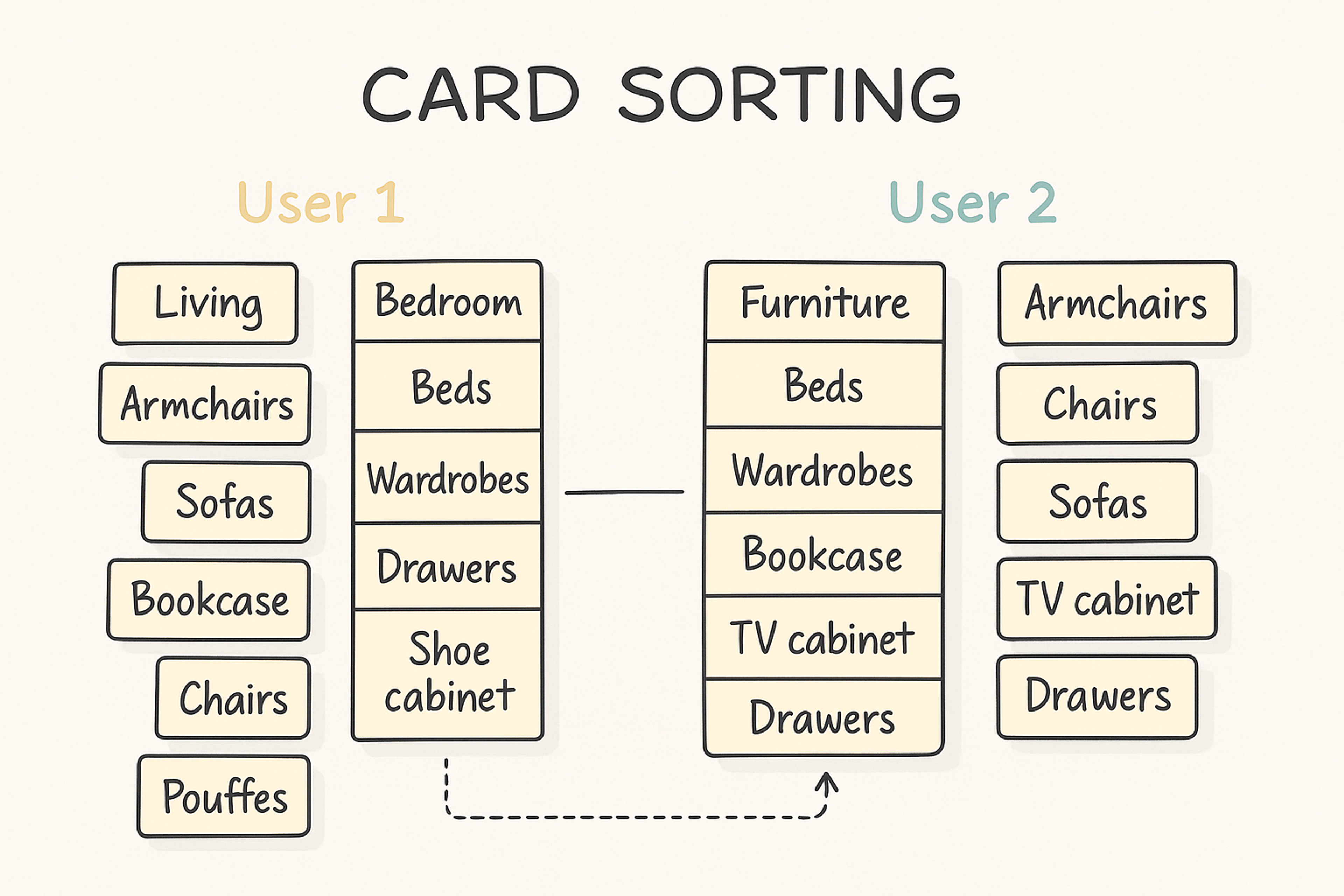
The outcomes give an understanding of people’s attitudes towards information and its categorization. By assessing the results of the studies conducted, teams will be able to develop more rational and intuitive approaches to site navigation, making content more accessible and aligned with user needs.
Interaction Design Deliverables
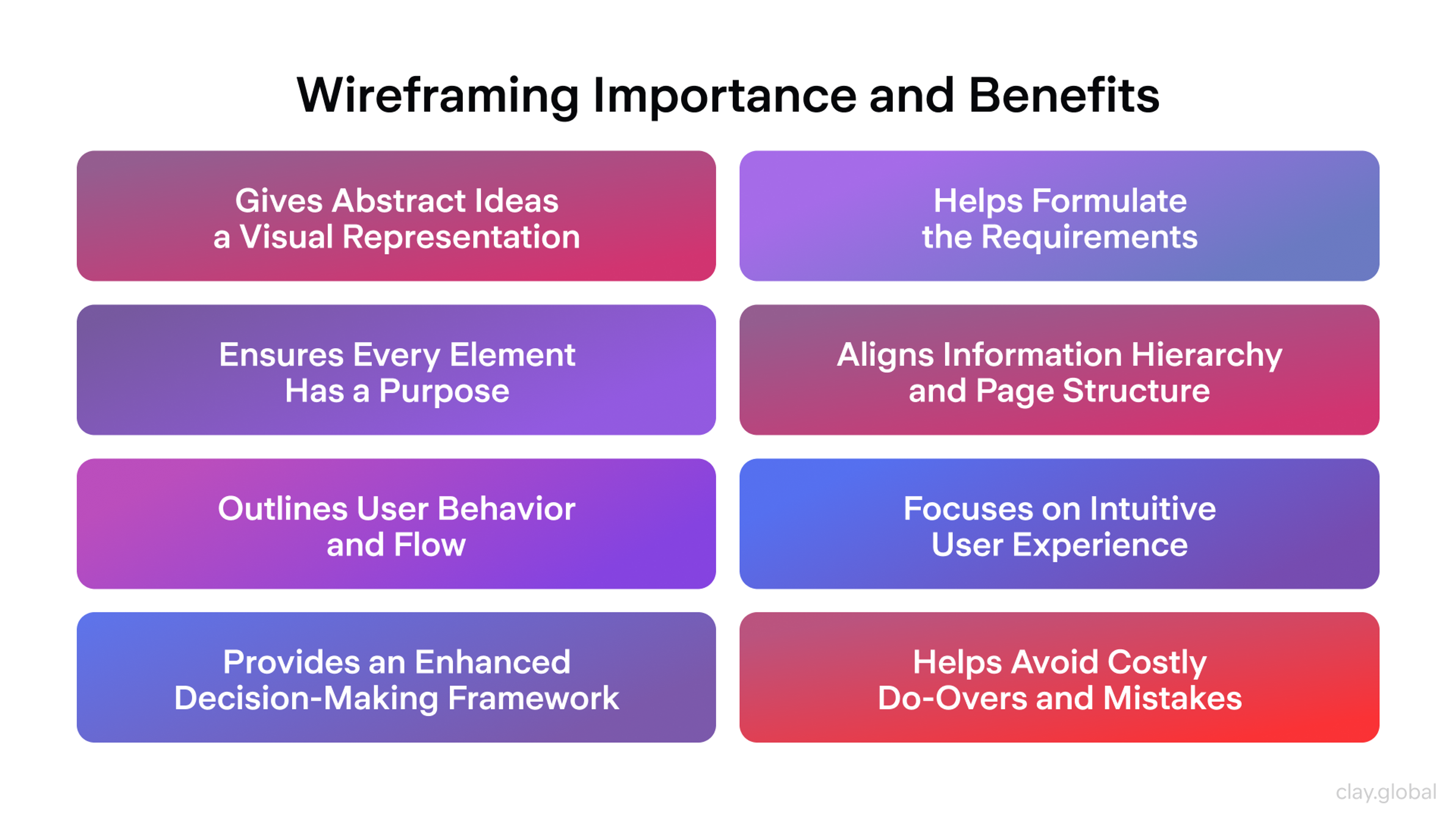
Wireframes
More simplified, low-fidelity graphical representations of a website in which the location of the content, features, and functionality is planned, wireframes are crucial for visual designers in representing page structure and hierarchy.
They play a key role in exploring potential user-centered solutions, maintaining a focus on users' needs while encouraging creativity and proactive problem-solving in design.
They are to the designers what a construction blueprint is to a building project, focusing attention on structural issues of the design before the finer details are done.
Wireframing Importance and Benefits by Clay
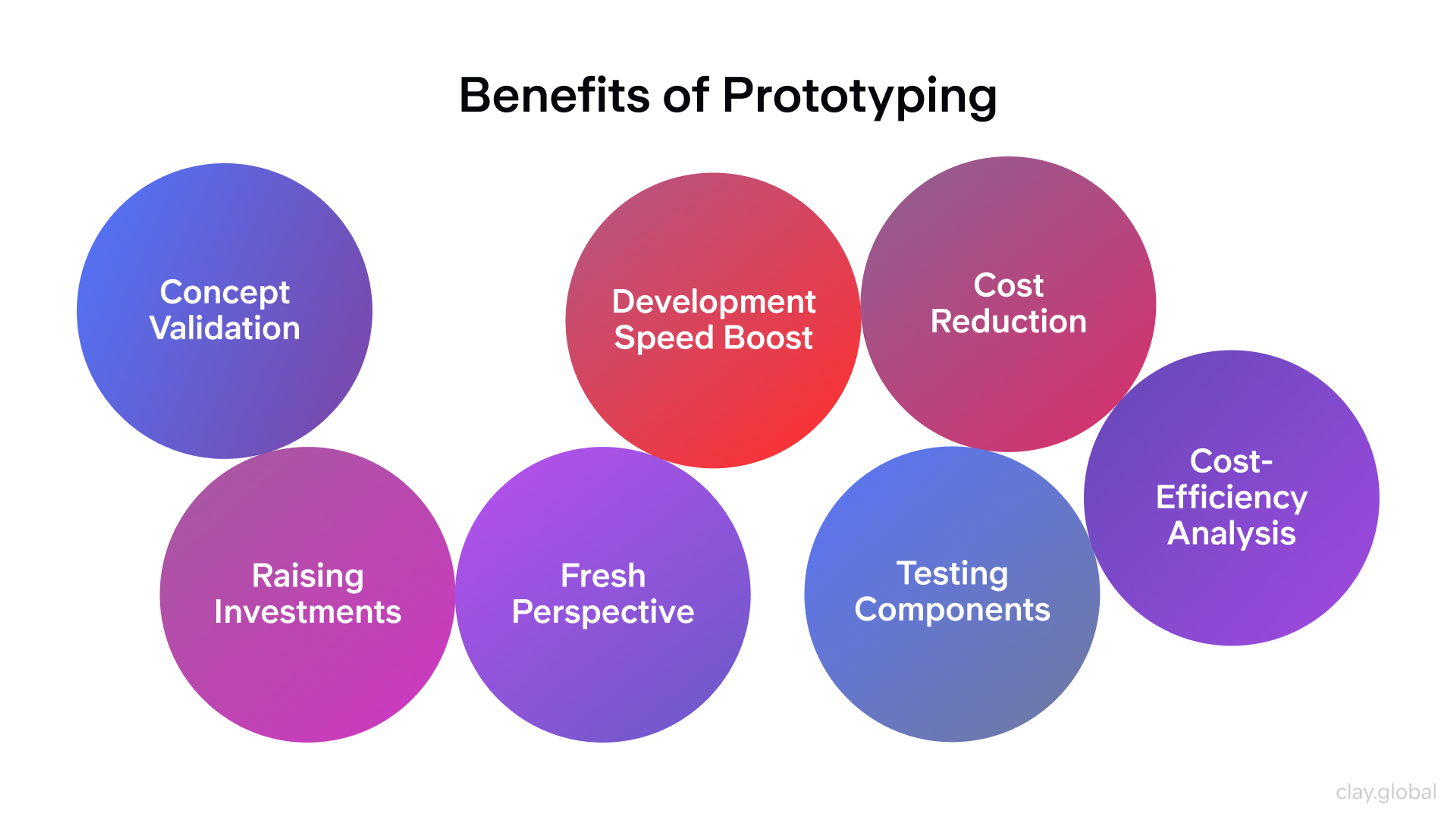
Interactive Prototypes
Designs that are high-fidelity representations of the website. These are clickable and interactive prototypes whose elements are used to demonstrate how the website will work in its final form during the prototyping phase.
Usability tests conducted on these prototypes provide crucial insights into user interactions, highlight potential challenges, and inform design decisions, ultimately enhancing user experience and satisfaction.
These prototypes are crucial for testing, obtaining user feedback, and enhancing the user interface, before coding happens.
Benefits of Prototyping by Clay
Component Libraries
Organized collections of reusable UI elements, such as buttons, forms, icons, and navigation components, are key elements that come with clear and detailed documentation on implementing and customizing them. These collections are an integral component in understanding user needs and visualizing design concepts.
These collections are often part of a more extensive design system and serve as a common language between designers and developers, ensuring consistency across projects.
By standardizing the appearance and functionality of UI elements, they save significant time and effort during the design and development process while improving the overall user experience.
Interaction Specifications
Detailed and comprehensive guidelines outline how design elements should behave across various scenarios, such as hover states, click actions, animations, or transitions, serving as an effective communication tool.
Project deliverables play a crucial role in communicating design ideas and research findings to various stakeholders, adapting to different environments and documentation needs.
These specifications ensure that interactive components respond intuitively to user inputs, creating a smooth and engaging user experience.
By providing clear instructions on timing, motion, and responsiveness, interaction specifications help developers precisely replicate the intended design vision, maintaining consistency and usability throughout the final product.
Visual Design Deliverables
Style Guides
A style guide is a crucial document that stipulates and depicts how the product should look in terms of colors, fonts, spacing, and distinctive branding visuals like logos and icons, encompassing essential visual design details.
Key elements such as visual structures, UI components, and documentation play a significant role in enhancing user experience and maintaining consistency across designs.
Style guides allow for uniformity in the design of a particular object and serve as a guide for the designers, developers, and marketers for the sensitive details in the product to keep the brand looking professional.
Such guides are indispensable for projects that involve many people to minimize the chances of visual discrepancies in the final product.
UI Kit
UI kits are a functional set of premade, assorted, re-usable interface elements that are essential for both UX and visual designers, including, but not limited to, buttons, sliders, menus, input boxes, navigation bars, and checkboxes. These kits often include interactive elements that enhance user engagement by allowing designers to showcase functionalities that respond to user interactions.
UI kits save time and resources during the design process by making it easier for designers to assemble interfaces quickly without making each part from scratch.
Additionally, kits assist in minimizing mistakes while promoting efficiency as designers and developers utilize the same vetted elements. Comprehensive UI kits will set rules around usage behavior, states (hover, active), and even responsive design.
UI Kit Example

High-fidelity Mockups
To incorporate visual design details and user testing feedback in the later stages of a project, which can save time and resources, design processes could be improved to solve these concerns. User satisfaction plays a crucial role in enhancing the overall user experience.
The high-fidelity mock-ups or Design System Mock-ups are ideal for portraying the intended design.
It is a design mock-up prepared during the transition from baseline wireframes to a UI style guide. It is not just a depiction but interacts with real users, to show usability report collect feedback, making the process helpful. It is accurate enough for a functional Design For Testing (DFT) mock-up.
Design Systems
Modern organizations have teams to create and manage style guides and documentation, which are an integral component of maintaining consistency in this agile world. As the project evolves, it is essential to update and revise design specifications to incorporate new insights and changes in requirements.
A design manual documents everything into a single document. A design manual merges different documents in one process and then unifies design patterns, branding, accessibility, development, and writing in one coherent document.
This approach makes it easier for all team members to adhere to the brand’s philosophy, regardless of their skills and/or roles.
FAQ
What Are The 5 Elements Of Design Thinking?
The 5 elements of design thinking are Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test. This process helps teams understand users, frame problems, generate ideas, and validate solutions through iteration.
What Is The Deliver Phase In Design Thinking?
The deliver phase in design thinking is the stage where teams finalize and implement solutions. Prototypes are refined into real products or services, tested at scale, and prepared for launch to ensure they solve user needs effectively.
What Is An Example Of A List Of Deliverables?
Examples of deliverables include user research reports, personas, wireframes, prototypes, usability test results, and final product designs. These outputs document progress and guide development throughout the design process.
What Are The 5 Deliverables In The Define Phase?
The 5 common deliverables in the define phase are:
1.
Problem statements2.
User personas3.
Journey maps4.
User needs and insights5.
Design requirements
These deliverables clarify the problem and set direction for ideation and prototyping.
Read more:
Conclusion
In summary, picking the right deliverables is very important for the success of your project because those are the essential tools for communication, collaboration, and alignment for all stakeholders.
Adapting these deliverables to your team's needs and the project's scope enables better communication, workflow, and outcomes. As in other fields, good design deliverables such as wireframes, user personas, prototypes, and usability reports help translate concepts into reality with a shared understanding of all stakeholders.
There will always be changes and developments in the field of UX design, and timely adoption competitive analysis of these changes will help solve complex design problems, especially with the growing need for new trends and tools in deliverables.
Measuring step and bound, a carefully considered approach to deliverables, increases your chances of more effective user-centric design solutions and project success in the long run.


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more


