Wireframes and prototypes are essential in the design phase because they help accelerate the product development process, thereby saving time and money. They help visualize designs, assess their functionality, and smoothen the process from ideation to execution. This stage supports interface prototyping by translating ideas into testable layouts early in the process.
What Are Wireframes?
A wireframe is an essential visual representation of a digital product like a website or an app. To create wireframes, designers use various methods and tools to outline the basic structure and navigation of the product. It serves as the basic structure of the product, emphasizing how a user will navigate through the product and its available features instead of focusing on finer details such as typography or color schemes.
Wireframes are often done at the beginning of the design process to aid designers, developers, and other stakeholders in visualizing the architecture of a project and ensure that everyone is on the same page about the user experience. This process forms the foundation of interface prototyping methodology, where structure and interaction are tested before investing in full visuals or development.
Wireframe for UX Projects by Clay
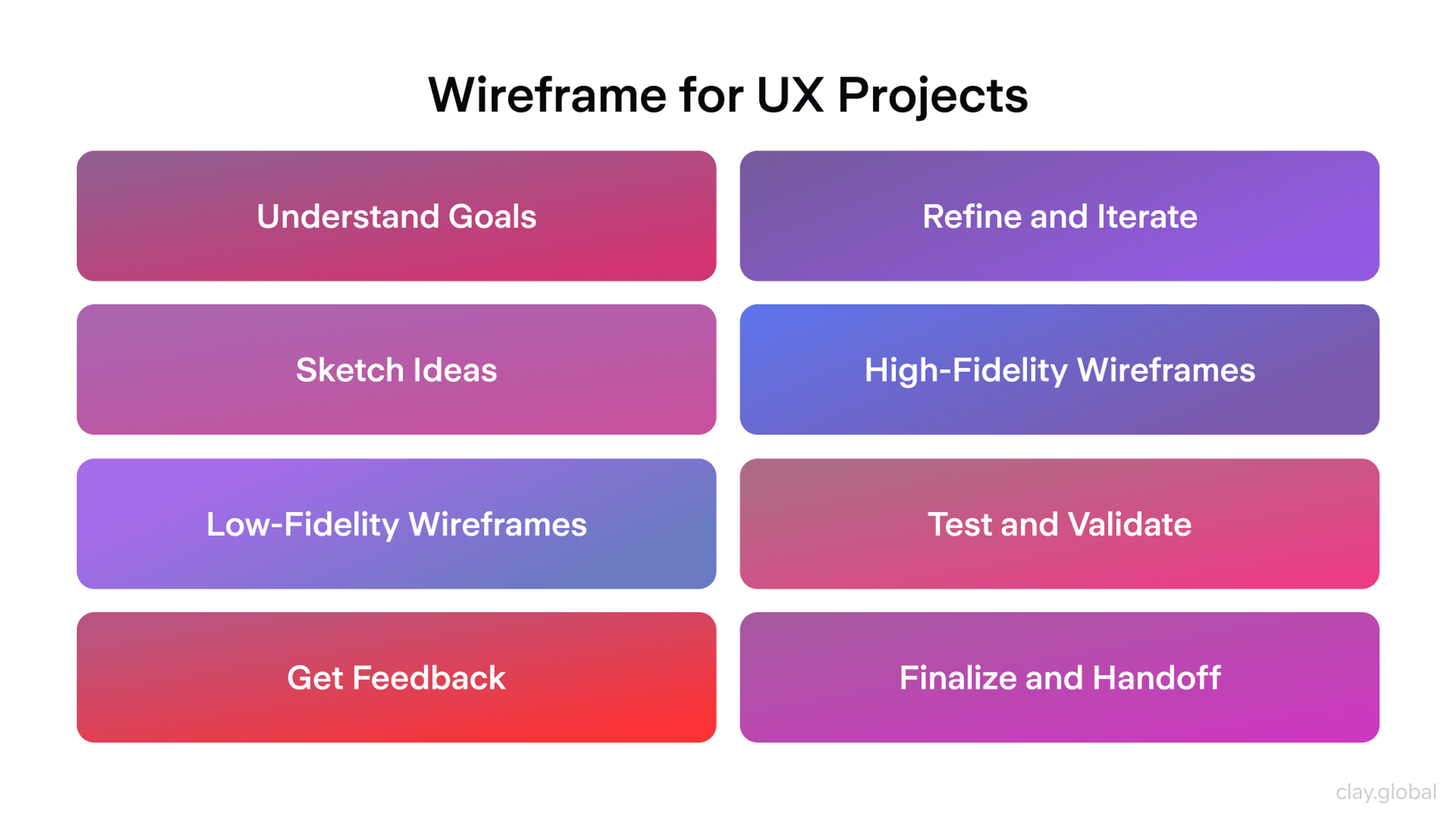
Clearly defined wireframes allow potential problems and obstacles to be recognized early, thereby helping save time and money. They also ensure that the designs created are practical and easy to use.
Different Types of Wireframes
Each wireframe has its own purpose in a project's design. Low-fidelity wireframes offer basic outlines of a product's layout without exhibiting complete functions. These sketches form a vital part of interface prototyping, allowing teams to iterate and polish the UX without diving into complex high-fidelity designs.
Difference Between Low, Mid, and High-Fidelity Wireframes by Clay
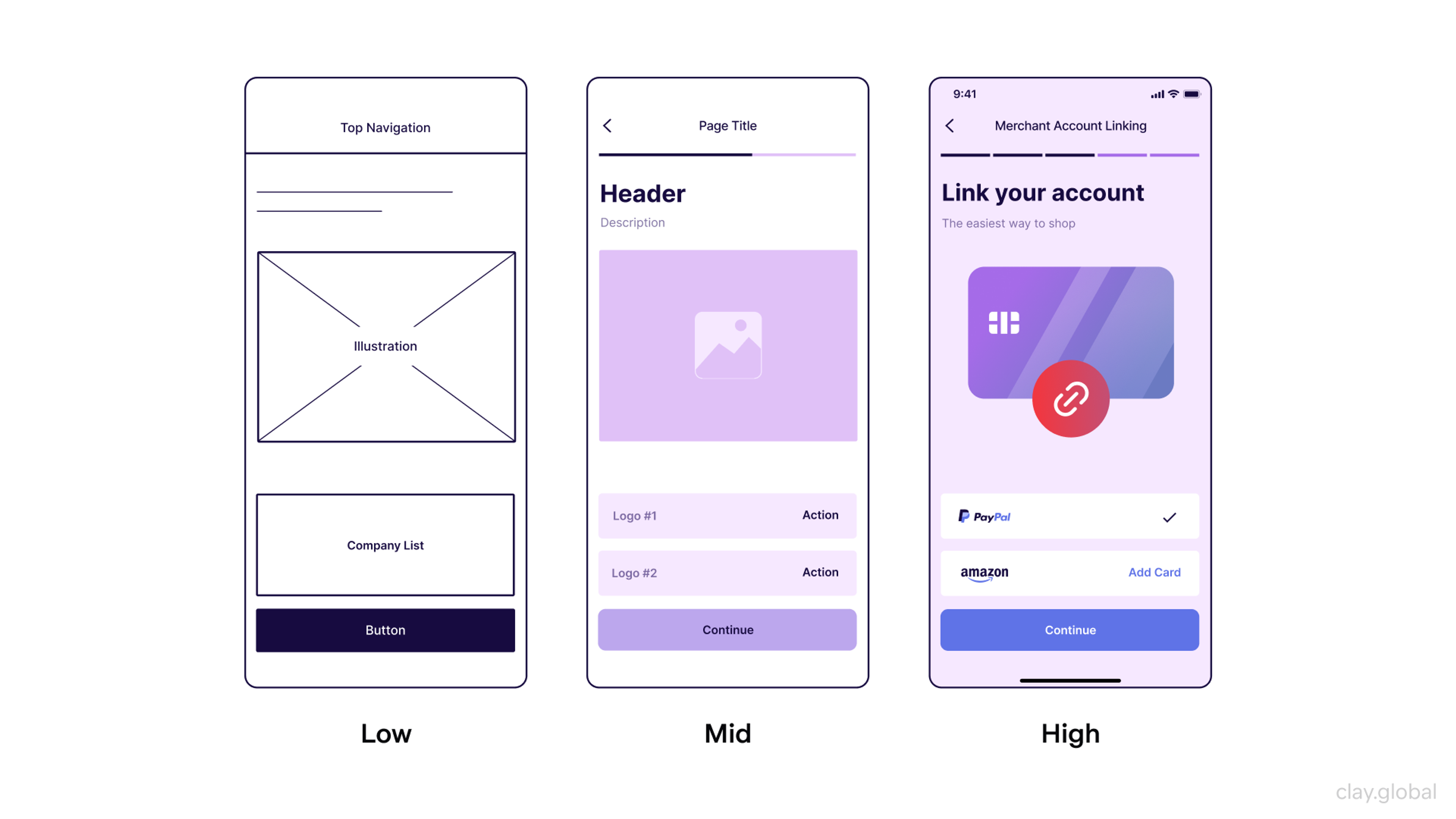
In terms of a project's workflow and structure, these wireframes act as a guide or frame of reference in the beginning, by defining the style and order of the content and the interactions a user can take in a digital product.
Low-fidelity Wireframes
Unlike high-level portrayals of your design, low-fidelity wireframes showcase the structure and arrangement of the design. These wireframes are cost-effective in identifying usability issues and are faster to iterate. Due to their simple format, they are also a powerful marketing tool for receiving customer feedback.
Low-Fidelity Wireframe by Clay
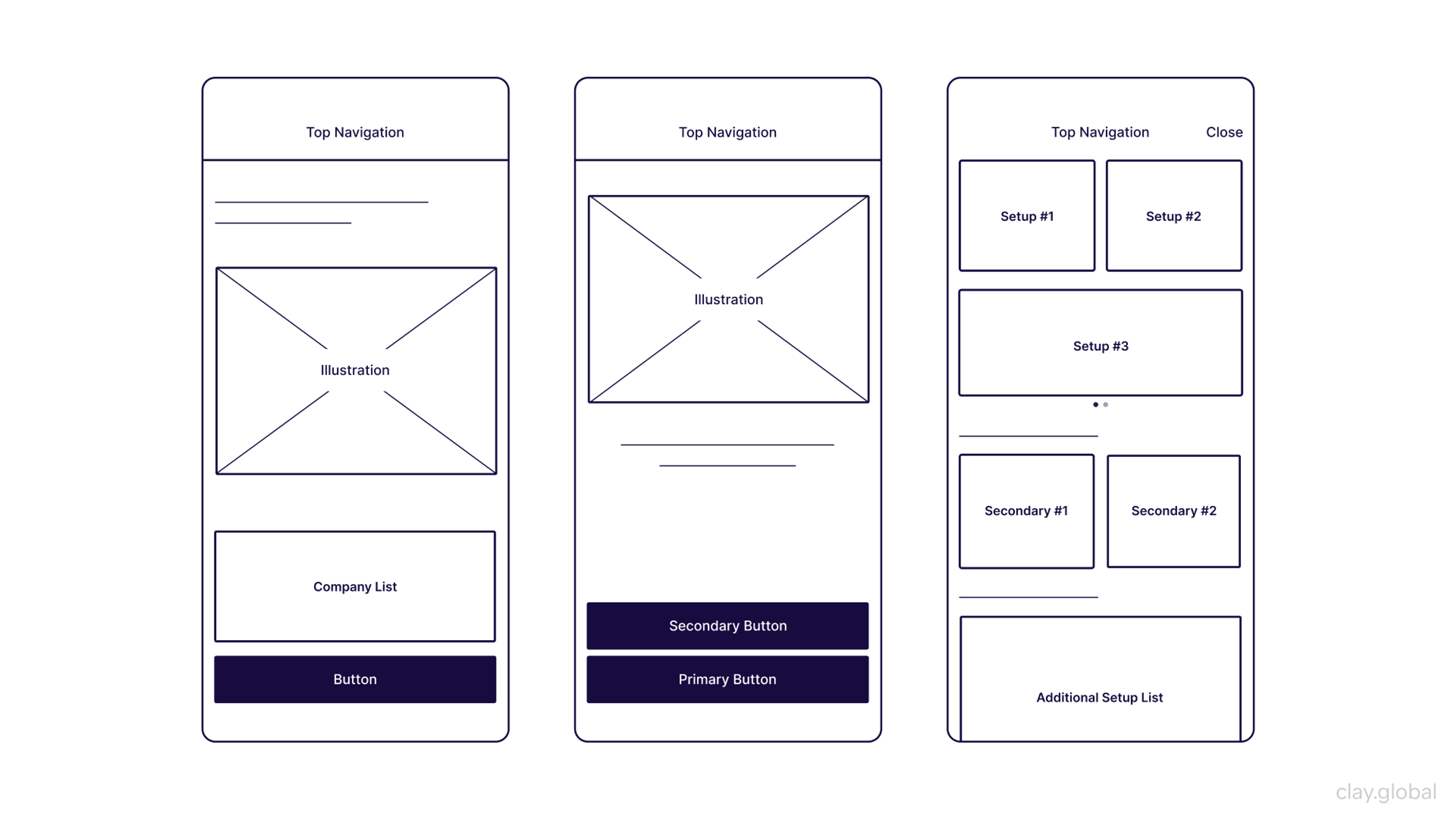
Low-fidelity wireframes make cooperating significantly more straightforward as they focus on placing big-picture concepts above design, allowing organizations to realize their vision. Rough sketches and placeholders can modify the conveyed messages without detracting from the project goals.
Low-level wireframes emphasize the user, which makes them a significant element in the design process because they allow teams to tackle issues users face without the distraction of detailed designs.
Mid-fidelity Wireframes
Mid-fidelity wireframes balance low-fidelity sketches and high-fidelity prototypes. They strike an optimum balance between functionality and detail. They are crucial to the design process, providing stakeholders, developers, and designers with an accurate representation of product layouts that are more advanced than low-fidelity sketches but less detailed than high-fidelity prototypes.
Mid-Fidelity Wireframe by Clay
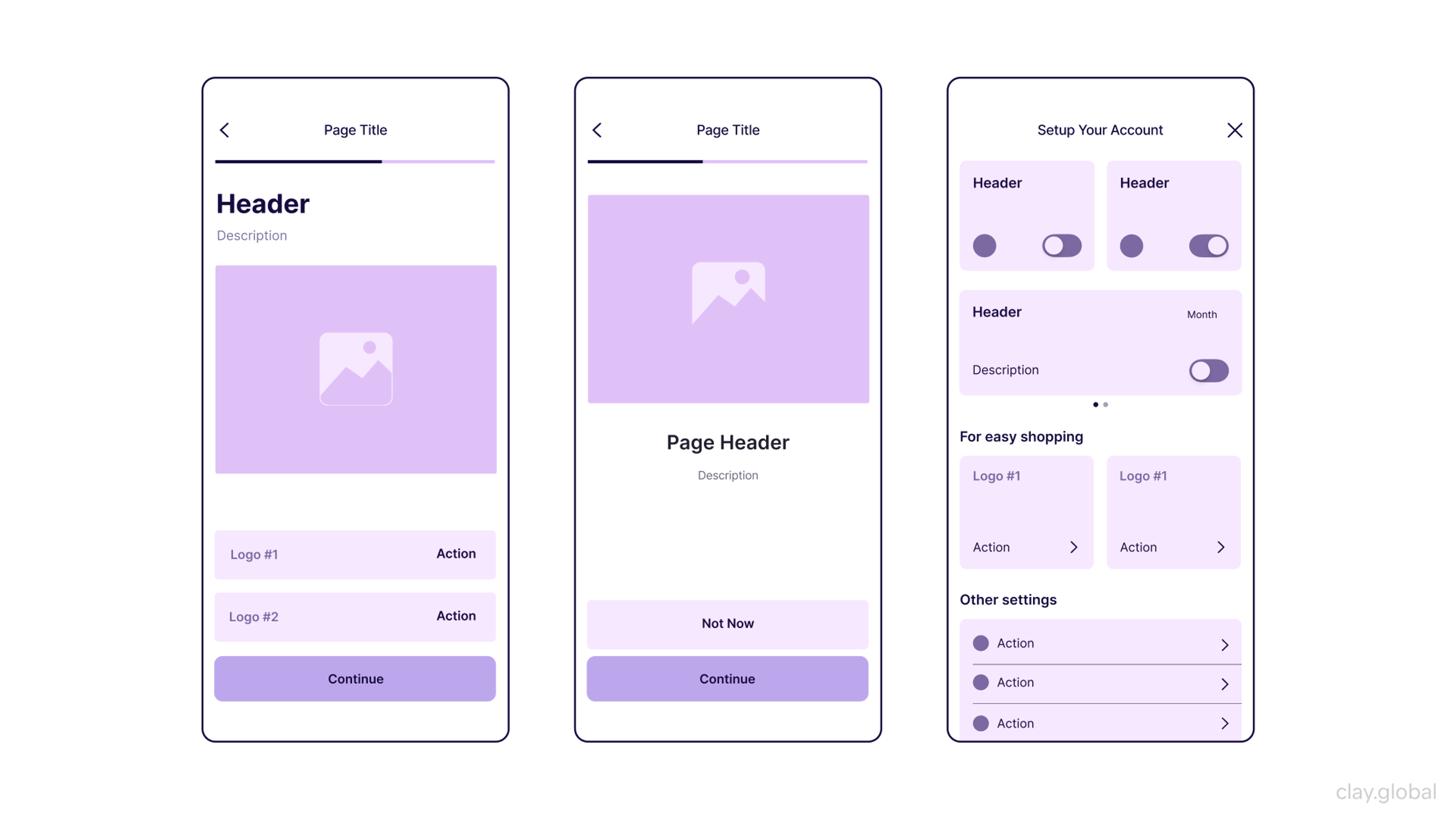
These wireframes primarily focus on the piece's spacing, structure, and overall hierarchy. There is no need to fuss over colors, typography, and complex details. They also allow for early usability testing and feedback gathering, which is received in the early stages of development to move to the more detailed phases.
These mid-fidelity wireframes are perfect for UI designers as they determine navigation, user flows, and interaction points. They allow for a user-centric design process and help ensure the final product keeps the user focused while maintaining a sturdy and functional base.
High-fidelity Wireframes
High-dreamy wireframes are the most intricate conceptions of a product. They represent everything between a sketch and a mobile application.
They are more refined than blueprints. They use actual typography, a suitable color palette, images in the correct context, and spacing. They present states of interaction, such as tap or hover. They mimic the real interface in aesthetics and usability.
Sending these wireframes for review clarifies the sight of the outcome. Developers, stakeholders, and project managers visualize the product that will be shipped. It speeds up the alignment of teams, enables the early detection of problems, and minimizes the time spent on confusion during coding.
Crafting these wireframes requires investment in the development of skills and time. The team tests flows, revising intricate particulars, filling in the gaps before handover, and touching everything. The moment everything comes together is when the team shifts its focus to development.
High-Fidelity Wireframes by Clay
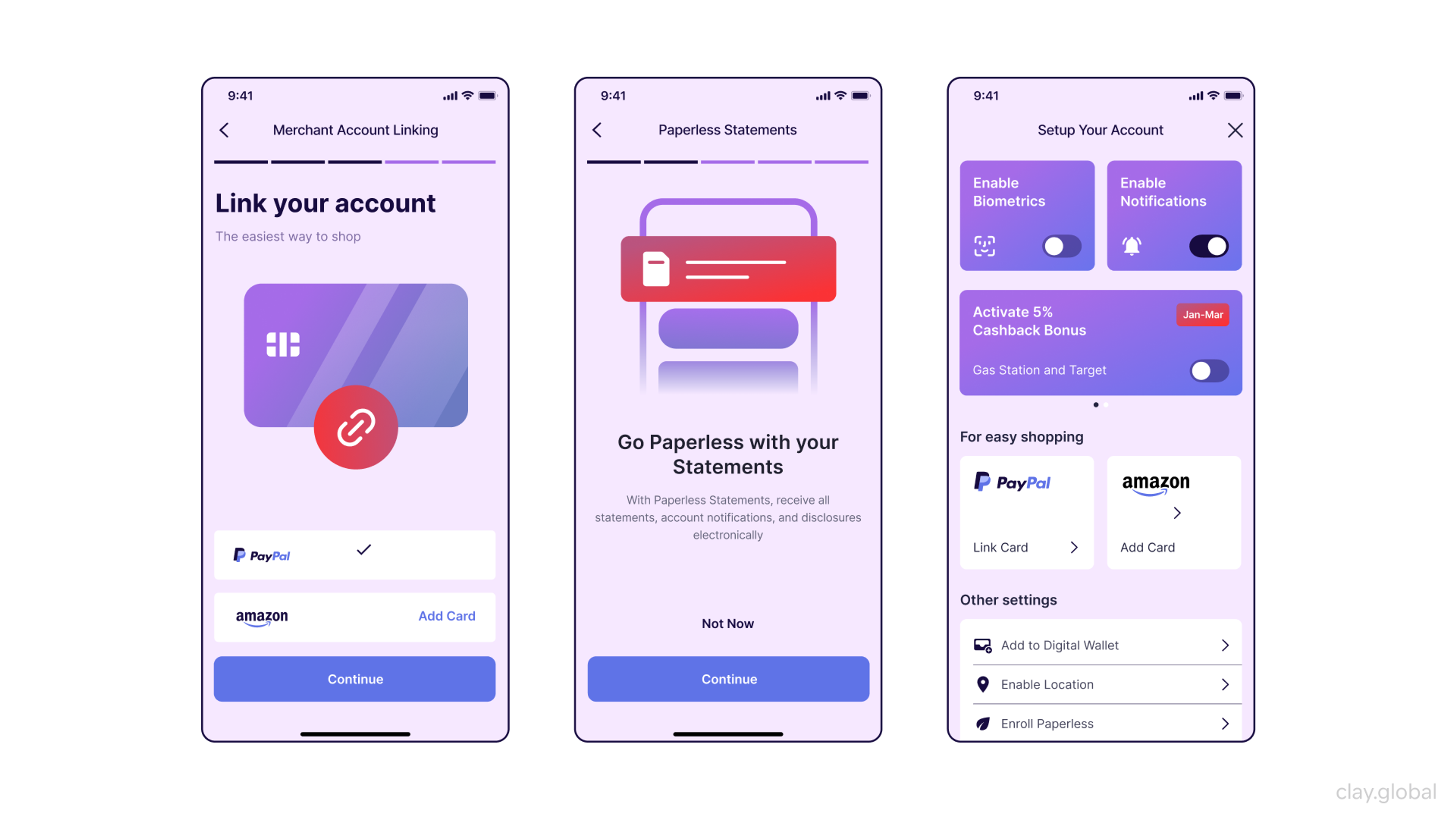
When to Use Wireframes?
Within the design process, wireframes are essential instruments. They provide a prime project sketch before in-depth visuals are used or development is done. But when, exactly, is the right time to use them?
- Along the Initial Steps of the Design Process: Wireframes are perfect for the first stage of the design process. They lay out the framework for a website, app, or product, focusing on the mechanics rather than the colors and distracting graphic elements.
- Defining User Flow: When sculpting a product, it's essential to consider users' experiences. Constructing a wireframe for a user flow helps outline the various processes, streamlining users' experiences. Good wireframes enhance refining moments in journeys by detailing interactions over numerous screens.
- Communicating Ideas: Achieving consensus before a project begins can be complicated. Wireframes allow you to seamlessly sell an idea to stakeholders, teams, or clients. Their effectiveness means that moving forward hinges on being in sync.
- Testing Concepts: Wireframes' preliminary stages allow them to be used for concept testing. Interactivity early on, before intricate blueprints are drafted, helps determine possible failures.
- Planning Development: The wireframe for your project will greatly help the developers. Built interactions, functions, and arrangements help fine-tune the wireframe, leading to a smoother build.
To help your ideas blossom, wireframes will help you frame your thoughts accordingly by ensuring that the basic principles of the component of the project in question are in depth. This prevents a hasty, incoherent advancement to the following stage of the project.
Wireframing Importance and Benefits by Clay
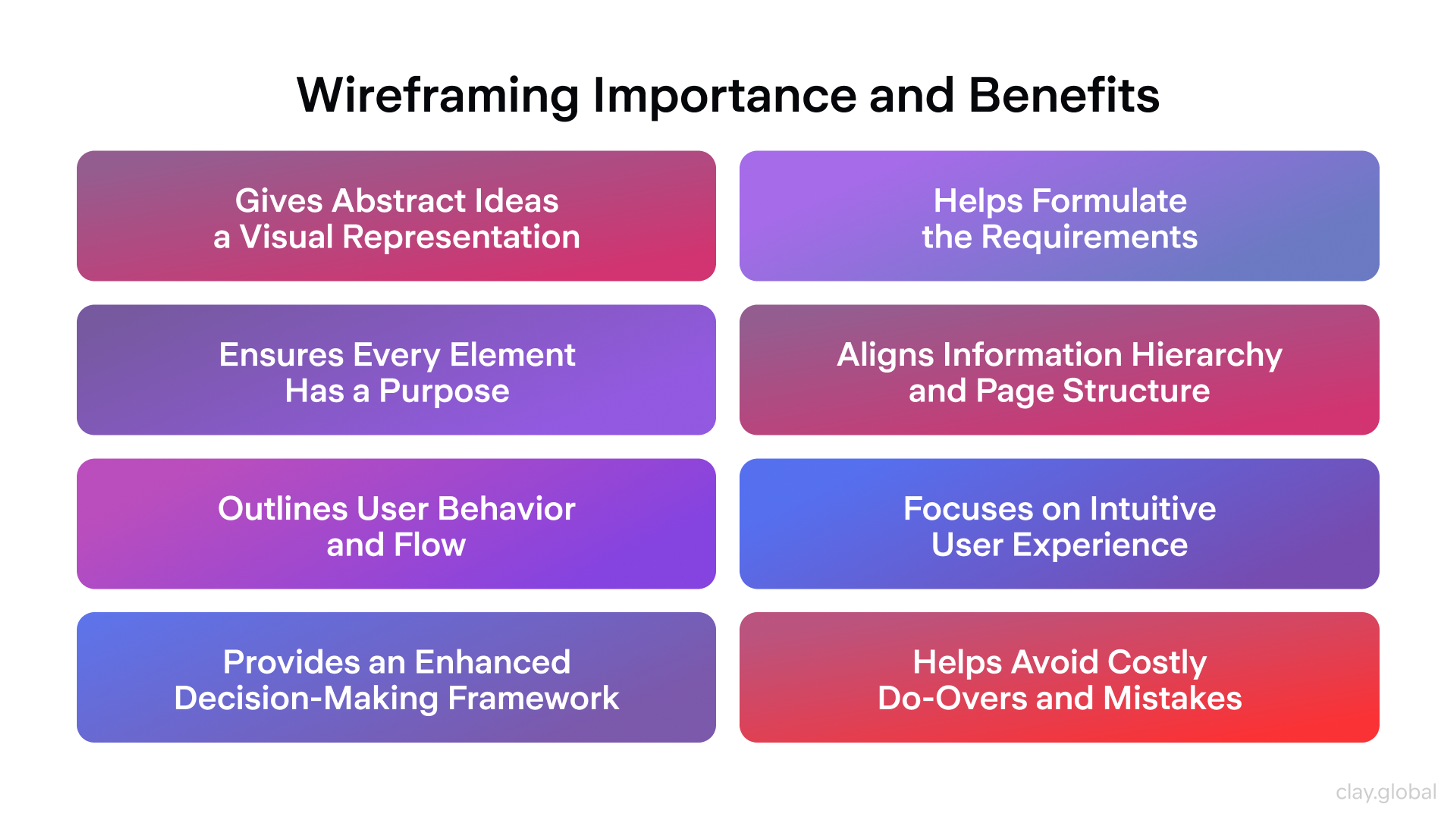
The Benefits of Wireframes
The wireframes serve as an outline for the application's skeletal outline, well-constructed and placed, before the centre stage of the project begins, where the application will be filled with comprehensive details, design, and construction.
Clarity in Structure: Preparing blueprints without layers of color or shadow helps arrange the spacing and elements. Structure and organization go hand in hand, and you can visually observe how screens interconnect. Neglecting this stage poses a risk of concealment and surprise later on.
Enhanced Communication: Wireframes establish a common language for stakeholders, designers, and developers. They illustrate user journeys and objectives. The team syncs early and accelerates.
Cost and Time Effectiveness: Wireframes identify risks and priorities early. We tackle the most critical elements first. This minimizes rework and costs.
Focus on Functionality: Interactive prototypes emphasize essential activities. Minor design adjustments can be postponed. The team aims for ease of use from the beginning. Wireframes eliminate distractions and put the user first. They accelerate design and development and position your product for future wins.
What Are Prototypes?
A prototype is an unfinished representative of a product or a model. These are built to evaluate an idea before it goes into large-scale production.
The most basic prototype is a low-fidelity wireframe. Its purpose is to outline a framework. It consists of simple boxes and words - no bright colors or intricate detail. It illustrates how data hierarchy works, the buttons' destinations, and the components' overall relationships.
Prototypes are a standard industry practice. Designers, engineers, and software developers use this approach. Some prototypes are simple drawings, while others are interactive mockups with clickable and scrollable features.
Prototypes Flow by Clay
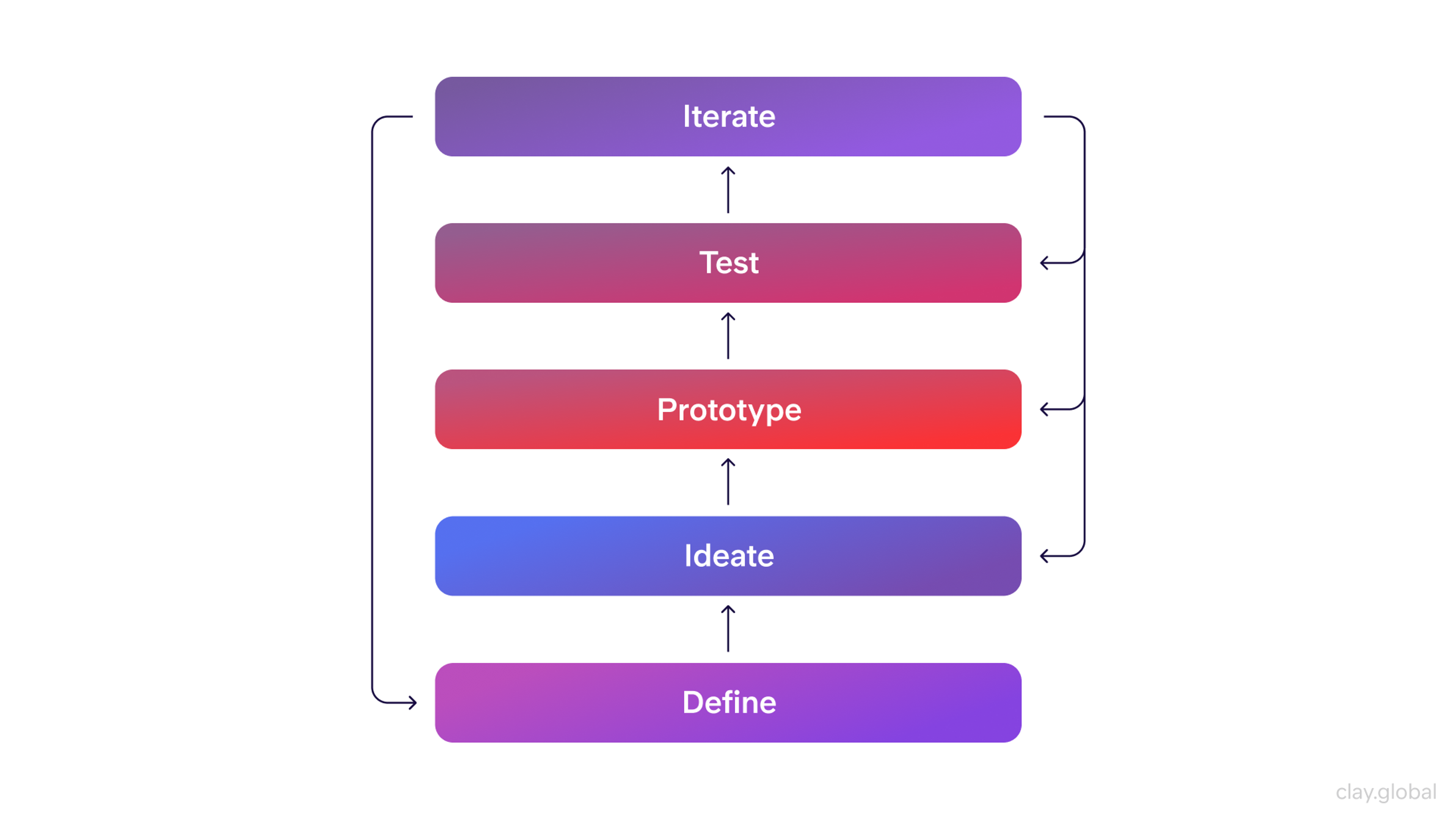
The primary objective is to ascertain if the idea works. Prototypes provide the data needed to enhance the product. Ideas are executed, knowledge is gained, and mini increments are produced. This focus and user-centric approach ensure that the objectives are accomplished.
The Different Types of Prototypes
Prototypes turn rough ideas into working plans. Each type helps differently. Some test a basic concept, and others refine the user experience.
Horizontal Prototypes
A horizontal prototype is wide but shallow. It shows the flow across an app or site. Features are not built in full detail. You can see how users move between key screens. This makes it easy to test big ideas and check if the layout guides the eye.
Horizontal Prototype by Clay
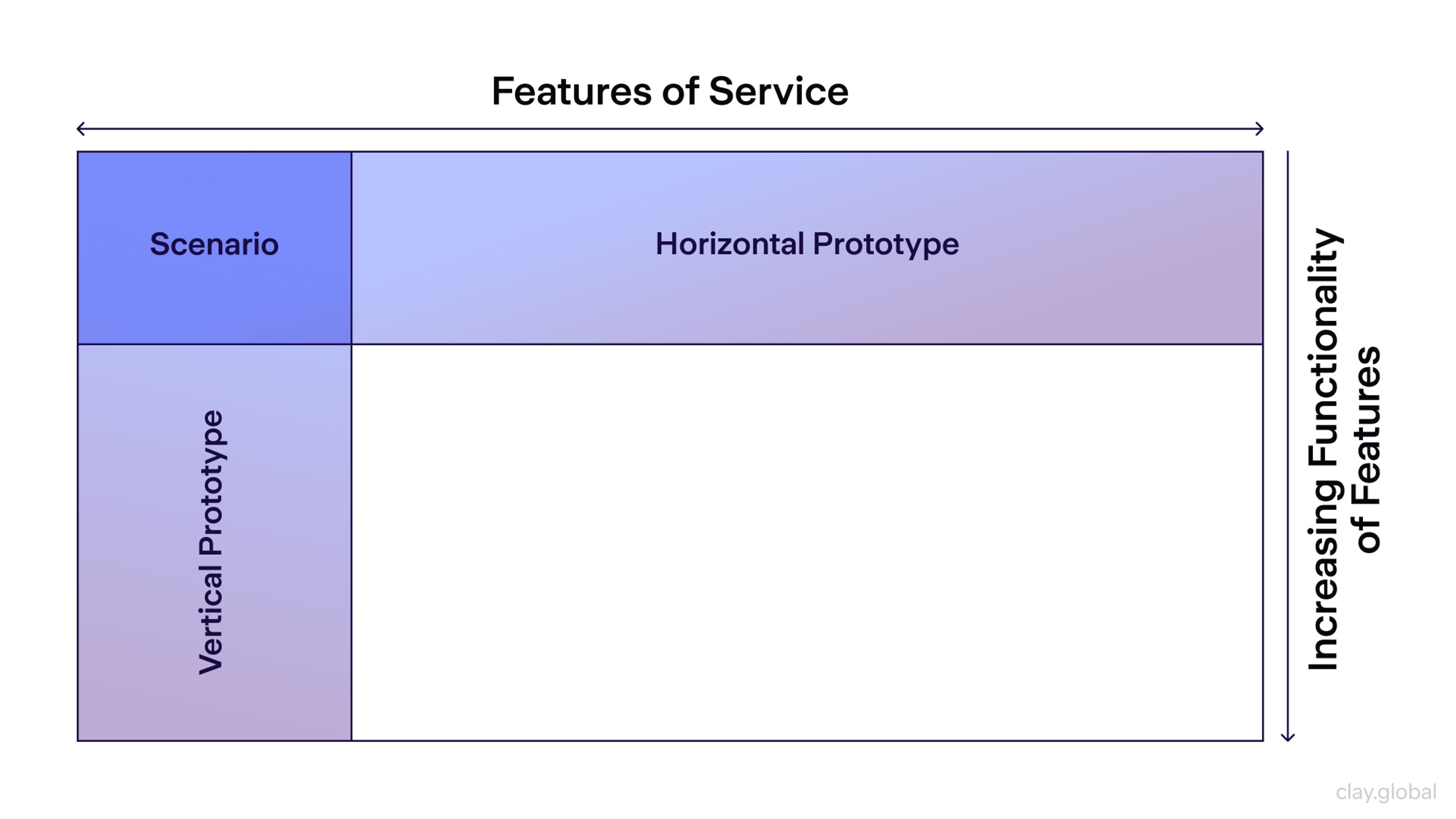
Why is Horizontal Prototyping Important?
- Feedback-Oriented: By providing a comprehensive view of the system, they make it easier to collect constructive feedback from users and stakeholders.
- Design Validation: They help ensure that the overall design and navigation work well before investing effort into deeper feature development.
Vertical Prototypes
Vertical prototypes are used in an interface design process to profoundly analyze one part of a project and set aside all other aspects. Contrary to horizontal prototypes, which give a broad snapshot of most product features, vertical prototypes focus on one or more sections of a product item's design or function and go into detail.
Vertical Prototyping by Clay
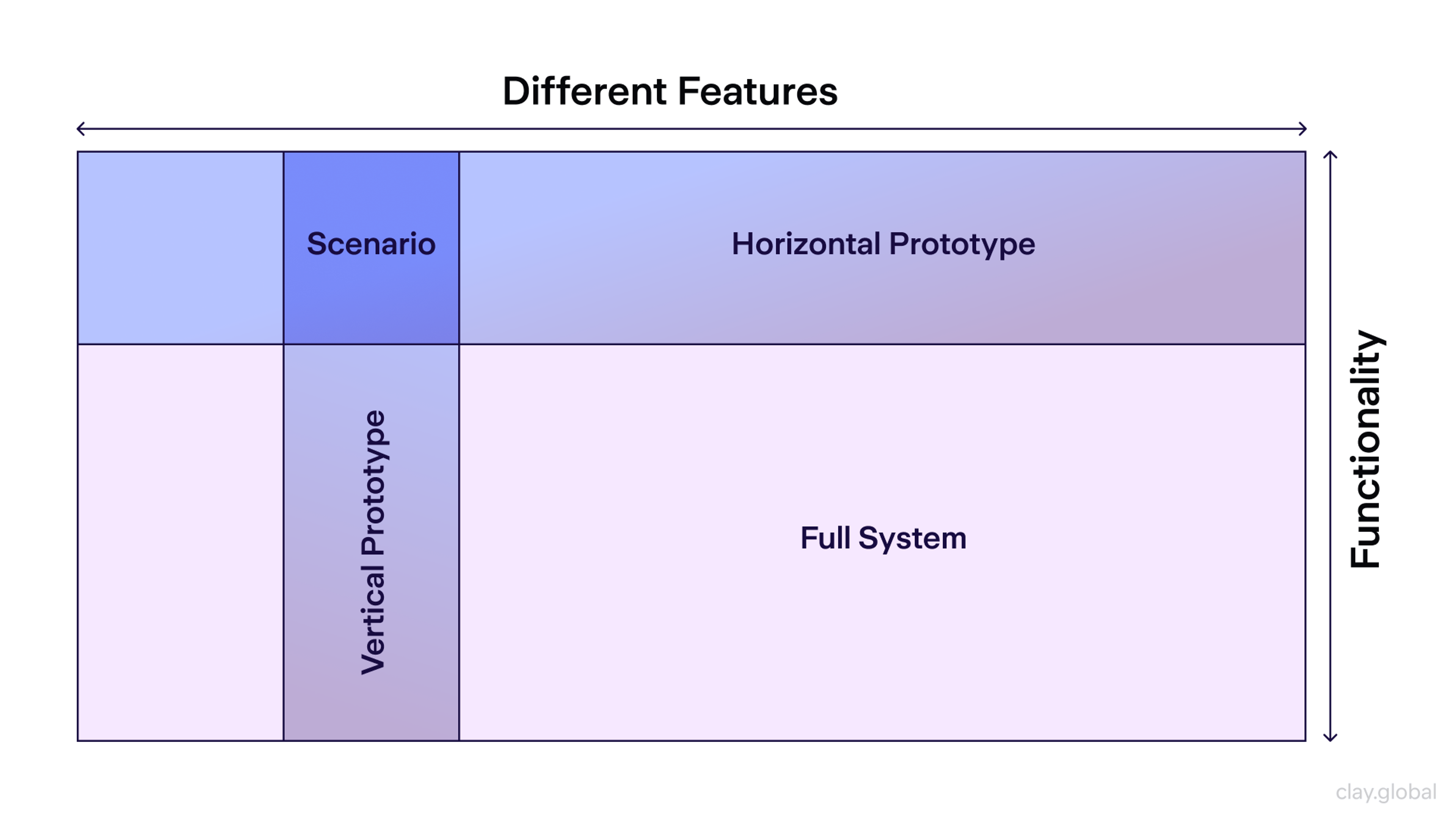
Why is Vertical Prototyping Important?
- Risk Reduction: Testing complex or risky features early minimizes the likelihood of costly mistakes later in the development process.
- Efficient Resource Use: Instead of spreading resources thin, teams can allocate time and effort to refining high-priority components.
Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping constructs a functional representation in the shortest amount of time. Most groups begin with wireframes. They illustrate user flows with pencil and paper before digitizing the drawings.
This method is also popular in product and software engineering. It swiftly transforms concepts into prototype representations, which makes it easier to identify and solve problems more efficiently than traditional techniques.
The process runs in short loops. You build a prototype, test it, gather feedback, and then modify the prototype. This cycle continues until the solution is satisfactory.
3D printing, CAD, and UI tools are standard tools used. These tools mistakenly spend more time in the real world and focus on meeting users' demands.
Why is Rapid Prototyping Important?
- Speed: It accelerates the development process, saving time and resources.
- Cost-Effective: Catching flaws early in the design saves money in the long run.
- Improved Collaboration: Teams can visualize ideas clearly, encouraging better communication and feedback.
When to Use Prototypes?
They are invaluable in the design and development stages, enhancing the visualization of ideas and creating more refined versions of the design before production.
The more pertinent query is, "When is the most advantageous point for implementing a prototype?" This query can be resolved by highlighting the three most beneficial situations for utilizing a prototype.
- Idea Exploration: Prototypes can be generated at any point throughout the process. In these instances, it is easier to facilitate discussions with stakeholders and team members to develop an adequate solution for a given problem.
- User Testing: Sketches and drawings can also gather users' opinions on a design. They can help pinpoint issues more proactively and resolve usability concerns.
- Cost and Risk Reduction: Prototypes help evaluate the feasibility of design aspects before investing in complete resources. Using prototypes as test beds to see how well design solutions fulfill user expectations and project objectives is better.
In other words, prototypes during any project's design, manufacturing, and development stages are of immense value. They help bring ideas to fruition at lower risks and greater user satisfaction.
The Benefits of Prototypes
Prototyping is a key step in design and development. Early versions let you see and test ideas before big spending.
Early Problem Identification: Prototypes reveal design and usability issues while changes are cheap. Fixing a paper model costs less than fixing a factory run.
Enhanced Creativity: Quick versions and feedback spark new ideas. Try a color, a button, or a feature and see how it feels.
Benefits of Prototyping by Clay
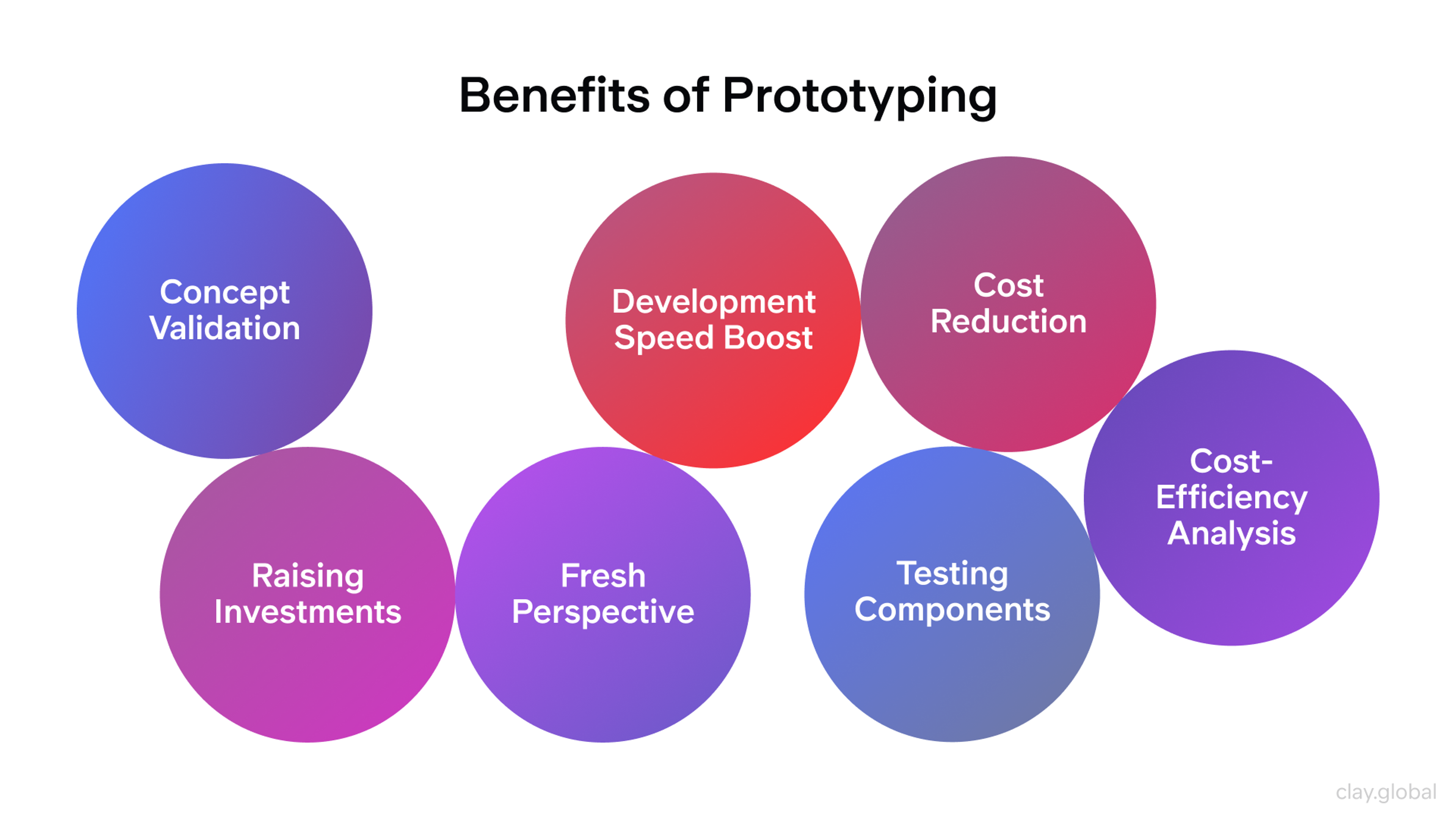
Better Market Validation: Show a model to real users or a focus group. Ask focused questions. Learn if your product is a “yes” or a “needs work.”
Faster Iteration Cycles: Prototypes shorten the feedback loop. You can go from sketch to better sketch in days, not weeks.
Prototypes smooth the path from concept to launch. They boost usability and cut costs by catching flaws early. A prototype is not just a step. It is the backbone of strong design and real innovation. Most design tools include wireframe templates, which help teams share and adjust ideas in real time.
Best Practices for Wireframe Design and Prototypes
Think about significant picture elements and focus on layout rather than individual small picture elements, such as icons. Remove excess elements. More white space is better than extra borders. Focus on the user: prioritize important content and ensure every path is unambiguous.
When layout and content support real, in situ copy, use the document as a test. Early in the process, an interactive prototype communicating intent can help steer design to resolve flows before code is written.
Set up regular reviews to stay in close alignment with the developers, objectives, and technological constraints. Share early work, collect critiques, and cycle quickly. This method enhances usability and saves time. Adherence to these processes will help create user-friendly, uncomplicated designs emanating from simple wireframes.
Future Trends in Design and Development
With ongoing modernization, the design and development aspects are accompanied by these promising trends:
- AI in Wireframing and Prototyping: Artificial Intelligence is single-handedly increasing the productivity and efficacy of designers in wireframing and prototyping tasks. Using AI-powered tools enables designers to work faster and receive helpful suggestions. They are also allowed to automate monotonous tasks to encourage creativity.
- New Tools and Technologies: Different tools and technologies, such as no-code platforms and VR/AR integration tools, are setting new benchmarks in the design industry. With innovations, designers are now able to develop immersive and interactive designs, such as VR/AR activations, that are more advanced than what was possible in the past.
- Emerging Industry Standards: User design accessibility and inclusivity have always been among the most discussed and center-of-attention topics. Changing design landscapes have incorporated ethical centers, which have shifted the focus of design applications towards sustainability.
The future of design revolves around technology and human creativity, changing how we interact with the digital world.
FAQ
What Are The Four C’s Of UI Design?
The four C’s of UI design are clarity, consistency, control, and comfort. These principles make interfaces easy to understand, predictable, user-driven, and pleasant to use.
What Is The Rule Of 8 In UI Design?
The rule of 8 is a spacing convention where padding, margins, and grids follow multiples of 8 pixels. It creates visual rhythm, improves alignment, and adapts well to different screen sizes.
What Is The UI Rule Of 4?
The UI rule of 4 is a layout guideline that divides content into four key zones: navigation, content, interaction, and feedback. It ensures users always know where to find core functions.
What Are The 4 UI Elements?
The four main UI elements are input controls (buttons, forms, fields), navigational components (menus, tabs, icons), informational components (tooltips, progress bars), and containers (cards, grids, sections).
Read more:
Conclusion
To summarize, recruiting top talent can make or break a startup. At the same time, it doesn’t have to waste too much of your time. With advanced AI, Rekroop simplifies the entire recruitment process, matching you with the best candidates who can hit the ground running. Focus on growing your business as we manage candidate sourcing. Sign up today to build your ideal team within minutes!


About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more

About Clay
Clay is a UI/UX design & branding agency in San Francisco. We team up with startups and leading brands to create transformative digital experience. Clients: Facebook, Slack, Google, Amazon, Credit Karma, Zenefits, etc.
Learn more


